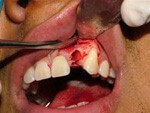
Acute periodontitis
 Acute periodontitis is an inflammatory lesion of periodontal tissues. The diagnosis of "acute periodontitis" is based on data subjective( collection of complaints, compilation of anamnesis) and objective( examination of the oral cavity, electrodontometry, radiography, biochemical, bacteriological studies) studies.
Acute periodontitis is an inflammatory lesion of periodontal tissues. The diagnosis of "acute periodontitis" is based on data subjective( collection of complaints, compilation of anamnesis) and objective( examination of the oral cavity, electrodontometry, radiography, biochemical, bacteriological studies) studies.
Periodontitis - a combination of tissues located between the root of the tooth and bone. This complex holds the tooth and directs the chewing pressure on the jaw. With inflammation, there is a rupture of the ligaments, bone resorption, which is manifested by reddening and swelling of the gum, the appearance of the syndrome of "enlarged" tooth, mobility. Lymphadenitis, swelling of the facial tissues is also possible. The patient notes pains of pulsating or noisy character, local. Treatment is realized by opening the cavity of the tooth, processing root canals, filling, prescribing antibiotics, antihistamines, analgesics if necessary, physiotherapy is not appointed in the acute period.
Causes of acute periodontitis
For etiology, the causes are divided into two main groups: infectious and non-infectious.
Microflora, represented by groups of microorganisms: streptococci, staphylococcus, yeast-like fungi, actinomycetes, etc., acts as a biological agent. In almost 100% of cases, the last stage of caries or its complication is the ancestor of infection. Getting through a top of a tooth, microorganisms allocate toxins, causing a necrosis of a pulp. This symbiosis causes persistent inflammatory changes that trigger the development of acute infectious periodontitis.
Non-infectious causes of acute periodontitis: trauma, irrational medical tactics with regard to medication during tooth healing. The development of acute traumatic periodontitis usually causes a shock or other gustatory mechanical effect on the tooth( during the chewing period, they suddenly bite a lot on bone or shot).For this effect, the applied force is important - the higher, the greater the consequences of changes in tissues. Varieties of injuries after such physical impact are represented by a bruise, fracture, subluxation, dislocation. This kind of periodontitis is also realized with mechanical damage to the periodontal during the cleaning of the root canal, unintended opening of the cavity during preparation. These consequences are related to iatrogenic cause( which is otherwise called a medical error).
The medicamentous form of acute periodontitis begins during the treatment of the tooth canal, in which strong drugs or chemicals( arsenic, formalin, resorcinol), as well as the filling material, go beyond the apex of the tooth. There is a reaction of sensitization on the got antigen, in consequence of which the allergy develops. Especially dangerous is acute arboreal periodontitis, which can cause systemic poisoning.
Symptoms of acute periodontitis
All manifestations are due to the stage of the flow of the process. From the pathogenetic side in the period of antigens influence in the body, the reverse response is triggered in the form of inflammation. In the phase of serous inflammation the patient notes a painful tendency, localized, progressing with the loading of the tooth, tapping. With prolonged pressure on the tooth or jaw joint, the pain is reduced for a short period. The patient is able to identify the source of irritation, light intervals between pains are rapid.
In the oral cavity: the opening is free, the gingival mucosa in the radius of the tooth is changed, the palpation along the transitional fold is sensitive, the carious cavity or filling is recently visualized, the probe is painless, the temperature sample is negative, the tooth is stable, the percussion is positive, there is no color change. It is possible to increase the small number of lymph nodes. The state of the organism is acceptable.
After 1-2 days, with the transition of exudate from serous to purulent and the start of acute purulent periodontitis, the patient's state of health becomes more complicated. The spread of pain through the network of the trigeminal nerve fibers is observed. The patient is unable to identify the causative tooth, the frequency of pain attacks increases. Thermal action, changing the perpendicular position to the horizontal, touching the tooth increases pain. A symptom of an "enlarged" tooth appears, the gum swells up, redness and tension are visualized. There may be swelling of the facial tissues, asymmetry. The general condition is characterized by malaise, weakness, sleep disorder, and lack of appetite. There is a fever. Regional lymph nodes are enlarged.
Forms of acute periodontitis
Acute periodontitis is present in various variations in the correlation from location, etiology, clinic.
At the site of the lesion: apical, marginal, diffuse. Acute apical periodontitis( acute apical periodontitis) - inflammatory phenomena occur in the apex zone. Apex is the upper third of the root from the crown, in which the root canal is joined by a solid apex of the tooth. Marginal( marginal) - the periodontal apparatus is damaged along the root. Diffuse - complete destruction of the ligamentous apparatus.
For etiology: is infectious, non-infectious( traumatic, medicamentous).
Acute infectious periodontitis is the response to the action of a group of pathogenic microorganisms( streptococci, staphylococcus, actinomycetes, fungi of the genus Candida, etc.).The infection can enter the periodontium three accesses: through the tooth channel( for long cure absence of deep caries, pulpitis) through periodontal compound( in periodontal diseases tissue) through the vascular system through the apex( blood, lymph somatic diseases).Acute medical
periodontitis - appears during cure tooth canal when due to improper tactics aggressive medications, such as phenol, resorcinol, arsenic or filling material fall into the apex of the tooth. The reaction of sensitization from the body leads to allergies..
Acute traumatic periodontitis - a consequence of injury( . Contusion, sprain, etc.) or due to iatrogenic causes( accidental opening of the cavity during dissection, mechanical trauma endodontic instruments at stages of processing and blending root fillings
By clinic: serous and purulent forms implemented throughTwo stages of inflammation. In the phase of alteration( damage or other intoxication), serous inflammation begins. In acute serous periodontitis, serous exudates appear in the causative. M site This exudate causes pressure on the nerves, causes pain Next there is a change of exudates from serous to purulent acute purulent periodontitis interdependent on the stage and localization
Stages: periodontal - pus is localized in periodontal formed microabscesses, there is a feeling of tooth elongation;...Endo-osseous - pus distributed into the bone, spreading further, subperiostal - accumulation of pus under the periosteum, swelling of the gums begins, severe pains, flux;Submucous - rupture of periosteum, release of pus in regional tissues, stihanie pains, face asymmetrically. This leads to provoke a response from a number of surrounding tissue( cortical and cancellous bone, soft tissues of the face), defines the beginning of acute periostitis, osteomyelitis of the jaw, admaxillary abscess, cellulitis, an inflammation of the paranasal sinuses( sinusitis).Acute purulent
primary cause of periodontitis is the mass input of infection in the body, in a subsequent developing glomerulonephritis, rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatic heart disease, acute sepsis.
Diagnosis of acute periodontitis
The diagnosis is based on the identified symptoms, the clinic, additional research methods( electrodontometry, radiography, biochemical, bacteriological studies).The presence of dead pulp, there is no reflex to the temperature effect and current, positive percussion, palpation, transformation on the roentgenogram with acute apical periodontitis in the form of an expansion of periodontium or fuzzy boundary of the cortical plate. Biochemistry of blood: moderate leukocytosis, ESR within the limits of the measure.
Differential diagnosis of : based on history, clinic and outcome of examinations. The difference between acute periodontitis and acute pulpitis: with the first pain is constant, with diffuse inflammation - paroxysmal, during the day, there is no response to heat, the gum is changed. The exacerbation of chronic periodontitis is characterized in the past by symptoms similar to acute periodontitis, changes on the roentgenogram are more pronounced and correspond to that stage of chronic periodontitis that preceded exacerbation. Periostitis, osteomyelitis differ on the x-ray by the scale spread of inflammation in the bone tissue, from the defeat of the periosteum( cortical plate) to the spongy substance.
Suppuration of the root cyst - as an outcome of chronic forms of periodontitis, which was previously preceded by an acute process, also has corresponding changes on the radiograph, blood tests will inform inflammation informatively. Acute odontogenic sinusitis is characterized by pain, head inclination forward strengthens it, informative data of X-ray, rhinoscopy.
Treatment of acute periodontitis
Based on the pathogenesis treatment involves two stages: the creation of an outflow for pus and the reconstruction of the appointment of the tooth.
Staging of anesthesia with pain syndrome. Opening and widening of the canal to create an outflow: preparation of the tooth for access( opening, opening of the cavity), use of manual and machine endodontic instruments, solutions and gels to expand the canal( gel Glyde( Dentsply), etc.).Conducting channel disinfection. Channel reaming and irrigation are carried out alternately.
In acute purulent periodontitis longer used resources effectively acting on purulent matter( 3-5% sodium hypochlorite( "Belodez"( VladMiVa) Chlorhexidine digluconate 2%( TehnoDent) et al.). Imposition of antiseptic dressings under the bandage( "Pulposeptin"(omega), "ANTISEPTIN"( OmegaDent) et al.). Selection of dressings depends on the clinical manifestations. Therapeutic( calcium- pad) in the apex region to reconstruct bone( «METAPEX»( Meta Biomed. Co., Ltd.), «Kalsept(OmegaDent), etc.) is effective in acute apical periodontitis.
SealChannel tion:. cleansing, disinfection, filling( a paste( «Endometasone»( Septodont), «Sealapex»( Kerr)), or gutta-percha( vertical( system «Thermafil»), lateral condensation): After the imposition of the root fillings make the final sealing and restorationCrowns in correlations from the IROPZ.
To recreate the tooth, materials may be needed: filling( glass ionomer, light), pins( glass ionomer, silver, anchor), tabs, crowns. In acute serous periodontitis, the root canal is placed in the first visit after a careful treatment of the canal. In acute traumatic periodontitis, since the action of the factor is short, it is not meaningful to eliminate the cause. It is necessary to eliminate the consequences of trauma and accelerate healing.
Acute medicated periodontitis, as mentioned earlier, occurs in response to the misuse of aggressive medicines( arsenic, formalin, phenol).Therefore, before applying the dressing with an antiseptic, you must carefully work out the channel using an antidote.
Acute arsenic periodontitis develops as a result of the impaired use of devitalizing materials( more than 24 hours in single-root teeth, more than 48 hours in multi-rooted).Therefore, in the first method, the root canal is heavily irrigated with an antidote( iodine-containing preparations - "Unithiol 5%"), one-time administration of the antidote to the mucosa with an anesthetic in the apex projection, impose an antidote under the bandage. After the disappearance of pain, the above steps are carried out.
In the absence of treatment, a complication of the condition, the tooth is removed, the periosteum is dissected for the exit of pus.
General treatment of acute periodontitis is antibiotics( "Tsiprolet", "Sulfadimetoksin" antihistamines( "Diazolin", "Suprastin"), analgesics, if necessary( "Ketorol", "Analgin"), attribute salt baths, rinse with warm solutionsantiseptics( ethacridine lactate( "rivanol"), potassium permanganate, furatsillina) after decrease of the inflammatory process shown fiziolechenie( UHF therapy, Helium-neon laser)
prevention and prognosis of acute periodontitis
Cures acute periodontium.that is almost impossible. This phenomenon is likely only in acute serous periodontitis, in the initial stage of reconstruction of serous fluid.
Acute suppurative periodontitis during conservative treatment, supported by therapy with systemic action, X-ray, biochemical research, be cured.
Bone restored tooth in acute apical periodontitisPerforms the necessary tasks.
In the absence of treatment, acute apical periodontitis is reclassified into chronic. It is not excluded the tooth extraction with time.
To prevent the onset of acute traumatic periodontitis, it is necessary to avoid injuries( sports and household genesis).With the appropriate cure, the scenario with systematic dispensary observation, X-ray control is safe. With properly conducted tactics, bone tissue re-formation and healing take place, the tooth functions in the jaw.
Tasks for acute periodontitis medication: to heal the tooth and exclude the ubiquitous effect of chemical and medicinal substances that penetrated the body to prevent systemic diseases.
In time spent treatment, antidote therapy will allow to keep health and a tooth as a microorgan and health of the organism.
In acute infectious periodontitis, the prophylaxis is the health of the macroorganism itself. The absence of systemic diseases, especially the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory tract, the use of a healthy lifestyle, adequate nutrition will minimize the risk of the sources of pathogenic microflora.
General prophylaxis of acute periodontitis will be the sanation of the oral cavity, a visit to the dentist according to the dispensary group.