Histological examination: indications for carrying out and decoding

Histological examination( the term "histology" originated from Greek words meaning "the study of tissues") is carried out by macro( micro) copies of tissue materials taken from organs and pathological formations by different methods.
In medicine, especially in theoretical disciplines, the name "pathomorphological study" is also used.
Histological examination of materials is indispensable for accurate diagnosis.Of particular importance is "histology" in the definition of human cancer, for dynamic observation of the course of treatment and accurate evaluation of the results.
Contents: What is the purpose of the histological examination? How is the material taken? Types of biopsy? Collection rules for the material? Histological examination: interpretation of the results. Organizational questions of the histological examination.. What is the histological examination for?
. The doctor diagnosing and treating the diseases appoints the patient a histologicalExamination for:
- accurate confirmation of an alleged, or unclear diagnosis;
- determining the stages of the pathological process;
- dynamic monitoring of the course of the disease;
- distinctive( differential) diagnosis of various diseases;
- establishing the prevalence of the tumor;
- determining the scope of surgical treatment;
- to control changes in tissues under the influence of radiation and cytostatic treatment.
How the material is sampled for histological examination
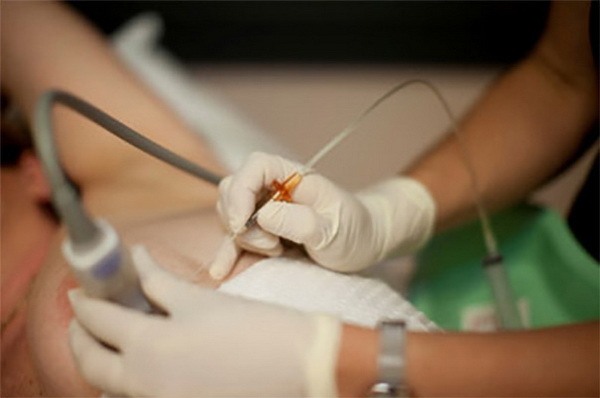
The method used for pathomorphological analysis of tissues is called biopsy.
Biopsy allows tissue sampling for macroscopic examination and cell diagnostics by microscopy.
 Biopsy is used as the main method for confirming data obtained with ultrasound, X-ray, MRI, computed tomography and other diagnostic techniques.
Biopsy is used as the main method for confirming data obtained with ultrasound, X-ray, MRI, computed tomography and other diagnostic techniques.
The most common biopsy is shown in case of new infections, for confirmation of liver inflammations( hepatitis), colon diseases, diagnostics of thyroid pathologies, gynecological diseases, urological and nephrological examination.
Biopsy types depending on the method of obtaining the histological material
The material for the histological examination is taken under visual control during the operative intervention.
They can be:
- individual fabrics;
- parts and entire organs;
- muscle;
- leather;
- mucous membrane of the bronchi, intestines, stomach and duodenum;
- lymph nodes;
- bone marrow;
- cervix;Prostate gland, etc.
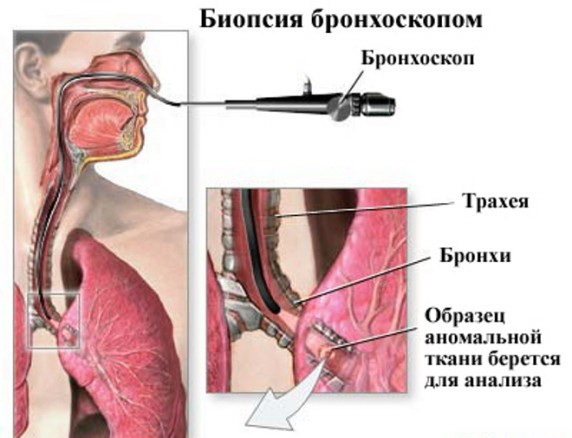
Biopsy types:
- excisional - the material is removed by excision in the surgical treatment of the whole pathological entity or organ;
- incisional - excision of part of pathological formation or organ;
- puncture - sampling of material for examination by puncturing an organ or tissue with a needle;
- aspiration - collection of material by a thin needle by suction from organs and formations having cavities filled with contents;
- Trepan biopsy - using a special thick needle, this method is used to collect bone materials;
- pliers - material is collected by "biting" from organs and tissues( with gastroscopy, colonoscopy, etc.);
- by curettage - internal walls( uterus, cavities);
Biopsy can be performed by an open method( external), the test material can be obtained by taking smears and washings.During the biopsy can additionally be used X-ray equipment, ultrasound.Biopsy is both diagnostic and therapeutic, that is, not just a fence of pathological formations is produced, but also their removal.
The biopsy method is used for both histological studies( study of tissue sections) and cytological( analysis of cellular structures).
Rules for sampling material
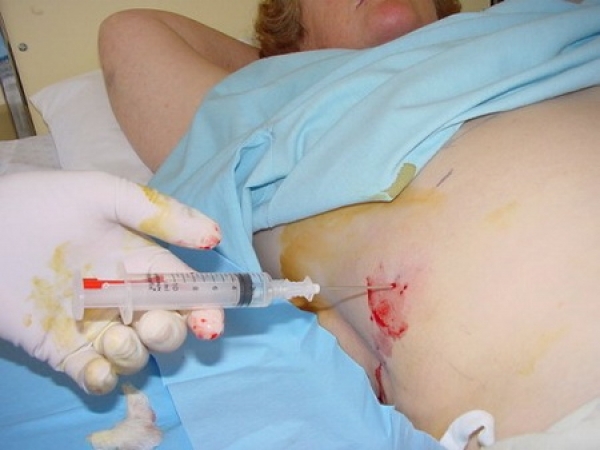 For histological analysis results, it is important that the material is taken from the desired location.It is best to take the place of the border with a normal tissue at the site, also do not use tissues damaged by necrotic changes or impregnated with blood.
For histological analysis results, it is important that the material is taken from the desired location.It is best to take the place of the border with a normal tissue at the site, also do not use tissues damaged by necrotic changes or impregnated with blood.
After sampling, the material must be urgently delivered to the laboratory.If there are delivery problems, fixation is required.Usually, formalin solution, or 70% medical alcohol, is used for these purposes.The volume of the fixative should be sufficient( not less than 20-30 times greater than the volume of the resulting tissue).Histological examination is usually carried out together with cytological( more simple and quick, giving a preliminary result).
Histological examination: interpretation of the results
The tissue analysis is performed by a pathomorphologist or pathologist.
For macroscopic diagnostics, the following is evaluated:
- size of the test material;
- color, density and consistency;
- pathological changes( softening, substitution and germination by other tissues, etc.).
Microscopy allows a detailed pathoanatomical analysis to be performed after analysis of the prepared tissue cut to reveal atypical tissue growth, other changes.
Based on the results obtained, the pathologist examines the clinical trial data from the medical history and draws a conclusion.In explicit cases, a final diagnosis is made.
In case of insufficient data, only a description of the detected changes can be made, which will help the treating physician in differential diagnosis with other pathologies.
In case of contact with a pathomorphologist of a material that does not contain pathological changes, a distorted diagnosis can be made.Therefore, it is very important to correctly select the tissue to be examined.
In disputed and unclear cases, a joint medical consultation is appointed.
Histological diagnosis is established according to accepted and approved classifications of the Ministry of Health, or WHO.
Organizational issues of histological examination

Histological analysis with correct organization and qualified material collection lasts within a week.Sometimes - up to 2 weeks( in case of examination of bone tissue).
The person in the laboratory delivers the person in charge with entries in special journals.In the laboratory the material is taken by a responsible laboratory assistant.
For long-term transport, it is important to follow the rules:
- careful packaging of the material( to prevent thermal effects and the battle of sampling vessels);
- on the packaging must be clearly marked with the address, patient data, the compartment in which it is located and the exact time.
- material is sent to only one laboratory.
The attending physician is responsible for checking the delivery and receipt of the analysis results.
For more information on the methods of histological examination, you will receive a video review:
Lotin Alexander, medical reviewer