Pulmonary haemorrhage: signs, diagnosis and emergency care
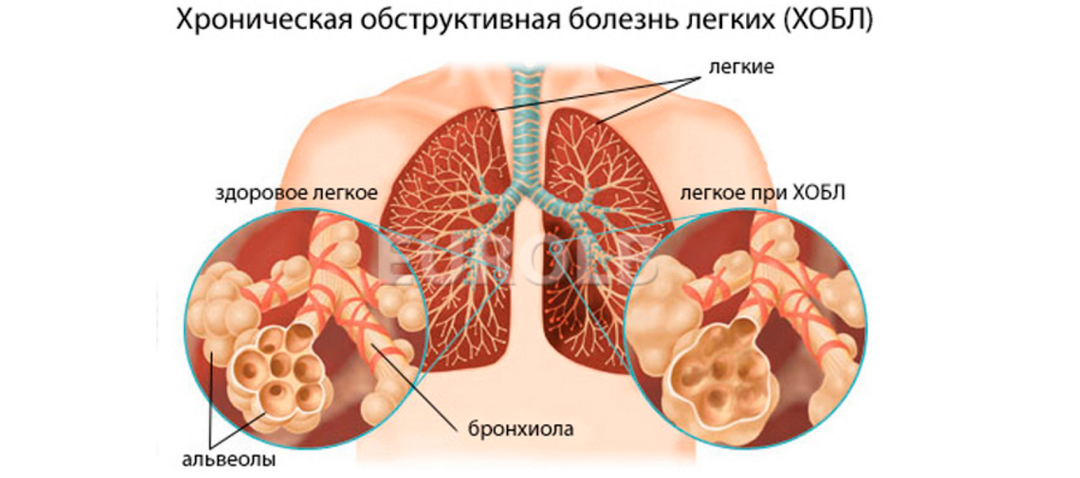
 Pulmonary haemorrhage is a pathological condition in which blood is released through the respiratory tract.In general, pulmonary hemorrhage develops when the integrity of the blood vessels of the bronchi and lungs is disturbed.Less often, it occurs with damage to the mediastinal organs, which in most cases still combine with damage to the lungs.
Pulmonary haemorrhage is a pathological condition in which blood is released through the respiratory tract.In general, pulmonary hemorrhage develops when the integrity of the blood vessels of the bronchi and lungs is disturbed.Less often, it occurs with damage to the mediastinal organs, which in most cases still combine with damage to the lungs.
Causes and mechanisms of development
Pulmonary hemorrhage may accompany( complicate) a number of diseases and pathological conditions - even those that do not directly affect the respiratory system . More often it is observed in male patients in the range of middle and advanced age, suffering from chronic diseases.
The reasons for which the integrity of the vessels of the respiratory system is violated and bleeding occurs is extremely high.Basically, these are conditions that lead to the destruction of the walls of the bronchi and lung tissue, rarely - the disease of the vessels themselves. Pulmonary haemorrhage is most often observed in such diseases and pathological conditions of the lung as:
- destructive( destroying) forms of tuberculosis;
- abscess;
- gangrene;
- disintegrating tumors( cancer);
- fungal diseases, primarily - aspergilloma, caused by the mold fungus Aspergillus fumigatus.
Which processes precede pulmonary hemorrhage
There is a very wide variety of forms of tuberculosis at which pulmonary hemorrhage can develop - in particular,
-
 infiltrative forms( they are characterized by the fact that tuberculosis affects the lungs as separateFoci, the altered tissues in which it is characteristic to disintegrate);
infiltrative forms( they are characterized by the fact that tuberculosis affects the lungs as separateFoci, the altered tissues in which it is characteristic to disintegrate); - fibrous-cavernous form( cavity formation);
- cirrhotic form( sprouting of the lung with a connective tissue);
- cavernous pneumonia( pneumonia caused by a tubercle bacillus and characterized by the formation of cavities).
Less frequent pulmonary hemorrhage occurs in such diseases and conditions as:
- bronchial carcinoid( endocrine tumor);
- bronchiectasis with marked cough syndrome;
- is a migrating foreign body in the tissue of the lung or in the lumen of the bronchus;
- lung infarction( necrosis due to oxygen starvation);
- endometriosis( migration of endometrial cells( inner layer of the uterus) into the thoracic cavity, which causes pulmonary bleeding during menstruation);
- insufficiency of sutures after operations on the lungs;
- Goodpasture syndrome( rejection of cells of own pulmonary alveoli);
- Wegener's syndrome( autoimmune inflammation of the walls of blood vessels - including bronchial and pulmonary);
- closed trauma of the lungs and bronchial tree;
- breakthrough of the aortic aneurysm( abnormal bulging of the wall) into the left main bronchus.This is a rare cause of pulmonary hemorrhage, but in this case it will be very pronounced.
Most often, pulmonary hemorrhage is observed due to the defeat of blood vessels of the circulatory system.
Signs of pulmonary hemorrhage
Pulmonary hemorrhage can begin:
- with minor hemoptysis;
- suddenly, against a background of good or, at least, a satisfactory condition.
It is impossible to provide for when pulmonary hemorrhage begins, there are no signs that precede it.
The blood that is released may be:
- scarlet;
- is a dark one.
It can stand out:
- through the mouth - in most cases;
- through the nose - less often.
The amount of blood does not depend on the amount of blood it leaves( through the mouth or nose).
Features of blood loss in pulmonary hemorrhage - it can stand out:
- with a trickle;
- jerks in the form of spittles( in case the diaphragm begins to shrink convulsively - the condition looks like a hiccup).
Blood for pulmonary hemorrhage may be allocated:
- in its pure form;
- together with sputum and / or saliva;
- in the form of a foam.
Blood discharged into the respiratory tract due to pulmonary hemorrhage usually does not collapse.
Almost immediately, there are common signs that are characteristic of any bleeding:
-
 pallor of the skin;
pallor of the skin; - weakness;
- dizziness;
- the retardation;
- increased heart rate and pulse;
- lowering blood pressure.
Flow characteristics
Depending on how much blood was released, pulmonary hemorrhages are divided into:
- small - up to 100 ml of blood;
- medium - up to 500 ml;
- large - more than 500 ml;They are also called profuse - uncontrolled.
 There is a small form of pulmonary hemorrhage - hemoptysis.It is manifested by multiple bloody streaks in the sputum or saliva. Hemoptysis differs from bleeding only by the amount of blood extracted. There is no clear distinction between pulmonary hemorrhage and hemoptysis.The blood loss can be the same for single bleeding with the exit through the respiratory tract of clean blood with minor impurities and with multiple hemoptysis, when the patient coughs up mostly sputum with blood veins, but with frequent coughing it will pour out quantitatively into blood loss, as if bleeding.
There is a small form of pulmonary hemorrhage - hemoptysis.It is manifested by multiple bloody streaks in the sputum or saliva. Hemoptysis differs from bleeding only by the amount of blood extracted. There is no clear distinction between pulmonary hemorrhage and hemoptysis.The blood loss can be the same for single bleeding with the exit through the respiratory tract of clean blood with minor impurities and with multiple hemoptysis, when the patient coughs up mostly sputum with blood veins, but with frequent coughing it will pour out quantitatively into blood loss, as if bleeding.
Clean, unalloyed blood can be released with significant pulmonary bleeding - it literally pours out of the respiratory tract, not having time to mix with the secretion of the bronchial tree. But in most cases, with pulmonary hemorrhage in the secretions, the following is detected:
- saliva;
- mucus;
- secret of the bronchial tree;
- in some cases - particles of pulmonary and bronchial tissue( if bleeding happened because of their disintegration).
In case of pulmonary hemorrhage, the blood can clear from the throat:
- at one time;
- with pauses;
- continuously.
Such nuances are important for diagnosing diseases that caused pulmonary hemorrhage.Thus, with the breakthrough of the lung ulcer, accompanied by the destruction of the lung tissue and the vessel passing through it, the blood will pour out into the lumen of the bronchi at the same time, and in the late stages of lung cancer characterized by destruction, it will cough continuously.
Even a one-time withdrawal of a small amount of bleeding from the respiratory tract means pulmonary bleeding and requires a full range of therapeutic measures.
Very often, prior to seeking medical help, pulmonary hemorrhage is given an incorrect evaluation, which deceives the doctor and affects the treatment. There are two extremes when patients and their associates:
- because of stress and fear subconsciously exaggerate the amount of blood that has been released through the respiratory tract;The
- underestimates the data on the released blood, forgetting to mention that some of its patients were swallowed or aspirated( inhaled back into the respiratory tract).
Because of this, the quantitative estimation of bleeding in pulmonary hemorrhage is approximate.
Consequences of
Severe pulmonary hemorrhage can quickly lead to death.The causes of death in pulmonary hemorrhage can be:
- instantaneous;
- remote.
The immediate causes of death in pulmonary hemorrhage include asphyxia - a sudden onset of suffocation due to blood accumulation in the respiratory tract, resulting in a disruption of gas exchange and deterioration of oxygen supply of tissues.
The long-term causes of death from pulmonary hemorrhage are in fact its complications:
-
 aspiration pneumonia( inflammation of the lung tissue due to stagnant phenomena provoked by the ingress of liquid secreted into the lungs);
aspiration pneumonia( inflammation of the lung tissue due to stagnant phenomena provoked by the ingress of liquid secreted into the lungs); - pulmonary heart failure;
- "subsidence" of the infection on blood clots left in the airways, the development of a purulent process with all the consequences, and in the first place, it is sepsis - a generalized infectious disease of the body.
Diagnosis of pulmonary hemorrhage
It is not difficult to detect the fact of pulmonary hemorrhage. More difficult to establish:
- which pathological process provoked the development of pulmonary hemorrhage;
- is a source of bleeding.
Since many pulmonary diseases can lead to many diseases and pathological ones, even with modern instrumental methods, their diagnosis can be difficult and delayed.
This pathological condition - from the category of those in the diagnosis of which the questioning of the patient about the details of the disease( collection of anamnesis) is no less important than the methods of instrumental and laboratory diagnosis.
Information that is required for accurate diagnosis:
- when bleeding occurred, how much blood was allocated, whether it had impurities;
- , was there previously any secretion of blood through the oral cavity, if yes - when was the last time, with what frequency, where and how was treated;
- presence in the anamnesis( medical history) of diseases of the respiratory system, cardiovascular system, blood;
- were there any diseases of the lungs, bronchi, heart, vessels, blood;Most important are hypertension, bronchiectasis, myocardial infarction;
- Does the patient have occupational diseases - diseases associated with harmful working conditions( for example, asbestosis of the lungs due to work in asbestos production)
Please note! The dark color of the isolated blood is a sign of bleeding from the vessels that form the pulmonary artery system, scarlet, bright blood is released from bleeding from the bronchial arteries.
Methods that are most commonly used to determine the source of pulmonary hemorrhage:
- X-ray diffraction in two projections;
- computed tomography is a more informative method, but inaccessible due to lack of equipment in a number of clinics;
- bronchoscopy.
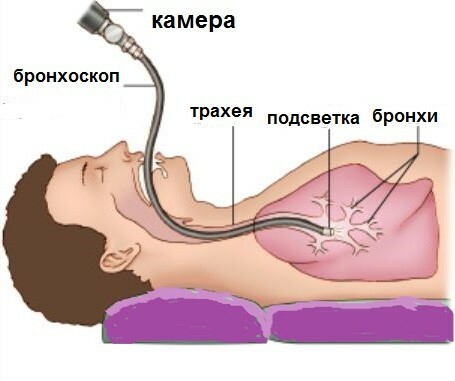
Bronchoscopy was previously considered contraindicated in pulmonary haemorrhage, fearing airway trauma and worsening of bleeding.Improvement of the equipment, medical skills and anesthetic support made it possible to use this method confidently in the diagnosis of pulmonary hemorrhage . To date, this is the only method that allows you to directly see the source of bleeding, or at least determine the bronchus from which blood is excreted. Bronchoscopes are used:
- rigid - thanks to it you can suck blood from the bronchial tree;
- is flexible - it allows you to inspect smaller bronchi.
If bleeding was observed before admission to the hospital and was no longer repeated - bronchoscopy is indicated in the first 2-3 days from the moment of its stop.It is in this time interval that it is possible to determine the source of pulmonary hemorrhage. The patient should not worry - if the bronchoscopy is performed correctly, bleeding does not occur.
 In some cases, in order to determine the source of pulmonary hemorrhage, use arteriography - X-ray examination of bronchial arteries with contrast.
In some cases, in order to determine the source of pulmonary hemorrhage, use arteriography - X-ray examination of bronchial arteries with contrast.
A general blood test will help to assess the degree of hemorrhage - by reducing hemoglobin, reducing the number of red blood cells, changing the color index.
These studies are carried out in urgent( urgent) order.In the non-urgent for the purpose of clarifying the diagnosis, sputum is examined, which is secreted with blood in case of pulmonary hemorrhage. The elements found in it will help clarify the diagnosis:
- acid-fast bacteria allow suspected tuberculosis with disintegration, which provoked bleeding;
- fragments of pulmonary tissue indicate the disintegration of cancer tissue or gangrene of the lung;
- purulent contents indicate a breakthrough of the abscess, because of which pulmonary hemorrhage could occur.
Differential Diagnosis
In some cases, pulmonary bleeding has to be distinguished from the gastrointestinal. This will help to make the following nuances:
- in case of pulmonary hemorrhage, bloody discharge - mostly bubbly, with a mixture of saliva, mucus and bronchial secretions, with gastrointestinal - with an admixture of gastric juice, intestinal secretions, food particles;
- with gastrointestinal bleeding, melena is observed - a semi-liquid stinking black stool that is not present with pulmonary hemorrhage;
- pulmonary hemorrhage precedes respiratory diseases( in particular, chronic, long-diagnosed), gastrointestinal - pathology of the digestive tract;
- blood that has spilled from the vessels of the respiratory system, has a neutral or alkaline reaction, and blood from the vessels of the gastrointestinal tract is acidic.

Bleeding may be from the upper respiratory tract, but impressionable patients regard it as pulmonary, thereby misleading the ambulance dispatcher.Such confusion is due to a significant accumulation of secreted in the bronchial tree, and the patient seems to have accumulated blood there.To exclude such bleeding, examination by an otolaryngologist is necessary.
Treatment and emergency care for pulmonary hemorrhage
Unlike external bleeding, the ability to effectively provide first aid outside the hospital is extremely limited. This patient should be immediately hospitalized in a hospital - preferably not by himself, but by an ambulance.
During transport of the patient:
- should not contain cough( containment occurs due to fear of losing more blood) - on the contrary it is necessary to cough up blood from the respiratory tract, it should be done without strain;
- for improving cough should be in a sitting or semi-sitting position.
During the diagnostic procedures and treatment activities in the hospital, the patient should be at rest if there is no need for movement and a semi-sitting position.
Pulmonary bleeding is stopped by methods such as:
- Pharmacological;
- endoscopic;
- X-ray-endovascular;
- surgical.
 The pharmacological method is the introduction of hemostatic, as well as antihypertensive drugs.Hypotensive drugs are administered to cause a so-called controlled hypotension - a decrease in systolic( upper) blood pressure to 85-90 mm.Gt;Art.It is at this level of blood pressure that there are improved conditions for physiological thrombosis( blood clotting, blockage of damaged arteries) and cessation of bleeding.
The pharmacological method is the introduction of hemostatic, as well as antihypertensive drugs.Hypotensive drugs are administered to cause a so-called controlled hypotension - a decrease in systolic( upper) blood pressure to 85-90 mm.Gt;Art.It is at this level of blood pressure that there are improved conditions for physiological thrombosis( blood clotting, blockage of damaged arteries) and cessation of bleeding.
The pharmacological method is effective in small and medium pulmonary hemorrhages - with its help, this bleeding can be stopped in 80-90% of patients. This method is also used in the prehospital stage if it is not possible to quickly hospitalize a patient in a hospital.
The endoscopic procedure for the treatment of pulmonary hemorrhage is the use of hemostatic methods with the aid of an endoscope. Use methods such as:
- diathermocoagulation( moxibustion of bleeding vessels with the help of an electric current supplied);
- laser photocoagulation( "sealing" of bleeding vessels by laser beam);
- occlusion( obstruction) of the bronchus through which blood is excreted.
Bronchial occlusion is used for severe pulmonary hemorrhage.Bronch is clogged:
- with a "gag" made of foam rubber sponge;
- balloon catheter made of silicone;
- gauze swab.
This method is used with caution and under control so as not to cause deterioration in ventilation of the corresponding part of the lung. In most cases, the duration of occlusion is 2-3 days. Thanks to the occlusion of the bronchus, it is possible:
- to prevent the ingress of blood into other fragments of the bronchial tree;
- to prolong patient preparation for surgery;
- in some cases finally stop the bleeding.
With the help of X-ray-endovascular occlusion, a bleeding vessel can be clogged.In most cases, blockage occurs after bronchial arteriography. Through a special catheter into the lumen of the vessel, the following are introduced:
- pieces of Teflon velor;
- beads of silicone;
- fibrin sponge;
- of the patient's own blood clots( autograft);
- if the vessel has a large diameter - a metal spiral, to which is attached a stream of threads from Teflon.
If all these methods do not help or help poorly, and pulmonary hemorrhage continues - resort to surgery. Operations for pulmonary hemorrhage can be :
- emergency - they are performed during continued bleeding;
- urgent - they are performed immediately after stopping bleeding by other methods;
- deferred - they resort to it, not mashing, after stopping bleeding, as much as possible full examination of the patient and preoperative preparation;
- planned - before they are carried out stop bleeding, examination and preparation for surgical treatment, but, in contrast to delayed operations, scheduled surgical interventions for pulmonary hemorrhage do not require haste, they are performed in the most convenient( in many ways) time.
Expectant tactics, which in some cases are practiced in surgery, with pulmonary hemorrhage is impractical, as it can lead to:
- recurrent pulmonary hemorrhage;
- pneumonia due to blood aspiration;
- progression of the disease, which caused bleeding.
Operations can be of varying degrees of radicality. Most often, excision of a fragment of the lung in which the affected area is located with a source of bleeding.
Less common( mainly with bleeding due to tuberculosis lesions) are performed:
- dressing of bronchial arteries;
- bronchus occlusion( obstruction);
- thoracoplasty( the plastic of the chest, due to which its shape changes and new conditions for its organs are created - in case of bleeding, the lung after thoracoplasty is compressed, because of the tightening of its tissues, the bleeding ceases).
During surgery and in the early postoperative period, it is important to remove blood and clots from the bronchial tree to prevent infection and the development of pneumonia.A bronchoscope is used to clean the bronchial tree.
With all these methods of stopping pulmonary hemorrhage, conservative therapy is conducted in parallel: the patient is given: whole blood or blood products( fresh frozen plasma, erythrocyte mass) -
- - to replace blood lost due to bleeding;
- saline solutions - to replenish fluid in the body;
- antibacterial drugs - to prevent aspiration pneumonia;
- for tuberculosis - antituberculous drugs.
Prevention
 The main prevention of pulmonary hemorrhage is to prevent the occurrence of diseases that can provoke bleeding, as well as the timely treatment of those provocative diseases that are already available.
The main prevention of pulmonary hemorrhage is to prevent the occurrence of diseases that can provoke bleeding, as well as the timely treatment of those provocative diseases that are already available.
Smoking should immediately abandon their addiction, because smoking exacerbates any pathological process in the respiratory system - nicotine acts destructively on the walls of the vessels.
Forecast
With prompt recognition of pulmonary hemorrhage and timely adequate treatment, the prognosis is favorable for life. Patients who underwent pulmonary hemorrhage should be monitored by a physician.
Threat to life comes with massive bleeding and the development of its consequences - first of all this:
- asphyxiation;
- aspiration pneumonia.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, consulting physician