Nevus: the main types, principles of diagnosis, prevention of melanoma
 Nevus( synonyms: birthmark, birthmark, pigment spot) - benign skin formation, characterized by the appearance of hyperpigmentation spots on the skin.Pigmented spots are very diverse in shape, size and color.The size of the nevi varies from one to two millimeters in diameter to huge spots of irregular shape in sizes of 10-20 centimeters.Pigmented nevi can not rise above the skin at all, be somewhat convex and even resemble warts.Their color varies from corporal to dark brown, almost black. Table of contents: Causes of nevi formation How often are nevi: epidemiology Classification of nevi
Nevus( synonyms: birthmark, birthmark, pigment spot) - benign skin formation, characterized by the appearance of hyperpigmentation spots on the skin.Pigmented spots are very diverse in shape, size and color.The size of the nevi varies from one to two millimeters in diameter to huge spots of irregular shape in sizes of 10-20 centimeters.Pigmented nevi can not rise above the skin at all, be somewhat convex and even resemble warts.Their color varies from corporal to dark brown, almost black. Table of contents: Causes of nevi formation How often are nevi: epidemiology Classification of nevi
Causes of nevi formation
Nevus is a local accumulation of nevocyte pigment cells, which are pathologically altered melanocytes responsible for normal skin color.The main difference between nevocytes and melanocytes is the huge concentration of melanin( natural pigment), which exceeds the normal concentration several dozen times.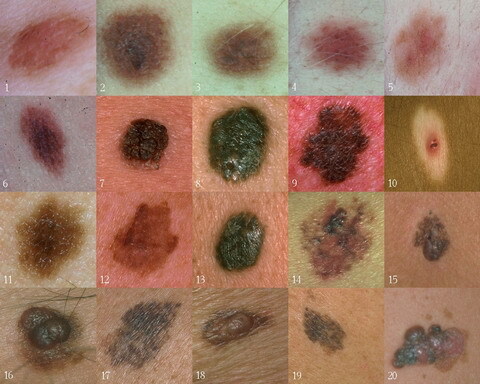 It is believed that pigment nevus is a congenital malformation of development, in which the migration of melanoblasts( melanocyte precursors and nevocytes) is disturbed.As a result, melanoblasts form compact congestions in the skin, which then turn into nevuses.The division of nevi into congenital and acquired is very conditional, many scientists believe that the acquired nevuses that arise in adults do not form anew, simply - they manifest themselves over time.
It is believed that pigment nevus is a congenital malformation of development, in which the migration of melanoblasts( melanocyte precursors and nevocytes) is disturbed.As a result, melanoblasts form compact congestions in the skin, which then turn into nevuses.The division of nevi into congenital and acquired is very conditional, many scientists believe that the acquired nevuses that arise in adults do not form anew, simply - they manifest themselves over time.
- exposure to pregnant women of radiation or toxic compounds;
- diseases of the urogenital tract in pregnant women;
- pathology of pregnancy, flowing with pronounced fluctuations of the hormonal background( threat of termination of pregnancy, toxicosis);
- genetic predisposition.
Acquired nevi appear throughout life.The provoking factors may be: hormonal "storms" in the adolescent period;
-
 ;
; - pregnancy, during which there are also fluctuations in the level of different hormones;
- oral contraceptive intake;
- infectious and allergic skin diseases: acne, dermatitis and the like;
- mechanical skin damage;
- Ultraviolet irradiation - the most powerful stimulator for the emergence and growth of nevi is the usual insolation, that is, exposure to sunlight.
How often are nevi: epidemiology
Up to 10% of children are already born with birthmarks( nevi).In the pubertal period, nevi are detected in 95% of adolescents.By 25-30 years, the number of nevi in one person is 35-40 on the average.Further, with age, there is a tendency to decrease the number of nevi, and to 85-90 years on the body there are isolated formations.
Classification of nevi
There is a generally accepted international classification according to which several groups of nevi are isolated, and each of these groups has a number of its varieties. The main forms of tumors include :
- Melanocytic nevi of epidermal origin.
- Melanocytic nevi of dermal origin.Benign dermal melanosis.
- .
- Congenital melanocytic nevi.
- Dysplastic melanocytic nevus or nevus of Clark.
- Other nevus-like formations.
Melanocytic nevi of epidermal origin
This is the most common type of nevi.Melanocytic nevi refers to acquired nevuses;On average, each person has from 5 to 15 similar formations.Appearance: round or oval shape with distinct edges;Smooth or slightly papillomatous surface;Color from reddish to brown. The melanocytic form of the lesions can be manifested in the following types:
- The border nevus is named because of the localization of the new cells - on the border of the epidermis and the dermis.It looks like a flat spot, the localization on the body - in any area.
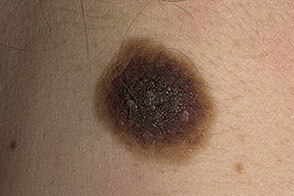
- Intradermal nevus of the skin( it is often called a mole) - looks like a dome-shaped formation from light brown to almost black.Can be covered with hair.Over time, as it grows, this nevus can become covered with papillomatous growths( papillomatous nevus), and also connect with the skin with only a thin stem.
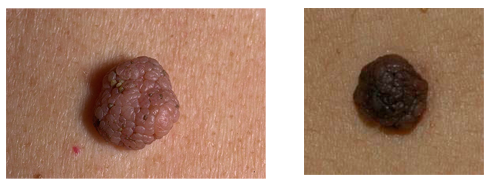
- Complex nevus - is a transitional form between the two previous types.It looks like a small papule with papillomatosis.It is extremely rare that the size is more than 1 cm.
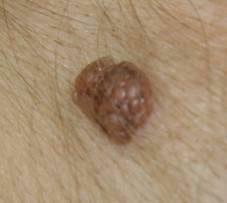
- A halo nevus( Settone nevus) is a special type of pigmentary lesion that has the appearance of a pigmented spot with its surrounding depigmentation zone.This zone is 2-3 times wider than the nevus itself.It occurs most often in adolescents and pregnant women and may eventually disappear.
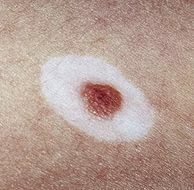
- A nevus of balloon-shaped cells is a rare variety of nevi.Practically no different from ordinary moles, but consists of special balloon-like cells.The diagnosis is made only on the basis of histological examination.
- Recurrent melanocytic nevus, also called pseudomelanoma, is formed as a result of incomplete removal of dermal or complex nevus.In this case, after a few weeks or months, a new tumor grows on the site of the removed tumor, usually larger in size.
- Spitz nevi( synonyms: spindle cell, epithelioid).Characteristic for children, is a single hemispherical nodule dense to the touch.Color: pink or brownish with a red tinge.A variant is the Reed's nevus, which is a 3-10 mm diameter formation in the form of a blue-black papule with distinct edges.The classic location is the hips and legs of women.

Melanocytic nevi of dermal origin
In this case melanocytes of the dermis become the source of non-carcinomas. This species also has a multiplicity of manifestations:
- A simple blue nevus - looks like a single nodule up to 10 mm in size, from gray to black with a bluish tinge.The surface of the nevus is smooth, the hair does not grow on it.Typical localization: face, hands, neck.It is found on the mucous membrane of the vagina and mouth.

- Cellular blue nevus, having the form of a blue node.Its differences from simple: more pronounced pigmentation and larger sizes - up to 3 cm. Potentially dangerous in terms of malignancy.Typical localization: buttocks, loin, sacrum, much less often - the dorsum of the hands and feet.
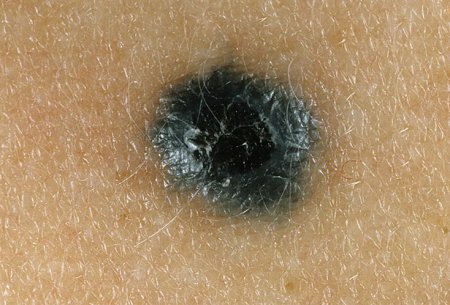
- Combined nevus - in one formation a combination of morphological features of simple blue, borderline, intradermal and complex nevus is determined.Outwardly similar to the nevus, whose elements in education are greater.
- A deeply penetrating nevus is another type of mixed nevus, in which components typical of complex, blue and Spitz nevi are found.Has the form of a pigmented papule or nodule, localized on the shoulder blades, neck and head.Outwardly, it differs little from a blue nevus.Benign dermal melanoses
These are the closest "relatives" of blue nevuses, having a typical appearance.
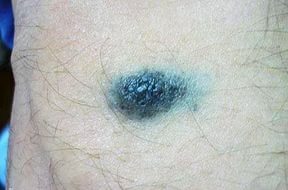
There are the following varieties of dermal melanosis: - Mongolian spot is a delimited oval spot, up to 10 cm in size, grayish-cyanotic or brown, localized on the lumbosacral region.Occurs in 80% of children of Mongoloid and Negroid races and only 1% of Caucasians.Usually disappears by 8-13 years.

- Nevus Ota( Ota) - marked skin pigmentation around the eyes and sclera.It looks like darker spots, located on one side of the face and prone to fusion.Typical for girls of Mongoloid and Negroid races.
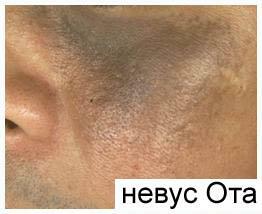
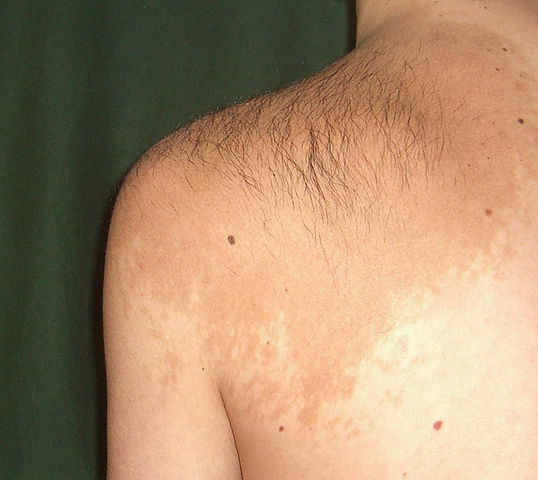
- Nevus Ito - almost not different from the nevus Ota, but localized on the lateral surface of the neck, in the supraclavicular area, near the scapula.
Congenital melanocytic nevi
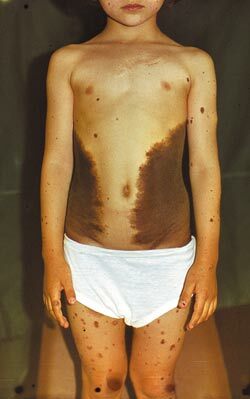 Synonyms of this variety are the verrucose or giant nevus.They occur in 1% of newborns.Can be represented by various elements: papillomatous, papular, nodal.Determined immediately after the birth of the child or in a few weeks. The following are distinguished in size:
Synonyms of this variety are the verrucose or giant nevus.They occur in 1% of newborns.Can be represented by various elements: papillomatous, papular, nodal.Determined immediately after the birth of the child or in a few weeks. The following are distinguished in size:
- small - up to 1.5 cm;
- medium - 1.5-20 cm;
- giant - more than 20 cm
Giant nevuses often resemble the form of "panties", bathing suit or are located in the form of "leopard skin".They grow with the child.
Dysplastic melanocytic nevus or nevus Clarke
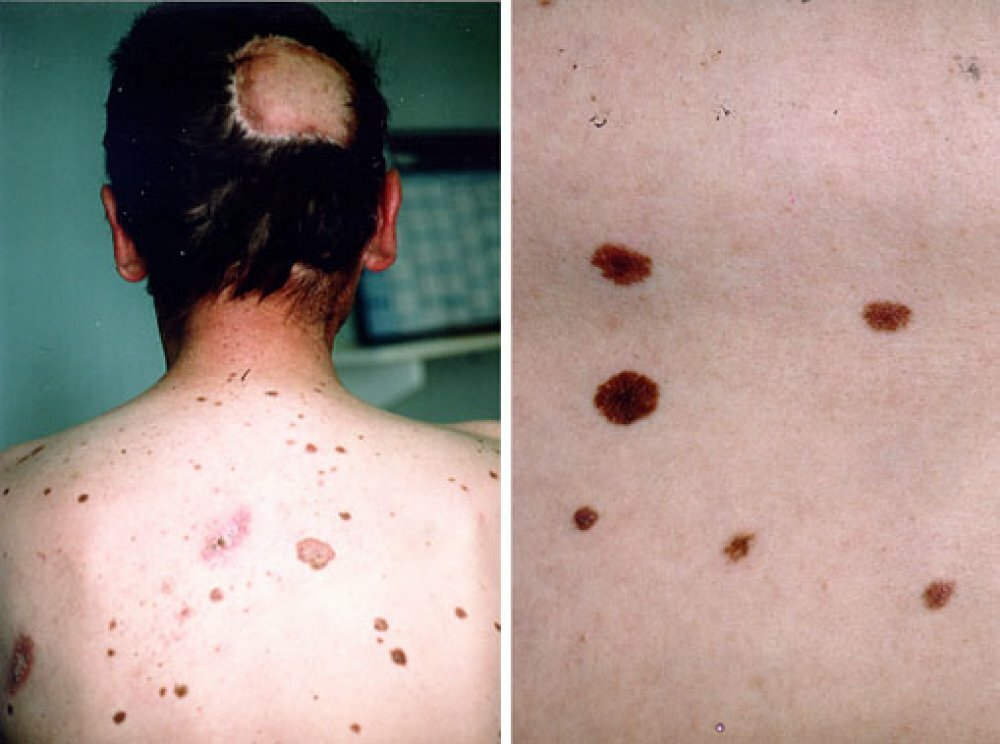 This is the most unfavorable neuromus in terms of malignancy, a frequent precursor of melanoma.Appears usually before puberty, and new elements occur right up to the old age.It looks like an irregularly shaped patch, up to 5 cm in size. Borders are often irregular, a zone of hyperemia( redness) can be seen along the edge.Favorite places of appearance: head, back, waist, buttocks and other places, constantly closed from sunlight.
This is the most unfavorable neuromus in terms of malignancy, a frequent precursor of melanoma.Appears usually before puberty, and new elements occur right up to the old age.It looks like an irregularly shaped patch, up to 5 cm in size. Borders are often irregular, a zone of hyperemia( redness) can be seen along the edge.Favorite places of appearance: head, back, waist, buttocks and other places, constantly closed from sunlight.
Other nevus-like formations
There are other skin formations, also called nevi, but in fact not being them.These are:
- hemangiomas;
- teratomas;
- sebaceous nevuses - formations localized most often on the head, resembling nevi, but not containing new cells and melanin;
- vascular nevi are areas of skin depleted of blood vessels and therefore have a paler color.
Other neoplasms of the skin that do not contain nevocytes and melanin - the so-called epidermal nevi - are also classified as nevi.Note: The main difference between epidermal nevi and moles is the absence of melanin-containing cells in their structure.The causes of neoplasms are the same, but the source of the tumor is other skin cells. Types of epidermal nevuses:
- papillomatous soft nevus - is a soft plaque of small size, color almost identical to normal skin;
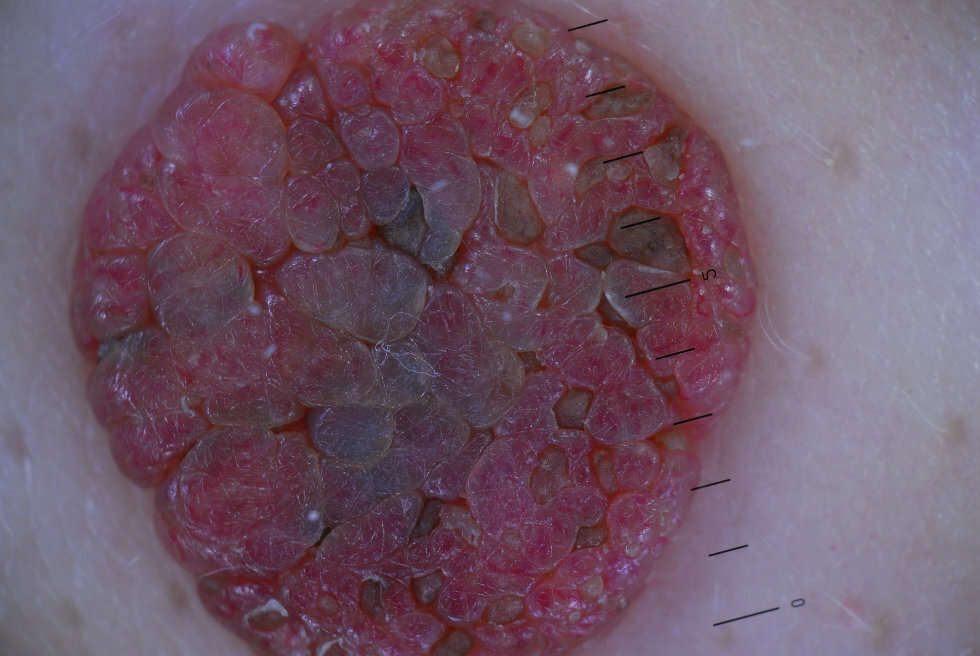
- warty epidermal nevus - most often an innate neoplasm.It has the appearance of dense warty tumors grayish or brownish in color from 1 to 4 cm in size. A characteristic location is limbs, especially along the course of nerves and large vessels;
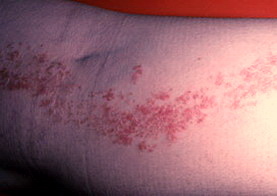
- Darier-like epidermal nevus.It is so named because of its similarity to skin rashes with Darya's disease.It looks like keratinized papules covered with the same crusts;
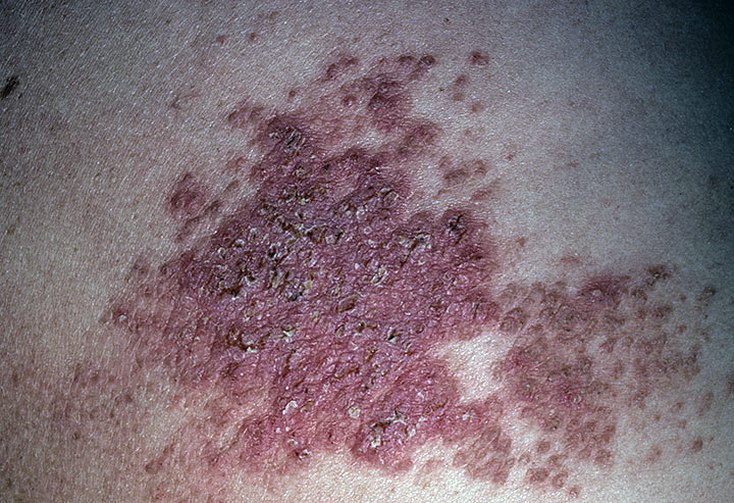
- Haley-Haley-like nevus is also named because of the similarity of the lesions to the clinical picture of the family bubble-eye Haley-Haley.It is manifested by inflammatory plaques with erosions and vesicles;
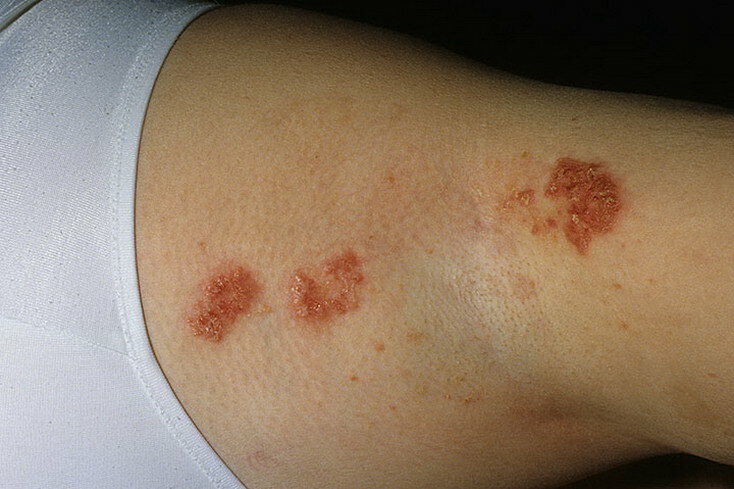
- Naevus Corniculatus - looks like filamentary papules with giant comedones located on them;
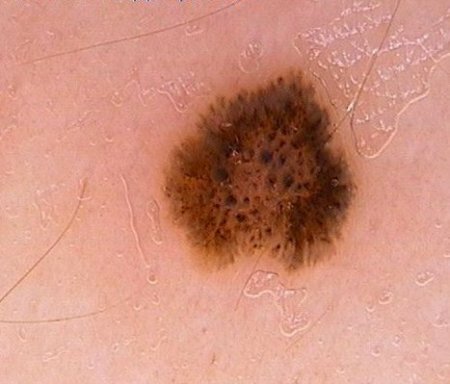
- dermal and lichenoid epidermal nevuses - resemble psoriatic rashes.

Diagnosis
It should be known that, focusing on the photo, nevi is extremely difficult to distinguish from each other.Finally, other methods of diagnosis help to establish the appearance of the nevus.To study birthmarks is necessary to reveal dangerous nevi and prevent their transformation into a malignant tumor - melanoma.Diagnosis begins with a conversation between the dermatologist and the patient. During the conversation, the physician establishes the following facts:
- how long ago an education appeared, it is acquired or congenital;
- whether the appearance( color, dimensions, boundaries) of the nevus changed;
- than caused changes - burns, injuries, combs, attempts to remove;
- whether attempts were made to remove and which method was used.
It is necessary to measure the nevus, describe its shape, color and other characteristics. Important! Biopsy of nevi with diagnostic purpose is not carried out! Any traumatic effect on a nevus can provoke its malignancy, therefore a histological examination is carried out only after the nevus is completely removed.In some cases, the method of taking a smear from the surface of the nevus can be used if it has cracks.It is recommended to perform a similar study in specialized cancer centers where it is possible to perform a radical removal of the nevus immediately after receiving the result of the study.The most effective way to study nevuses before removal is epiluminescent microscopy.The essence of the method is to study the nevus under a microscope directly on a person.To do this, the oil is applied to the neoplasm, providing the effect of epiluminescence( illumination), and then through the oil, the nevus is examined through a dermatoscope.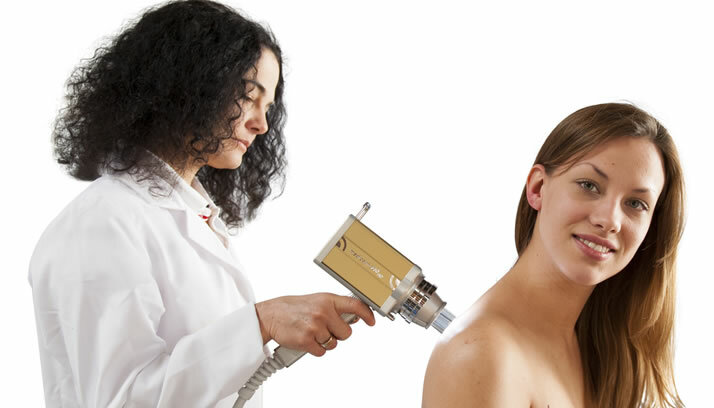 All the more popular today is the computer diagnostics of nevi, during which the photo of the nevus is compared with an extensive image base.The result of computer analysis suggests the most likely type of nevus.
All the more popular today is the computer diagnostics of nevi, during which the photo of the nevus is compared with an extensive image base.The result of computer analysis suggests the most likely type of nevus.
Complications of nevi
Large nevi can cause severe discomfort to a person due to constant irritation with clothing, which causes damage to them.In case of damage, there is itching in the area of the nevus and bleeding from its surface.However, the most dangerous phenomenon, to which nevi can lead, is the transformation of them into a malignant tumor - melanoma.Not all nevi are dangerous in this regard, the most malignant and predisposed to transformation are the blue nevus, the nevus Ota and the dysplastic melanocytic nevus.There are some signs, in which presence the risk of melanoma is significantly increased. Special attention should be paid to:
- large congenital nevi;
- occurrence of nevi in the senile age;
- a large number of nevi on the body - over 50 pieces at a time;
- frequent occurrence of new nevuses;
- the location of the birthmark in a place where they are subjected to a permanent mechanical action: on the neck, underarms, at the ankles, at the waist.
All nevi should be monitored closely, especially for large ones and located in uncomfortable places, and if the following symptoms occur, the oncologist should be consulted immediately. Symptoms of nevus degeneration:
- Fast growth - more than 1,5-2 times in several weeks.
- Rapid change in the color of the nevus, especially the acquisition of a black or dark blue color.
- Changing contours of the spot - smooth contours become scalloped, "torn".
- "Smearing" the boundaries of the nevus.
- Bleeding or permanent mowing of a mole.
- Skin peeling over the nevus.
Prevention of malignancy of nevi
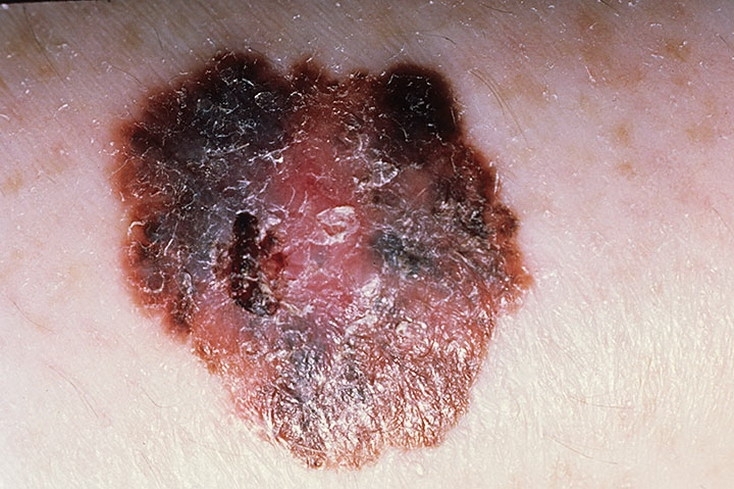
Melanoma

- Nevus Ota( Ota) - marked skin pigmentation around the eyes and sclera.It looks like darker spots, located on one side of the face and prone to fusion.Typical for girls of Mongoloid and Negroid races.

- Nevus Ito - almost not different from the nevus Ota, but localized on the lateral surface of the neck, in the supraclavicular area, near the scapula.

Congenital melanocytic nevi
 Synonyms of this variety are the verrucose or giant nevus.They occur in 1% of newborns.Can be represented by various elements: papillomatous, papular, nodal.Determined immediately after the birth of the child or in a few weeks. The following are distinguished in size:
Synonyms of this variety are the verrucose or giant nevus.They occur in 1% of newborns.Can be represented by various elements: papillomatous, papular, nodal.Determined immediately after the birth of the child or in a few weeks. The following are distinguished in size:
- small - up to 1.5 cm;
- medium - 1.5-20 cm;
- giant - more than 20 cm
Giant nevuses often resemble the form of "panties", bathing suit or are located in the form of "leopard skin".They grow with the child.
Dysplastic melanocytic nevus or nevus Clarke
 This is the most unfavorable neuromus in terms of malignancy, a frequent precursor of melanoma.Appears usually before puberty, and new elements occur right up to the old age.It looks like an irregularly shaped patch, up to 5 cm in size. Borders are often irregular, a zone of hyperemia( redness) can be seen along the edge.Favorite places of appearance: head, back, waist, buttocks and other places, constantly closed from sunlight.
This is the most unfavorable neuromus in terms of malignancy, a frequent precursor of melanoma.Appears usually before puberty, and new elements occur right up to the old age.It looks like an irregularly shaped patch, up to 5 cm in size. Borders are often irregular, a zone of hyperemia( redness) can be seen along the edge.Favorite places of appearance: head, back, waist, buttocks and other places, constantly closed from sunlight.
Other nevus-like formations
There are other skin formations, also called nevi, but in fact not being them.These are:
- hemangiomas;
- teratomas;
- sebaceous nevuses - formations localized most often on the head, resembling nevi, but not containing new cells and melanin;
- vascular nevi are areas of skin depleted of blood vessels and therefore have a paler color.
Other neoplasms of the skin that do not contain nevocytes and melanin - the so-called epidermal nevi - are also classified as nevi.Note: The main difference between epidermal nevi and moles is the absence of melanin-containing cells in their structure.The causes of neoplasms are the same, but the source of the tumor is other skin cells. Types of epidermal nevuses:
- papillomatous soft nevus - is a soft plaque of small size, color almost identical to normal skin;

- warty epidermal nevus - most often an innate neoplasm.It has the appearance of dense warty tumors grayish or brownish in color from 1 to 4 cm in size. A characteristic location is limbs, especially along the course of nerves and large vessels;

- Darier-like epidermal nevus.It is so named because of its similarity to skin rashes with Darya's disease.It looks like keratinized papules covered with the same crusts;

- Haley-Haley-like nevus is also named because of the similarity of the lesions to the clinical picture of the family bubble-eye Haley-Haley.It is manifested by inflammatory plaques with erosions and vesicles;

- Naevus Corniculatus - looks like filamentary papules with giant comedones located on them;

- dermal and lichenoid epidermal nevuses - resemble psoriatic rashes.

Diagnosis
It should be known that, focusing on the photo, nevi is extremely difficult to distinguish from each other.Finally, other methods of diagnosis help to establish the appearance of the nevus.To study birthmarks is necessary to reveal dangerous nevi and prevent their transformation into a malignant tumor - melanoma.Diagnosis begins with a conversation between the dermatologist and the patient. During the conversation, the physician establishes the following facts:
- how long ago an education appeared, it is acquired or congenital;
- whether the appearance( color, dimensions, boundaries) of the nevus changed;
- than caused changes - burns, injuries, combs, attempts to remove;
- whether attempts were made to remove and which method was used.
It is necessary to measure the nevus, describe its shape, color and other characteristics. Important! Biopsy of nevi with diagnostic purpose is not carried out! Any traumatic effect on a nevus can provoke its malignancy, therefore a histological examination is carried out only after the nevus is completely removed.In some cases, the method of taking a smear from the surface of the nevus can be used if it has cracks.It is recommended to perform a similar study in specialized cancer centers where it is possible to perform a radical removal of the nevus immediately after receiving the result of the study.The most effective way to study nevuses before removal is epiluminescent microscopy.The essence of the method is to study the nevus under a microscope directly on a person.To do this, the oil is applied to the neoplasm, providing the effect of epiluminescence( illumination), and then through the oil, the nevus is examined through a dermatoscope. All the more popular today is the computer diagnostics of nevi, during which the photo of the nevus is compared with an extensive image base.The result of computer analysis suggests the most likely type of nevus.
All the more popular today is the computer diagnostics of nevi, during which the photo of the nevus is compared with an extensive image base.The result of computer analysis suggests the most likely type of nevus.
Complications of nevi
Large nevi can cause severe discomfort to a person due to constant irritation with clothing, which causes damage to them.In case of damage, there is itching in the area of the nevus and bleeding from its surface.However, the most dangerous phenomenon, to which nevi can lead, is the transformation of them into a malignant tumor - melanoma.Not all nevi are dangerous in this regard, the most malignant and predisposed to transformation are the blue nevus, the nevus Ota and the dysplastic melanocytic nevus.There are some signs, in which presence the risk of melanoma is significantly increased. Special attention should be paid to:
- large congenital nevi;
- occurrence of nevi in the senile age;
- a large number of nevi on the body - over 50 pieces at a time;
- frequent occurrence of new nevuses;
- the location of the birthmark in a place where they are subjected to a permanent mechanical action: on the neck, underarms, at the ankles, at the waist.
All nevi should be monitored closely, especially for large ones and located in uncomfortable places, and if the following symptoms occur, the oncologist should be consulted immediately. Symptoms of nevus degeneration:

Melanoma
The danger of melanoma is that the tumor, even at small sizes, tends to give metastases - to the liver, brain and other organs.Mortality with this tumor is 45-50%, so it's better to try not to prevent its occurrence.It is impossible to completely prevent the appearance of melanoma, but, adhering to simple recommendations, it is possible to significantly reduce the risk of degeneration of nevus neoplasm in melanoma.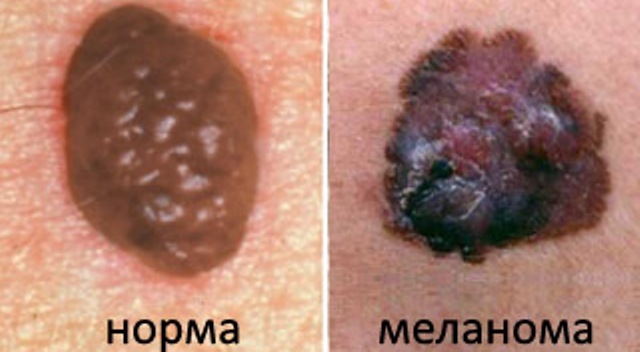 So, recommendations for the prevention of melanoma:
So, recommendations for the prevention of melanoma:
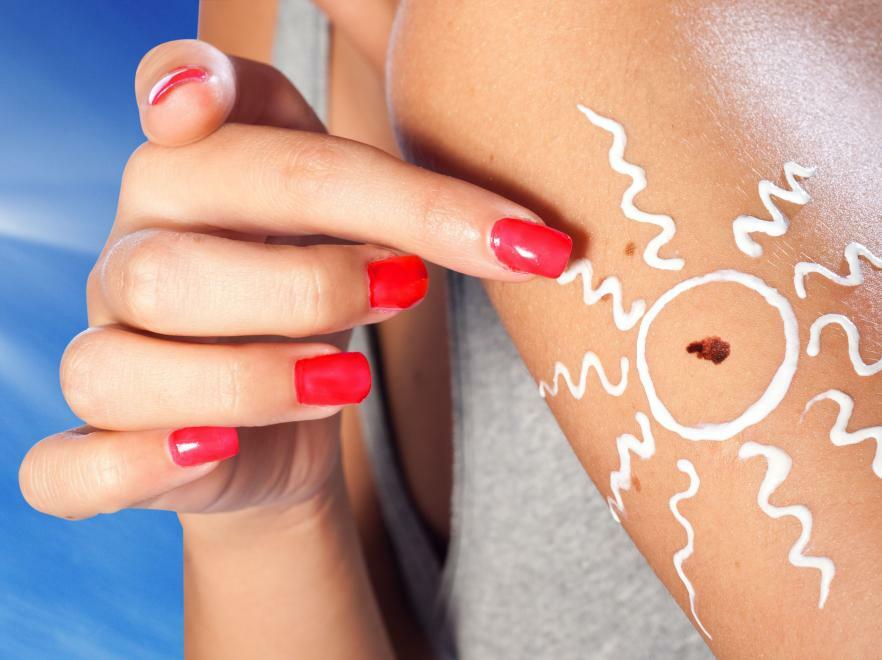
- Reduce the exposure time to sunlight.Exclude being in the sun during its maximum activity - from 11 am to 5 pm.
- To try to exclude completely getting of ultraviolet radiation on potentially dangerous nevi, including - and during visiting of a sun deck.
- Avoid injuries to moles.
- If you have at least one of the above mentioned signs of transformation, you should immediately contact the dermatoonologist.
It should be noted that sunscreens do not reduce the degree of irradiation of the nevus with ultraviolet light!In the early stages of melanoma is completely curable. Roman Gudkov, resuscitator,