Sexually Transmitted Infections( STIs) - what do you need to know?
The abbreviation of STI refers to an infection that is sexually transmitted. STIs are diverse and cause sexually transmitted diseases( STDs).Such infections can be hidden and chronic, or may be acute with severe symptomatology and clinical picture.
Contents of
- 1 What is related to sexually transmitted infections in men
- 2 Local diseases affecting the genitourinary and reproductive systems of men
- 3 Symptoms typical for STI
- 4 Diagnosis
- 5 Treatment of
- 6 Recommendations
What concerns STIs in men
Most sexually transmitted infections affect both men, And women, or rather their reproductive system and urogenital tract. There are many classifications of STIs. The most understandable and widespread is the classification of the causative agent that caused the disease.
The following sexually transmitted infections can be identified:
- Viral. HPV or human papillomavirus;HIV infection that causes acquired immunodeficiency and subsequent transition to AIDS;Genital warts;Herpesvirus.
- Bacterial nature. Gonococcus, which causes gonorrhea;Pale treponema, causing syphilis;Mycoplasma, causing mycoplasmosis, similar to Ureoplasma, causes ureoplasmosis and Chlamydia, which causes chlamydia.
- Fungal infections. The fungi of the genus Candida are pathogenic and cause candidiasis of the urethral mucosa.
- Protozoal infections. These are infectious diseases caused by protozoa, such as trichomonas and, accordingly, the disease is called trichomoniasis.
- Parasitic infections. Parasitic infections are rare and largely depend on the quality of personal hygiene of a man. To such infections carry a scabies and a pubic pediculosis.
All these infections affect the reproductive system and the genital tract in men. This is especially true of men who have an active sex life with several partners. Currently, STIs are very common in countries with progressive growth and acquire high epidemiological significance.
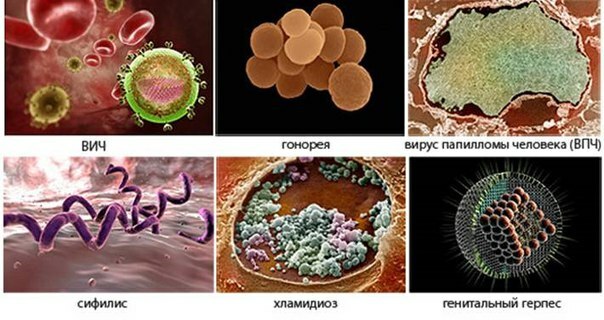
Fig.1 - Some of the infections are sexually transmitted.
Most sexually transmitted pathogens are not stable in the environment. They are rapidly destroyed or inactivated when exposed to environmental factors such as dry air, ultraviolet radiation, low or high temperatures. It is for this reason that the route of transmission of such infections, most often, is sexual, and not contact.
In addition to the main transmission pathway - sexual, different infections have a different effect on the body in different ways. Part of the infection affects only the urogenital tract and has a local form of the disease: candidiasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, ureoplasmosis and others. However, the other part can cause systemic phenomena with the defeat of many organs and systems. For example, with syphilis, ulceration occurs on the penis, which is called the primary chancre, but the infection, getting into the bloodstream, is transmitted to all organs and tissues, where it is fixed and begins to multiply. In time, untreated and untreated syphilis goes into a latent form. Gradually, syphilis destroys the majority of body tissues, including the nerve and connective tissue.
The only symptom characteristic of HIV infection is lymphadenopathy - enlargement of lymph nodes and frequent catarrhal diseases. Over time, HIV infection passes into the stage of severe immunodeficiency. This stage is called "acquired immunodeficiency syndrome" and is terminal.
Local diseases affecting the genitourinary and reproductive systems of men
These infections include gonococcus, chlamydia, uroplasm and mycoplasma, as well as fungi of the genus Candida.
These infections are characterized by the defeat of the male's external and internal genital organs. Diseases can occur in an acute form and cause inflammation of various parts of the urogenital tract - urethritis, prostatitis, epididymitis, vesiculitis. Viral infections, such as herpesvirus and human papillomavirus, cause the formation of ulcers on the penis. They can also lead to benign and malignant neoplasms in the penis, prostate and testicles. A typical lesion is the presence of such neoplasms as genital warts.
In chronic form, STDs may not give any clinical picture. In such a case, the current is considered to be hidden.
Symptoms typical for STIs
For latent infections affecting the male genitalia, there are characteristic symptoms. However, their severity depends on the individual properties of the organism and the pathogen itself. Despite this, most infectious agents cause similar and typical symptoms:
- Discharge from the urethral canal. Allocations can be either colorless or curdled( whitish).Discharges can emit a sharp and specific unpleasant odor, which should already alert the man.
- Itching and burning. Unpleasant sensations in the groin and along the urethra are a clear sign of inflammation of the urethra and the presence of pathogenic flora in it.
- Pain syndrome. Pain can be in the groin, in the sacral region, in the scrotum or penis. Pain occurs due to inflammation and swelling of tissue affected by infection. In a number of cases, pains do not have a clear localization and are determined in the pelvic area. The pain can be blunt noon and sharp cutting.
- Discomfort during sexual intercourse and ejaculation process. Soreness during ejaculation occurs when the organs of the male reproductive system are affected( vesiculitis, orchitis, prostatitis).
Diagnostics of
If a patient is suspected of having an STI, the urologist assigns a standard diagnostic complex to carry out a differential diagnostic search and a clinical diagnosis.
Before starting treatment, the urologist examines and collects the patient's illness and life. During the examination, the physician conducts a physical examination with the definition of specific symptoms that help establish a preliminary diagnosis.
Since a full diagnostic examination takes several days, treatment begins with the use of antibiotic therapy and broad-spectrum antibiotics. The doctor prescribes symptomatic therapy aimed at eliminating inflammatory processes in the urogenital tract, pain syndrome and reducing the swelling of the tissues. This approach significantly increases the effectiveness of the final pathogenetic( pathogen-directed) therapy.
The standard of instrumental and clinical laboratory examination includes:
- Taking a smear from the urethra for subsequent bacteriological inoculation.
- Bacteriological seeding and microscopy of cultures formed with the definition of sensitivity to antibiotics. The goal of the stage is to establish the exact cause that led to the disease.
- Ultrasonic diagnosis of small pelvis, prostate and scrotum organs.
- PCR diagnostics. Polymerase chain reaction allows you to find the causative agent of a viral etiology and find out which disease the patient is sick with.
- ELISA.Immunoenzyme analysis reveals specific pathogens and intracellular parasites that are not detected when taking smears from the surface of the urethral canal.
The above studies help establish the final diagnosis and begin pathogenetic - highly effective therapy of the disease. And ultrasound diagnosis, a general blood test, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and a general urinalysis will tell about the course and severity of the disease. This largely forms the ongoing drug therapy.
Treatment of
For effective and full-value treatment of STI, complex therapy is used:
- antibiotic therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- treatment with topical preparations;
- antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy;
- treatment aimed at eliminating symptoms.
Most , sexually transmitted diseases, are completely curable . is considered incurable as an HIV infection, herpesvirus and papillomavirus infection. These infections can not be completely removed from the body. But with the observance of the right way of life and the timely course of taking supportive and antiviral drugs, it is possible to significantly reduce the rate of progression of diseases.
Infections of bacterial origin are well suited to antibacterial therapy using targeted( sensitive to certain bacteria) antibiotics.
Recommendations
If you are diagnosed with STIs, do not delay the visit to the urologist. Many sexual infections cause irreversible violations in the reproductive system of the male body, lead to serious and even life-threatening complications. Treatment of advanced and chronic forms of STDs entails long-term therapy, and then a recovery period.
Watch a video about common and dangerous STIs:
Recommended for viewing: