Hypolactation: causes, signs, stages, prevention and treatment
 Breastfeeding is a unique opportunity given to a woman by nature to give the baby everything necessary for normal physical and mental development, protect him from disease, from birth to form an inseparable, close relationship with him.In order to take advantage of this opportunity, the nursing mother should try to maintain a good lactation as long as possible( formation in the mammary glands and excretion of milk from them).
Breastfeeding is a unique opportunity given to a woman by nature to give the baby everything necessary for normal physical and mental development, protect him from disease, from birth to form an inseparable, close relationship with him.In order to take advantage of this opportunity, the nursing mother should try to maintain a good lactation as long as possible( formation in the mammary glands and excretion of milk from them).
Concept and classification of hypogalactia
 The term "hypogalactia" is derived from two Greek words: "hypo"( little, not enough) and "galactos"( milk).It means he lacks secretion of milk by the mammary glands of a woman breastfeeding a baby.By the time of occurrence, hypolactation occurs early and late.It is considered early if it occurs within 10 days after birth, and later - if from 11 days onwards.
The term "hypogalactia" is derived from two Greek words: "hypo"( little, not enough) and "galactos"( milk).It means he lacks secretion of milk by the mammary glands of a woman breastfeeding a baby.By the time of occurrence, hypolactation occurs early and late.It is considered early if it occurs within 10 days after birth, and later - if from 11 days onwards.
Types of hypogalactia depending on the cause:
- Primary or true hypogalactia accounts for less than 5% of all cases of milk deficiency in nursing women.Usually it happens early.
- Secondary hypogalactia, the causes of which are always not unique and closely related.It develops after 1-2 months after childbirth( sometimes later), and the deterioration of lactation is usually preceded by sufficient secretion of milk.
Depending on how much the mother does not have enough milk to provide the daily need of the baby, 4 degrees of hypogalactia are allocated:
- I degree - milk deficit does not exceed ¼( 25%) of the daily requirement;
- II degree - half( 50%) of the amount of milk required for a child per day is not enough;
- III degree - lack of milk reaches 75%( 3/4) of the daily requirement;
- IV degree - the deficit exceeds ¾( 75%) of the daily requirement for milk.
Causes of primary hypolactation
- Neuroendocrine disorders in the body of the mother that occurred during pregnancy and childbirth or occurred earlier;
- complicated course of pregnancy and childbirth;
- later application of the baby to the chest, absence or weakness of the sucking reflex in the prematurely born or immature baby.
Causes of secondary hypolactivation
- Psychological:
- the mother's lack of psychological mood and desire to feed the baby with breast milk;
- experience due to lack of skills of applying to the breast, expressing milk and establishing a feeding regimen.These worries are aggravated by the inattentive and indifferent attitude of medical personnel in the maternity home, and then in the children's consultation, which is not often, but it happens;
- influence of advertising in magazines and on television, promoting modern artificial mixtures that can replace mother's milk;
- stressful situations, fatigue, overwork.
- Physiological and pathophysiological:
- prolonged separation of the mother with the baby, for example, due to illness of one of them;
- prescribing a woman hormonal drugs that inhibit the formation of milk;
- non-compliance with the breastfeeding regime of the day, unbalanced and defective food;
- violation by the mother of the feeding regime of the child, early disorderly and untimely introduction of lures in the form of soups, mashed potatoes, cereals, cottage cheese;
- diseases of the mother: diseases of the genital organs( adnexitis, cysts, tumors, etc.) and extragenital pathology( heart diseases, diabetes, hypertension, etc.);
- child's diseases, which are unconditional contraindications to natural feeding: malformations, severe prematurity, etc.
- Social:
-
 bad habits of a nursing mother( alcohol abuse, smoking, etc.);
bad habits of a nursing mother( alcohol abuse, smoking, etc.); - social disorder, conflicts and quarrels between family members;
- forced mating with work or study.
Which of the women is at risk for development of hypogalactia?
Obstetricians-gynecologists predict the probability of hypogalacty development in every woman planning to become pregnant.Further, they assess the level of risk throughout the entire pregnancy, during childbirth and in the postpartum period.Reproductive and physical health of a woman is an important factor on which it depends on whether the baby will receive mother's milk after birth and how long and in what quantities the mammary glands will secrete it.
Doctors classify women at the risk of developing hypolactation as women with the following diseases, pathological conditions and history:
- Pregnant age to 18 and after 30 years;
- work in harmful production;
-
 bad habits( smoking, drug use, etc.);
bad habits( smoking, drug use, etc.); - single parent( single mother);
- foci of chronic infection in the body( chronic tonsillitis, chronic pyelonephritis, etc.);
- endocrine diseases( thyroid pathology, obesity, diabetes, etc.);
- heart and vascular disease;
- anemia;
- early or too late onset of menstruation, later establishment of a cycle;
- diseases of the genital organs( dysfunction of the ovaries, cysts and tumors, inflammatory processes, etc.);
- spontaneous interruptions of previous pregnancies and medical abortions in the anamnesis;
- pathology of pregnancy( threat of miscarriage, severe form of gestosis, etc.);
- premature delivery;
- belated birth;
- complicated course of labor( large blood loss, weakness of labor, etc.);Caesarean section of the
- ;
- complicated postpartum period.
Symptoms of breast milk deficiency
A woman breastfeeding a baby, decreases the amount of milk immediately.Firstly, after feeding she can not decant the remnants of milk, as she did before.Before feeding, there is no feeling of breast fullness with milk, and it does not flow with a trickle when pressing on the chest.Not as vividly as before, a subcutaneous venous network of mammary glands is expressed.
The child also immediately reacts to underfeeding:
- worries during sleep, but especially during and immediately after feeding;
- feeds water eagerly between feeds;
- rarely and unpronally urinates, stool is rare and lean, "hungry";
- is not good in weight.

Important: , when one or more of these symptoms appear, you do not need to immediately supplement the baby with a mixture!Confirm hypogalacty can only a pediatrician after a series of control weights.He also selects a suitable mixture for the child and calculates the amount needed for the pre-breastfeeding.
What is a lactation crisis
Lactation crises are repeated short( usually 3-4 days) periods of decreased milk secretion caused by hormonal changes in the body of a lactating woman.And they, in turn, are caused by the growth of the child and, correspondingly, by the growing needs of it in breast milk.If this happens not smoothly, but irregular, the mother's organism "gives out" lactation crises.But wait for the onset of such unpleasant moments breastfeeding woman should not, because they may not be at all.If lactation crises occur, most often at the 3rd or 4th week and at 3-4, 7-8 months of the baby's life.
Please note: the main thing to do if there is not enough breast milk is - do not get nervous and panic!And in any case, do not start to feed the baby from the bottle with a pacifier!
The lactation crisis is not true hypogalactia.And you can cope with it with the help of simple measures: each feeding to put the baby to one, and then to the second breast and increase the number of feedings per day.
Prevention of breast milk deficiency is a serious exercise that includes several stages:
- Every woman who gave birth to a girl must understand that her daughter is also a future mother, and that the longer she isWill feed the baby with breast milk, the more likely that her future grandchildren are not threatened with hypogalactia.
- When planning a pregnancy, a woman must undergo an in-depth medical examination.In cases of detection of anemia or other diseases, as well as the detection of foci of chronic infection in the body, she is obliged to undergo a course of prescribed therapy by the doctor.
- During pregnancy, she must strictly observe the regime of the day, fully and nutritionally balanced.For 1.5-2 months before the proposed delivery, she needs to start preparing the breasts for lactation( massage, contrasting douches, etc.).

- During childbirth for a powerful stimulation of milk secretion, doctors try to attach the newborn to the mother's breast right in the delivery room.
-
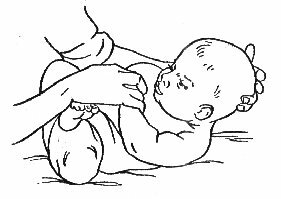 In the postpartum period, a woman after each feeding should express the milk from her breast until the last drop.She should see to it that the baby, when sucking, grasped the mouth of the nipple together with the areola.If, for some reason, the newborn can not be applied to the breast, during the approximate hours of feeding, the woman should massage the mammary glands herself and maximally express the milk from them.
In the postpartum period, a woman after each feeding should express the milk from her breast until the last drop.She should see to it that the baby, when sucking, grasped the mouth of the nipple together with the areola.If, for some reason, the newborn can not be applied to the breast, during the approximate hours of feeding, the woman should massage the mammary glands herself and maximally express the milk from them. - After discharge from the maternity home, the lactating mother must eat properly( 3200-3500 kcal per day, the volume of the liquid drunk - at least 2 liters).Multiplicity of meals - 5-6 times a day, about 30-40 minutes before feeding the baby.A woman should rather and fully rest, not forgetting about the day's sleep and fresh air.What if there is not enough breast milk.
.Methods of treatment of hypogalactia
- Mode of operation and hygiene:
- frequent application of the baby to the breast during the day, exclusion of a prolonged night break between feedings;
- strict adherence to a woman's regime of day and rest during the entire lactation period;
- a complete and balanced diet of a nursing mother using special dietary products( dry mixes) for nursing mothers, if appointed by a doctor;
- wearing only cotton fabrics that will prevent the formation of nipple cracks;
- after each feeding, decantation without the remainder of milk from the breast that the baby sucked.Bubbling of this breast with hot water from the shower with simultaneous massage of it and decanting the remnants of milk.Multiplicity of the procedure - 2 times a day for each breast, duration - 10 minutes.
- Phytotherapy with a lack of breast milk involves the use of vegetable decoctions and infusions to stimulate the secretory function of the mammary glands.The lactogenic effect is provided by seeds of cumin, anise and dill, fennel fruits, hop cones, nettle grass, walnuts, beans.But before using any recipe of traditional medicine, it makes sense to consult a pediatrician and an obstetrician-gynecologist in order to avoid undesirable consequences.
- Drug therapy involves the appointment of a nursing mother with a shortage of breast milk vitamin preparations containing nicotinic acid, tocopherol acetate( vitamin E), B vitamins, ascorbic acid, etc. Glutamic acid, biostimulating drug "Apilac", hormone oxytocin and other drugs.Special schemes for the therapy of hypolactation with drugs have been developed.But they can be used only strictly according to the prescription of a pediatrician or obstetrician-gynecologist.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures, namely UV and ultrasound, are used in conjunction with other activities.
- Methods of alternative medicine, such as homeopathy, acupuncture, acupressure, are well proven in the fight against hypogalactia.But any of them requires a preliminary consultation of a specialist doctor.
Important: the most important thing in the treatment of hypogalactia is the desire of a woman to breastfeed her baby and the firm belief that she should and can do it.Otherwise, neither the most qualified doctors, nor the proven methods of traditional and alternative medicine will help.
Zaluzhanskaya Elena Aleksandrovna, pediatrician