Types of pathology of the digestive tract
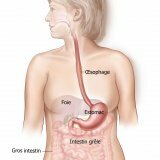
The purpose of the gastrointestinal tract is the digestion of the food that enters it, and splitting it into proteins, carbohydrates, fats and vitamins, all kinds of microelements and water. All these substances are necessary for the life of the human body. The process of digestion becomes possible due to the effect on the food of digestive enzymes. They lay out food to the right ingredients, and then the transfer of nutrients into the blood. And already the blood performs the function of the transport system, distributing a stock of proteins, fats and carbohydrates and other microelements to each organ of our body. Enzymes are produced by various glands of the digestive tract - salivary, stomach and pancreas, liver and small intestine.
The liver performs the function of the filter in the body, it passes through itself the blood that moves from the intestine. The liver produces bile and sends it to the gallbladder. When food enters the small intestine, bile and enzymes from the pancreas begin to flow there.
If we highlight the main stages of the intestine, we see that nutrients are absorbed and distributed throughout the body in the small intestine, and feces and water form in the large intestine.
Various diseases that affect the digestive tract, interfere with its normal functioning, and therefore, the normal functioning of the body as a whole.
The main types of pathology of the digestive tract:
- gastritis;
- stomach ulcer;
- duodenal ulcer;
- cholecystitis;
- cholelithiasis;
- pancreatitis;
- colitis;
- intestinal dysbacteriosis.
Gastritis is a disease of the stomach, in which its walls become inflamed. This leads to pain, nausea and a decrease in appetite. Gastritis can be of two types:
- Hyperacid, characterized by a level of increased acidity. An excess of gastric juice is produced, the patient has an increased appetite. Unpleasant sensations are a constant heartburn. With further progression, the disease develops into a stomach ulcer;
- Hypoacid, gastric juice is produced less than required by the body, there is a process of atrophy of the stomach mucosa. It seems to the patient that the stomach is constantly full. There is a lack of appetite. With further development, it can grow into a stomach cancer.
Gastric ulcer - it is characterized by the formation of ulcers( wounds) in the stomach mucosa. This is due to malnutrition, the use of poor-quality products, bad habits and eating disorders. Ulcers can form with constant starvation, when the human stomach is empty for a long time, and gastric juice continues to be produced and corrodes the walls of the stomach. Gastric juice for the cleavage of food contains hydrochloric acid, which affects the mucous walls of the empty stomach. The cause may be bacteria that live on the walls of the stomach. With peptic ulcer there are pronounced hunger pains, there are internal bleeding, in some severe cases - perforation or opening of an ulcer.
Duodenal ulcer. With increased acidity, the gastric juices along with digested food, active pancreatic enzymes and bile will enter the duodenum. With increased activity of these enzymes, the gut will be prone to inflammation with subsequent ulceration. Ulcers in the gut, as well as on the surface of the stomach mucosa, may be accompanied by bleeding, and in the worst case, perforation.
Ulcers are the first step towards the development of cancerous tumors.
Cholecystitis - this disease manifests itself in the inflammation of the gallbladder walls, it can be provoked by bacteria and microbes that settle in the bile putty, or the presence of stones. With cholecystitis, pain on the right side of the lower ribs, nausea and vomiting are felt. And also the temperature can rise strongly.
Gallstone disease causes severe unbearable pain attacks, accompanied in some cases by jaundice due to elevated levels of bile. Bile ducts can be clogged with stones, then surgery is required. Cholecystitis is accompanied by inflammation of the bile ducts of the liver and pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas. The cause of pancreatitis is often overeating and abuse of alcohol and spicy and fatty foods. When the pancreas is overloaded with food, it tries to process it faster, and secures more enzymes than usual. As a result, they do not have time to fully enter the small intestine and irritate the pancreas itself.
Symptoms - pain in the left hypochondrium, sometimes covering the entire body, nausea and vomiting. Against the background of pancreatitis, there is sometimes an extremely serious complication of pancreatic necrosis - the death of the tissues of the pancreas. And they, along with the enzymes, enter the cavity and cause its inflammation. In fact, one process can lead to the pathology of the digestive tract.
Types of pathology of the intestine are also different:
- enteritis - inflammation of the small intestine;
- colitis - inflammatory processes of the large intestine;
- gastroenterocolitis - the defeat of all parts of the stomach and intestines. This is an acute inflammation.
leads to these all the inflammations of the pathogenic microflora, which enters the body together with food. Usually, under the influence of digestive enzymes of all glands, it dies. But sometimes, due to disruption of the body, all these bacteria survive and actively multiply in the digestive tract. Acute inflammation of the digestive system is manifested by fever, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting.
There are useful lactoids and bifidobacteria in the intestines, they are important for the state of health, if it dies, then the flora remains defenseless and various diseases arise due to the development of pathogenic microflora. Useful bacteria very often die after a long reception of antibiotics, and it is necessary to take a number of measures to restore them, otherwise the dysbacteriosis of the intestine begins.