Smallpox: symptoms, treatment, prevention
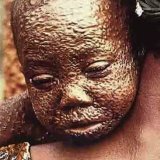
Smallpox is a disease that is very contagious. The patient's body is covered with a strong rash. Curing, in very frequent cases, smallpox leaves deep scars on the skin. This article will describe in detail the disease - smallpox: symptoms, treatment, prevention.
Smallpox is of two types, differing in the type of rash:
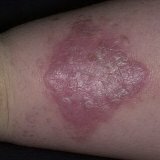
- The first type is characterized by a rash, the vesicles of which have a clear or light purulent fluid. This type is less dangerous and does not pose a significant threat to human life.
- The second type is a bubble of black with a slightly bluish tint, sometimes bruises appear around. This is a very dangerous type of smallpox, if you do not start treatment in time, then it can end fatal.
Causes smallpox virus, which is extremely resistant to temperature changes. It is transmitted in two ways:
- Air-droplet;
- Contact.
Rarely, but still occur the most severe manifestations of smallpox.
Symptoms of smallpox
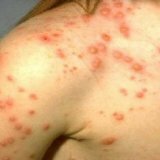
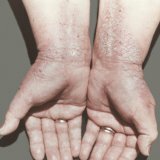
The first 7-14 days of illness can go unnoticed, be in a so-called latent form or incubation. And in some patients smallpox manifests itself more quickly, others develop all 14 days. At the end of this period, the person begins to suffer the strongest fever, it chills and a pain hurts his back. In addition, there is sluggishness, rapid fatigue, severe dizziness. The neck is very sore and almost does not move. There is stiff neck muscles. These symptoms do not pass for a while. After a while( again, each in different ways), the temperature drops, but the rash begins to appear gradually. First the pills are pale with a clear liquid inside and mostly on the face. Gradually, this rash passes to the entire body, the bubbles are filled with a thick yellow purulent fluid. The temperature rises again. During this period, dizziness intensifies, the patient constantly sleeps. He starts hallucinations and delirium. Places affected by the rash are very painful.
So, it is worth mentioning all the symptoms of this disease:
- Fever;
- Temperature;
- Dizziness;
- Headache;
- Chills;
- Back pain;
- Rigidity of the neck muscles;
- Rash;
- Hallucinations.
After a while, usually it's 8-10 days, with proper treatment, the vesicles begin to dry up and the temperature decreases. Under the action of drugs begins to recede smallpox. Symptoms disappear.
Treatment of smallpox
Treatment of the disease begins with immediate hospitalization and isolation of the patient for the entire duration of the course of the illness since the onset of the first symptoms.
But in general for a long time against this disease there was no effective treatment. Scary in the literal sense of the word, the disease carried away thousands of lives. There have even been epidemics, which are known to this day. But the magic treatment flourished. For example, the patient was dressed in all the red. For some reason, it was believed that this color has the ability to lure smallpox out.... And he lured out, only it did not help.
At the end of the 19th century, the German doctor Hubert proposed a treatment that was nototonic at that time. He offered the already sick people a vaccine. Such vaccination was daily and allowed to significantly alleviate the course of the disease called smallpox. The treatment was quite effective. It is still not clear why multiple vaccinations have not become widespread. To date, smallpox is treated with very different methods.
Modern clinical treatment of smallpox provides, first of all, antiviral therapy. For this, the patient is prescribed a drug called metisazone. This drug for effective treatment should be taken at a dosage of 0.6 grams, twice a day. The course of antiviral therapy usually lasts 5-6 days.
At the next stage of treatment, the patient is prescribed an immunoglobulin intramuscularly, which is an excellent anti-inflammatory therapy. Dosage of the medicine depending on the complexity of the course of the disease can be from 0.3 to 0.6 grams per day. At the same time, various antiseptic ointments and lotions are prescribed on the affected areas of the skin, which help to avoid the attachment of additional bacterial infections. Because the skin during the course of the disease is vulnerable enough.
If they were not able to protect themselves from bacteria and they still penetrated the skin, it is necessary to block them and prevent them from spreading beyond the focus of inflammation. For this purpose macrolides, semisynthetic penicillins, cephalosporins are prescribed. These are antibiotics that have a wide spectrum of action.
At the final stage of treatment, the patient is intramuscularly injected with colloidal and crystalloid solutions. These measures are necessary for detoxification. It occurs at a time when the bubbles begin to form a purulent fluid. Actually, this fluid is the main infectious moment. A patient is considered contagious until the complete separation of all scales. In particularly severe cases or according to indications and contraindications, plasmapheresis and ultrafiltration are used.
Plasmapheresis is the removal of the infected contents from the body by removing the liquid component of the blood. The procedure is carried out using a special apparatus and lasts about an hour and a half.
Ultrafiltration is the purification of blood by molecular separation of its particles into diseased and healthy ones. Just like the first procedure, the ultrasound consists in passing the patient's blood through a special apparatus.
Both these devices are designed in such a way that 100 percent exclude infection with hippatitis and AIDS and other infections.
Prevention of smallpox
The only way to avoid a terrible disease called smallpox is vaccine prophylaxis. This vaccination is mandatory and is given to all in childhood. The grafted people either do not become infected at all, or if the infection does occur, the disease proceeds very easily without complications, severe forms and deep traces on the skin.