Treatment of mycosis depending on the site of localization
 Mycosis is a very common dermatological disease.According to statistics, they are diagnosed in 20% of people.Their development is due to fungal microflora, and an important predisposing factor is weakened immunity.Fungi can affect the skin, hair and nails of a person.The source of infection is a sick person.You can get infected on the beach, as well as in public places with high humidity - baths and saunas.It will not be difficult to "pick up" the fungus, picking up the rail in transport, wearing someone else's slippers at a party, or using a towel that the infected person wiped.
Mycosis is a very common dermatological disease.According to statistics, they are diagnosed in 20% of people.Their development is due to fungal microflora, and an important predisposing factor is weakened immunity.Fungi can affect the skin, hair and nails of a person.The source of infection is a sick person.You can get infected on the beach, as well as in public places with high humidity - baths and saunas.It will not be difficult to "pick up" the fungus, picking up the rail in transport, wearing someone else's slippers at a party, or using a towel that the infected person wiped.
The tactics of treating mycosis directly depends on the location of the lesion and its area.For the treatment of fungal infections, both systemic action drugs and antifungal agents for topical topical application are used.
Table of contents: How to treat a foot fungus How to treat a dermatomycosis of the head?What to do with fungus nails?Mushroom mycosisHow to treat a foot fungus
Stop - this is the most frequent fungal localization.
With squamous form of lesion, 1-2 times a day, apply creams with fungicidal effect on the feet and treat the skin with antiseptic solutions.
The most effective antifungal agents are:
- Clotrimazole;
- Ketoconazole;
- Terbinafine;
- Itraconazole;
- Naphthyfin.
In the evening hours, it is recommended to wipe the affected area with 2% alcoholic iodine solution.
With an acute form of local funds is usually not enough.Patients are prescribed injections of calcium gluconate( IV or IM), and for ingestion - Chloropyramine( single dose - 0.025 g, multiplicity - 2-3 times a day) and calcium pantothenate( 0.5 g each).
Topical preparations:
-
 Resorcinol( applied 1-2 times a day for 2 consecutive days);
Resorcinol( applied 1-2 times a day for 2 consecutive days); - Potassium permanganate( pink solution of potassium permanganate, feet are treated twice a day);
- Boric acid( a drug is used as an alternative to potassium permanganate);
- Miconazole( ointment form is applied twice a day, the course is 1-1.5 weeks).
Antifungal medicines for systemic action are prescribed if local therapy does not produce the desired effect.The duration of the course therapy is from 3 to 4 weeks.
Terbinafine should be taken daily at 250 mg per day, and Fluconazole - once a week( 150 mg each).The scheme of taking Itrakezla is as follows: during the first week - 200 mg per day, and then to the end of the course - 100 mg.
To get rid of the accompanying bacterial microflora, it is recommended 1-2 days to additionally use the following antibacterial ointments and creams:
- Gentamicin;
- Neomycin;
- Betamethasone.
Important: if in the course of examination the dermatologist detected hyperkeratosis, i.e., intensive keratinization of the epithelial layer of the skin, then before detachment of creams and ointments it is advisable to carry out a detachment of keratinized tissues.Otherwise, active components of drugs will not practically penetrate deeper layers of skin, and treatment will be ineffective.
How to treat head dermatomycosis?
For effective therapy of fungal diseases affecting the scalp, combined therapy is practiced.It involves taking systemic drugs inside and using external drugs, the most effective of which are antifungal shampoos.
 The most common antifungal shampoos are:
The most common antifungal shampoos are:
- Nizoral;
- Cebosol;
- Keto plus;
- Mycosorrh.
The active ingredient of these agents is ketoconazole.
Systemic preparations:
-
 Griseofulvin - a pill that helps cure such varieties of mycoses as trichophytosis and microsporia.In diagnosed microsporia, the dose is calculated from the calculation of 12.5 mg / kg for adult patients and 22 mg / kg for children.When trihofitii adults are prescribed a similar dose, and children - 18 mg / kg.Multiplicity of taking tablets - 3 times a day.The course is continued until laboratory studies show complete absence of fungus on the head.
Griseofulvin - a pill that helps cure such varieties of mycoses as trichophytosis and microsporia.In diagnosed microsporia, the dose is calculated from the calculation of 12.5 mg / kg for adult patients and 22 mg / kg for children.When trihofitii adults are prescribed a similar dose, and children - 18 mg / kg.Multiplicity of taking tablets - 3 times a day.The course is continued until laboratory studies show complete absence of fungus on the head. - Itraconazole.The drug is not prescribed for oral administration to children of any age.Adults need to take 100 mg per day for 1-1,5 months.
- Terbinafine.The dose of Terbinafine for children weighing up to 20 kg is 65 mg per day, from 20 to 40 kg is 125 mg, and for weights over 40 kg, 250 mg.Adult drug is prescribed at 250 mg per day.The duration of the course varies from 1 to 3 months.
If there is a fungus of the scalp, 1-2 times a day, use one of the following creams:
- Mycosorr;
- Nizoral;
- Batrafen;
- Mycospores;
- Bifosin.
Drugs for topical application have a positive effect only after arresting the inflammatory process.If infiltrates and suppuration are observed on the scalp, dried crusts should be removed from the skin before application.In this case, anti-inflammatory drugs( rivanol, salicylic ointment or furatsilin solution) and antiseptics are used.The chronic form of mycosis may require the removal of the stratum corneum of the skin with special ointments.
Important: if the fungal lesion of the scalp is diagnosed in a toddler who is breastfeeding, the systemic drug should be taken by his mother.The child will receive the necessary therapeutic dose with her milk.
What to do with a nail fungus?
 If there is a fungal lesion of the nail bed and plates, in some cases, systemic therapy is required.However, it is often possible to dispense with local drugs.According to the indications, the doctor can prescribe a combination therapy;All depends on the specific type of pathogen( determined after a laboratory analysis of scrapings), the stage of development( i.e., "neglect") of the disease, as well as the area of the focus.
If there is a fungal lesion of the nail bed and plates, in some cases, systemic therapy is required.However, it is often possible to dispense with local drugs.According to the indications, the doctor can prescribe a combination therapy;All depends on the specific type of pathogen( determined after a laboratory analysis of scrapings), the stage of development( i.e., "neglect") of the disease, as well as the area of the focus.
Limited to conducting local therapy is possible with the so-called.Distal-lateral form of mycosis, if not more than 1/3 of the nail is affected.With other forms of mycoses and more extensive lesions, only local therapy is ineffective, as active components will hardly penetrate into the deep layers of the skin and can not completely eliminate the causative agent of the infection.
Systemic preparations against nail fungus:
- Terbinafine( effective against Trichophyton rubrum and T. Mentagrophytes);
- Itraconazole( broad spectrum antifungal agent);
- Fluconazole( kills dermatophytes Epidermophyton floccosum and yeast-like fungi).
Note: Terbinafine is sold under the names Lamisil, Exifin and Terbizil.Analog Itraconazole - Orungal, and Flukonazola - Diflucan.
Terbinafine is taken with mycosis of the nails on the hands for a month and a half, and with fungal nail lesions - 2 times longer.The daily dose is 250 mg.
Itraconazole is taken twice daily for 7 days.With mycosis of the nails, the course is repeated after a 3-week break.
Duration of the course of treatment Fluconazole - from 2 to 6 weeks( 50 mg daily or 150 mg once a week).
Creams and solutions from mycosis of nails:
- Ketoconazole;
- Clotrimazole;
- Oxiconazole;
- Cyclopyrox;
- Naphthyfine;
- Terbinafine.
They need to be applied on a daily basis 1-2 times until a healthy nail plate grows.
A good therapeutic effect allows you to achieve antifungal lacquers that can be used in parallel with conventional cosmetic.This dosage form does not give side effects.
The best antifungal varnishes are Loceril( Amorolfin) and Batrafen( Cyclopyrox).
Mushroomed mycosis
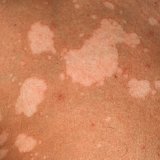
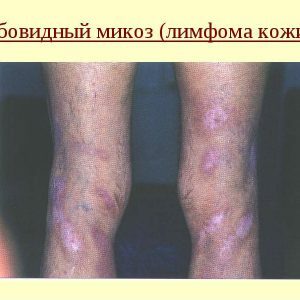 One of the most dangerous dermatological manifestations is considered to be a hard-to-treat mushroom mycosis. In fact, this disease can not be attributed to fungal lesions, tk.In the development of the disease parasitic fungi do not take any part. Yes, and the specific cause of the pathology to this day is not known to doctors.Some specialists see viruses as the main source of danger, others - a genetic malfunction.
One of the most dangerous dermatological manifestations is considered to be a hard-to-treat mushroom mycosis. In fact, this disease can not be attributed to fungal lesions, tk.In the development of the disease parasitic fungi do not take any part. Yes, and the specific cause of the pathology to this day is not known to doctors.Some specialists see viruses as the main source of danger, others - a genetic malfunction.
Everything that relates mushroom mycosis with mycosis true - the external similarity of clinical manifestations and the development of pathology against the background of immunodeficiency.In the early stages, the skin of the patient is covered with spots of a reddish-cyanotic shade.Affected areas strongly itch.Symptoms of early stages are similar not only to signs of fungal damage, but also to the clinical manifestations of eczema and psoriasis.As the pathological process develops, the spots are infiltrated, reddened or reddish-brown, then transformed into plaques that form whimsical patterns.In the latter stages, cyanotic or reddish-yellow formations grow on their place, sometimes reaching quite large sizes and resembling tomatoes or oranges.
Since mushroom mycosis is a T-cell tumor, its treatment is aimed at slowing the development of the tumor.
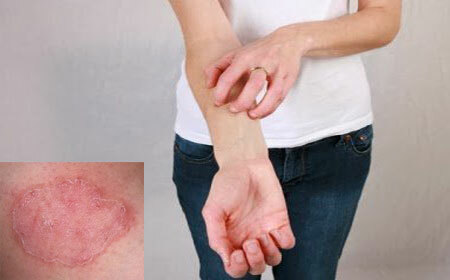
Suspend the growth of formations in the initial stages help:
- steroid ointments;
- vitamins( C and B);
- sanatorium treatment.
With the progression of the disease, this complex of activities is complemented by the intake of antitumor drugs, corticosteroids, cytostatics.At later stages, phototherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed.
Plisov Vladimir, medical reviewer