Pancreatitis: symptoms and treatment

Pancreatitis is a disease that affects the pancreatic tissue and proceeds in two main forms - acute and chronic.The occurrence of chronic pancreatitis is rarely associated with acute pancreatitis.Let us consider in more detail each of the forms of this disease.
Table of contents:Forms of pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is a pathology of the pancreas, at which autolysis occurs - "melting" of the body cells with its own enzymes.
Chronic pancreatitis is a disease with pronounced inflammatory-dystrophic changes in the tissue of the organ that does not go away after the cause of the disease has been eliminated.The result of chronic pancreatitis is sclerosis of the gland with oppression of its basic functions.
About 70% of patients with acute pancreatitis are women, especially at the age of 50 to 70 years.
In recent decades, there has been an increase in patients with chronic pancreatitis.This form is also more often affected by women, but the age category is earlier - from 30 to 50 years.
Acute pancreatitis
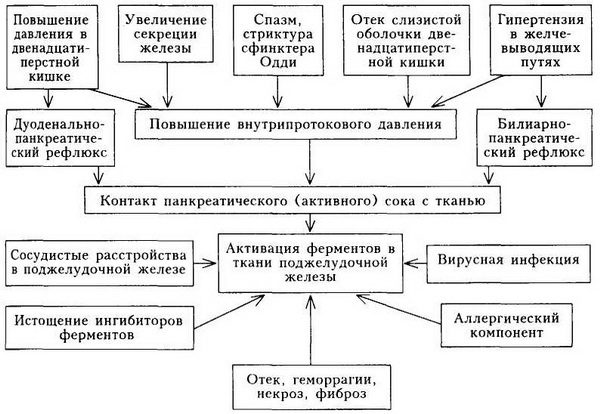
The main causative mechanism for the onset of the disease is a factor that promotes increased pressure in the ducts of the gland.In addition, the development of the pathological process contributes to the throwing into the ducts of the body of substances that lead to the activation of the enzymes of the gland itself, leading to its destruction.
The main causes of acute pancreatitis:
- diseases of the gallbladder and biliary tract;
- chronic alcoholism and polytoxicomania;
- traumatic pancreatic injury;
- Vascular pathology - atherosclerotic changes, thromboembolism, inflammatory-degenerative processes in the vascular wall;
- some types of infectious diseases - hepatitis( inflammation of the liver), parotitis( inflammation of the parotid gland);
- proximity to the duodenal ulcer contributing to the onset of pancreatitis in its inflammation and ulcerative processes;
- occlusion of the passage of the gland by stones, or tumor tissues;
- long-term use in large doses of hormonal drugs;
- exposure to toxic substances;
- presence of diabetes mellitus, especially severe forms, accompanied by coma;
- Collagen diseases - systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis;
- violation of diet - overeating in combination with alcohol intake.
Alcohol directly causes damage to the body cells, leading to a dramatic increase in the release of pancreatic enzymes.There is a delay in the release of pancreatic juice( due to the swelling of the sphincter of Oddi, the muscle that facilitates the secretion of the gland into the duodenum).
The mechanism of development of acute pancreatitis is shown in the picture:
As most diseases, acute pancreatitis can occur in forms:
- easy;
- average;
- heavy.
Note: structural forms of the disease will not be considered due to their specific complexity and importance only for doctors.
Symptoms of acute pancreatitis
We distinguish two types of symptoms - subjective, felt by the patient and objective, which can be seen by the doctor when examined.
Subjective complaints:
- intense, piercing pain in the peripodal region.The pain often gives back, simulates heart pain, "shoots" in the right shoulder.Pain syndrome is growing and can lead to pain shock;
- persistent nausea and vomiting, not bringing relief.Irritation of the diaphragmatic nerve leads to a painful hiccup.There is a pronounced abdominal swelling caused by impaired motor function of the transverse colon;
- severe form is accompanied by bloody vomiting, enlarged abdomen( fluid in the abdominal cavity), decreased or no urine, a violation of consciousness.
Objective features:
- jaundice sclera and skin( due to violation of outflow of bile with pancreas secretion);
- blue fingertips, face, the appearance of spots on the abdomen( local circulatory disorders), pronounced dyspnea;
- strong pallor with a painful attack;
- in the first days of the onset of the illness temperature increase;
- frequent pulse, not corresponding to temperature;
- bloating, especially in the left areas;
- during percussion( tapping with the fingers of the abdomen) the doctor hears dullness of the sound due to the appearance of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- examination of the abdomen is painful, accompanied by the appearance of specific signs characteristic of acute pancreatitis.

Laboratory diagnosis of acute pancreatitis
In a clinical blood test, the following is observed:
- increase in the number of erythrocytes caused by loss of the liquid part of the blood;
- low level of hemoglobin;
- an increase in the number of leukocytes with a predominance of neutrophils and a decrease in lymphocytes, as well as a decrease in the number of eosinophils;
- the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation can be dramatically increased.
Note: is a specific laboratory indicator of acute pancreatitis is an increase in the activity of the pancreatic enzyme-amylase, both in blood and in urine.
Blood sugar level is increased.
When acute pancreatitis is clearly determined by the increase in values, the so-called acute phase parameters.There is a change in the proportions of protein content, increased blood transferase( ALT and AST), especially ALT.
Instrumental diagnostics
With , the ultrasound of the abdominal organs can detect an increase in the pancreas and the presence of stones in the ducts.
X-ray diagnosis of establishes an intestinal paresis( a breach of contractility), signs of a decrease in lung sites( atelectasis) and the presence of effusion in the pleural cavity.
The gastroduodenoscopic method reveals edematous stomach and 12 duodenal ulcer.
Vessel examination - angiography of , allows to see deformed and displaced arterial vessels, congestion of contrast medium in them due to stagnant phenomena.
Treatment of acute pancreatitis
Note: treatment depends on the severity of the disease.
Conservative treatment of mild severity of acute pancreatitis:
 Therapy begins with the appointment of bed rest and complete abstinence from food.The first three days a patient can only fluid.Then crackers with unsweetened tea.Gradually the menu is expanded by slimy broths and porridges, mashed potatoes.In a week, the patient is assigned a 5p table for Pevzner.
Therapy begins with the appointment of bed rest and complete abstinence from food.The first three days a patient can only fluid.Then crackers with unsweetened tea.Gradually the menu is expanded by slimy broths and porridges, mashed potatoes.In a week, the patient is assigned a 5p table for Pevzner.
Medically required to neutralize gastric juice.To this end, antacids and H2 blockers, anticholinergics are prescribed.
Pain relievers are used to reduce pain.Treatment of mild degree is usually 2 weeks.The patient is recommended to follow a diet.
Conservative treatment of moderate and severe forms of pancreatitis:
Bed rest and diet are the same as with mild.Additionally, a suction of gastric contents is performed by the probe.
From drugs to painkillers, holinolitikam and blockers of H2-receptors hormones are added.
Loss of fluid is replenished by intravenous drip injection of plasma, Polyglucin, Glucose solution.
Protein loss is compensated with drugs Albumin, blood, blood substitutes.
Intoxication of the body is removed additionally by the introduction of diuretics.
Excessive activity of pancreatic enzymes is blocked with antifoam agents - Contrikal, Trasilol.
Blood microcirculation disorders are supplemented with Heparin, Dextran.
To prevent bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed.
Surgical treatment of acute pancreatitis
Surgical treatment is indicated in case of development of diffuse inflammation of the peritoneum, suppurative complications, increasing mechanical jaundice and destruction of the gallbladder and ducts.

Complications of acute pancreatitis
Early:
- shock;
- acute cardiovascular and renal failure;
- bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract;
- brain damage - encephalopathy;
- Purulent complications( abscesses and phlegmon).
Late:
- narrowing and deformation of the ducts of the pancreas, choledocha( common bile duct), duodenum.
Forecast and prevention of acute pancreatitis
Note: mortality in acute pancreatitis is very high - 20%, up to 15% of patients recover, the rest have recurrences of pancreatitis.
Patients after recovery are recommended to have a follow-up at a gastroenterologist, follow a diet, and sanatorium treatment.
Chronic pancreatitis
 The development of chronic pancreatitis is facilitated by:
The development of chronic pancreatitis is facilitated by:
- cholelithiasis, which causes congestion of pancreatic "juice" and inflammation of the gland tissue;
- chronic alcoholism( direct damaging effect of alcohol and its derivatives on the gland tissue);
- diseases of the stomach and duodenum( cause the contents of the intestine to be thrown into the pancreas and cause its enzymatic activity, leading to tissue death and sclerosis);
- vascular diseases - atherosclerotic lesions, essential hypertension, collagenoses;
- long-term use of corticosteroids - "drug pancreatitis";
- penetration of ulcers of the duodenum into the pancreas;
- infectious pathology - hepatitis, tuberculosis, malaria, mumps, brucellosis and others;
- endocrine and metabolic diseases.
Classification of chronic pancreatitis
According to Shelagurov AA, the following are distinguished:
- Chronic recurrent pancreatitis( phases - exacerbations and remissions).
- Chronic pancreatitis with persistent pain syndrome.
- Pseudotumoric form.
- Latent( sluggish) form.
- Sclerosing form.
Features of complaints and clinical manifestations in chronic pancreatitis
Subjective complaints are manifested:
- Syndrome of inflammatory-destructive changes - attacks of shingles and debilitating pain in the upper abdomen.The pain occurs after taking hot and cold dishes, fatty and sweet, especially alcohol causes the pain syndrome.The pain is increasing in the supine position on the back and at night.Patients complain of fever, severe weakness, sleep disturbances, headaches( signs of intoxication), increased appetite( in which patients are afraid to eat, as the pain intensifies sharply against the background of eating).
- Syndrome of impaired external secretion.It is manifested by loss of weight( the result of impaired absorption and quick evacuation of food), dry skin, brittle nails( beriberi), post-eating weight in the stomach, nausea, often vomiting, stool disorders( both constipation and diarrhea).
- Syndrome of impaired internal secretion.It shows signs of diabetes, as a result of a drop in glucagon levels in the blood.
Objective symptoms:
- Patients externally emaciated.
- Pallor and icterus of the skin, inflammation in the oral cavity( deficiency of essential vitamins) are observed.
- Forced position in the bed - legs with bent knees, which the patient presses against the abdomen to relieve pain.
- Specific "pancreatic" symptoms when palpating the abdomen.
Additional diagnostic criteria
 Laboratory tests are similar to those for acute pancreatitis.Among the features is the loss of a large amount of nitrogen.
Laboratory tests are similar to those for acute pancreatitis.Among the features is the loss of a large amount of nitrogen.
Additionally noted - stinking and voluminous stool undigested fatty foods( steatorrhea).
Pancreas ultrasound in chronic pancreatitis reveals a variety of calcifications, pseudokistoznyh formations, a sharp expansion of the ducts, fibrosis of the tissue and a decrease in the size of the organ.
Angiography determines a large number of aneurysms of the arteries.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis
The main efforts should be aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease.In passing, it is necessary to eliminate the inflammatory process, to conduct supportive therapy.
 The stage of exacerbation requires a diet of 5n with the restriction of "heavy" fats and proteins, with the predominance of lungs for the assimilation of carbohydrates.The first two days you can refrain from eating.Unsweetened tea is recommended from the liquid.
The stage of exacerbation requires a diet of 5n with the restriction of "heavy" fats and proteins, with the predominance of lungs for the assimilation of carbohydrates.The first two days you can refrain from eating.Unsweetened tea is recommended from the liquid.
Medication - fighting pain and spasms.With severe pain, drugs.
As with acute pancreatitis, antiferment preparations( Gordox, Pentoxyl), antacids and H2 receptor blockers are prescribed.
Antibiotics and bacterial preparations are administered in developing infectious complications.
For severe body weight loss, non-anabolic and anabolic steroids.
In the remission phase, you should follow a diet, take vitamin complexes, enzymes( Festal, etc.)
Note: for complications shows surgical treatment.
Prognosis and prophylaxis of chronic pancreatitis
Systematic observation in the gastroenterologist, diet and regimen dramatically reduce the possibility of recurrence of the disease.Remissions are long, up to 5-7 years.Periodically, it is necessary to undergo preventive treatment, get rid of bad habits and alcohol intake.
For more information about the symptoms, forms, causes of development and methods of treatment for pancreatitis, you will receive this video review:
Alexander Lotin, medical reviewer



