Prostatitis: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
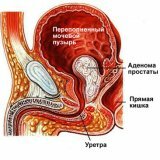
The development of prostatitis is due to the anatomical structure and peculiarities of the blood supply to the prostate. The prostate gland is located in the pelvic area. The anatomical structure of this gland differs in many respects from the structure of other glands of the human body: it consists of several sections, and the glandular tissue itself is located only in one of them. The glandular tissue of the prostate gland includes a large number of small glands, each of which has its own outflow duct. All these small ducts merge into large ducts. In all ducts, both large and small, there are sinuses - that is, cavities in which the accumulation of prostatic juice( a secretion of prostatitis) occurs. The danger is that the prostatic juice often becomes a wonderful base for nutrition and the development of all kinds of bacteria, and the cells that make up sinuses are an excellent nutrient medium for the life of various sexual infections, among them chlamydia, ureoplasma, mycoplasmas and viruses.
Blood supply to the prostate also has its own peculiarities: the blood flow velocity in the prostate is rather low, since this gland is supplied with blood only from eight to ten small vessels due to the lack of its own main blood vessel. As a result, in the tissues of the prostate gland can be formed congestive( i.e., stagnant) changes. In addition, it contributes to the emergence of an infectious disease. All these features of the prostate not only determine the complexity of any changes in the structure of the prostate gland, but also explain the existing variety of forms of prostatitis.
Currently, there is no complete and comprehensive classification of this disease. However, in practically all the classifications presented, acute and chronic forms of prostatitis are isolated.
The symptomatology of the acute form of the disease is brighter than that of chronic prostatitis, moreover, the treatment of acute prostatitis includes the administration of antibiotics( and in rather large doses).Sometimes surgical intervention is necessary - then purulent foci are removed from the prostate gland.
Prostatitis: symptoms
Symptomatic of acute prostatitis is expressed very clearly, so the question of the need for a visit to the doctor disappears by itself. So, in the acute form of the disease there are:
- increase in body temperature;
- acute pain in the groin, perineum and above the pubis;
- pain when urinating;
- decreased potency;
- deterioration of general health, etc.
With chronic prostatitis the symptoms are not so pronounced, moreover, complaints can be absent altogether. There are cases when people suffering from chronic prostatitis do not pay attention to the symptoms of the disease, for example, problems with potency during sexual intercourse, they explain chronic fatigue or a great psychological load. In order to diagnose this form of prostatitis as early as possible, it is necessary to undergo examinations from a specialist from time to time.
Chronic inflammation of the prostate is characterized by:
- short-term pain in the groin, perineum or pubic region;
- decreased libido( that is, sexual desire);
- change of time during which the sexual intercourse lasts( it is possible both to increase the duration of sexual intercourse, and rapid ejaculation, which does not disturb earlier);
- change in the nature of feelings during sexual intercourse, that is, a decrease in sensations during orgasm;
- the presence of excreta( especially in the morning) with urination - prostatirea.
Prostatitis: diagnostics
There are two types of diagnostic methods for this disease: general examination methods and special methods.
The first ones are: blood tests( biochemical, clinical, HIV test, hepatitis C and B markers, on RW ) and urinalysis.
The second kind of methods includes:
- prostate secretion study;
- digital rectal examination;
- analyzes that detect the presence of sexually transmitted infections;
- ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidney;
- transrectal examination of the prostate with ultrasound;
- uroflowmetry, i.e. the study of urine leakage. It is prescribed for suspected inflammation of the prostate;
- blood test for PSA;
- prostate biopsy. It is prescribed in order to exclude the presence of prostate cancer.
Prostatitis: treatment of
Treatment of prostatitis, especially its chronic form, is quite complicated. Doctors from all over the world consider this disease very insidious. Unfortunately, in some cases, treatment may not help, but to remove the manifestation of symptoms and provide a sustained and persistent remission modern medicine is fully capable. And if the patient strictly adheres to the prescribed treatment and follows all the recommendations of the doctor, the symptoms can disappear without a trace.
Treatment of inflammation of the prostate gland should not only be properly selected, but also complex. So, doctors recommend:
- antibacterial therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- immunocorrective therapy;
- prostate massage;
- changing the way of life.
Each of these methods is very important, and excluding at least one of them can lead to a lack of results.
In addition, prostatitis can be treated with traditional medicine methods, having consulted with your doctor beforehand. Remember that treatment with folk remedies can be combined with traditional treatment, but in no case should it be replaced!
Prostatitis: prevention
The main requirement for prophylaxis of prostatitis is to exclude from its lifestyle all the possible risks of developing the disease. So, it is necessary to normalize the diet, restrict consumption of fatty and spicy foods, do not abuse alcohol, do not overcool the body, adhere to an active lifestyle and maintain your weight in a normal state.
It should be remembered that prostatitis can form as a result of prolonged abstinence, as sperm stagnation occurs and blood circulation in the prostate gland worsens, therefore the sex life should be regular. Often, prostatitis develops because of the presence of sexually transmitted infections, so during sexual intercourse it is necessary to use contraceptives. At the first signs of inflammation of the prostate, you need to see a doctor, but it is best to take preventive examinations at the urologist at least once a year.