Pulmonary heart: diagnosis and treatment
 Pulmonary heart - a pathology, in which there is an increase in the size of the right heart( atrial and ventricular) due to increased pressure in the small circle of the circulation.In turn, hypertension in a small circle develops as a result of damage to the bronchi, lungs, pulmonary vessels and changes in the shape of the chest.
Pulmonary heart - a pathology, in which there is an increase in the size of the right heart( atrial and ventricular) due to increased pressure in the small circle of the circulation.In turn, hypertension in a small circle develops as a result of damage to the bronchi, lungs, pulmonary vessels and changes in the shape of the chest.
Causes of different forms of pulmonary heart
Patients with diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems should remember that the chances of pulmonary heart disease are very high due to the fact that it causes a large number of very diverseDiseases and conditions. In many cases, the onset of a pulmonary heart is the result of a triggered state due to an erroneous diagnosis or an incorrect treatment strategy.This ultimately results in an overload of the right side of the heart and the development of a pulmonary heart.
This disease occurs:
- acute with severe course;
- acute with subacute flow( the process ceases, the state is the average between acute severe and chronic);
- chronic.
Each of the forms can arise as a result of very many reasons - they can be divided into three large groups:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- diseases of the bronchopulmonary system;Changes in the thorax( thoraco-diaphragmatic).
- .
Cardiovascular causes of acute pulmonary heart disease with severe course:
- massive pulmonary embolism;
- gas embolism of arteries( plugging of gas contents);
- fatty embolism of arteries( cessation of blood flow due to massive accumulation of fatty particles);
- Tumor embolism of arteries( clogged conglomerates of tumor cells penetrated into the blood stream);
- parasitic embolism of arteries( clogging of eggs by parasites);
- pulmonary thrombosis( differs from thromboembolism in that a thrombus forms in some part of the vessel and clogs it - while embolism is occlusion by particles brought with a blood flow);
- pulmonary vein thrombosis.
Changes in the broncho-pulmonary system that can lead to the development of an acute pulmonary heart with severe course are:
- severe asthma attack, up to asthmatic status;
- massive pneumonia;
- pneumothorax( presence of air in the pleural cavity, in which the norm is negative pressure);
- pneumomediastinum( massive accumulation of air in the mediastinum - a segment of the chest between two lungs).
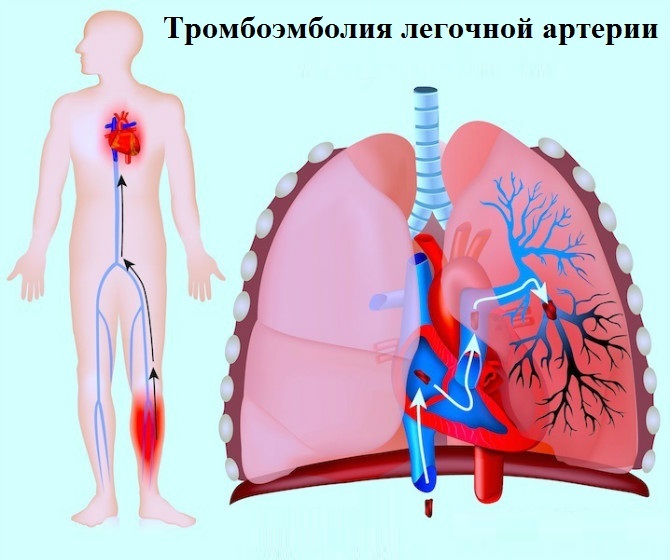
Most often, an acute pulmonary heart with a severe course develops due to thromboembolism( clogging of a thrombus) of the pulmonary artery( PE of ).In turn, PE that provokes the onset of the pulmonary heart occurs when:
-
 atrial fibrillation( frequent chaotic atrial contractions);
atrial fibrillation( frequent chaotic atrial contractions); - hypertension;
- pathological changes in the vessels of the small circle of blood circulation - primarily, increased blood pressure, stagnation and microcirculation disorders;
- pathological changes in blood coagulability - increased coagulability and oppression of the anticoagulant system;
- ischemic heart disease( oxygen starvation of the myocardium);
- heart defects caused by the development of rheumatism;
- phlebothrombosis( inflammatory changes in the wall of veins with thrombotic deposits);
- vascular pathologies in the pulmonary artery system - systemic atherosclerosis( deposition of fatty plaques on the inner wall of the vessels) and vasculitis( inflammation of the vessel walls with subsequent destruction);
- of chronic hypodynamia( in particular, if it is necessary to have a prolonged bed rest after trauma, surgery, coma, etc.);
- surgical interventions on the veins of the lower extremities and pelvis.
A vicious circle is formed: the pulmonary artery suffers from cardiovascular diseases, which in turn leads to a pulmonary heart. In the past 8-10 years, clinicians have noted an increase in the incidence of pulmonary heart disease associated with an increase in the incidence of pulmonary embolism.
Cardiovascular causes of acute pulmonary heart disease with subacute :
- embolism of one or more branches of the pulmonary artery( not the main trunk);
- thrombosis of the same branches, characterized by frequent relapses;
- arteritis of the pulmonary artery system( inflammatory process in the vascular wall of various origin - most often bacterial).
Changes in the broncho-pulmonary system that can lead to the development of an acute pulmonary heart with a subacute current are:
-
 lung infarction( necrosis of one of its sites);
lung infarction( necrosis of one of its sites); - Valve( or valve) pneumothorax( a condition in which air enters the pleural cavity, but can not go back because of a barrier in the form of a valve formed by nearby organs);
- acute inflammation of the lungs, affecting most of the lung tissue;
- severe form of bronchial asthma( up to the development of asthmatic status);
- is a cancerous lymphangitis of the lung( inflammation of the lymphatic vessels of the lung due to the massive accumulation of cancer cells brought with lymph flow in them).
Changes in the chest that are capable of causing an acute pulmonary heart with a subacute current is a chronic hypoventilation( deterioration in the ventilation of the lung) that can occur in pathological conditions such as:
- botulism( a toxicoinfectious lesion of the nervous system,Coming after eating food infected with pathogens of botulism);
- poliomyelitis( spinal cord involvement by poliovirus);
- myasthenia gravis( autoimmune muscle damage with their characteristic fatigue).
Cardiovascular causes of development of chronic pulmonary heart:
- primary increase in arterial pressure;
- thromboembolism of pulmonary artery branches;
- arteritis;
- vasculitis - inflammation of the vascular wall with its destruction, in particular, allergic, obliterating( due to blockage), nodular, lupus origin;
- atherosclerotic changes in the wall of the pulmonary artery;
- a decrease in the lumen of the pulmonary artery and pulmonary veins due to external pressure( aneurysmatic aortic dilatation, mediastinal tumors, and so on);
- repeated embolism;
- resection of the lung( removal of the segment of lung tissue).
Changes in the broncho-pulmonary system that can lead to the development of a chronic pulmonary heart:
- diseases accompanied by a decrease in bronchial lumen( bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive bronchitis( as well as its shape with an asthmatic component), pulmonary fibrosisConnective tissue), emphysema);
- pathology, in which the bronchi undergo pressure from the outside( fibrosis, granulomatosis).
Changes in the chest, due to which its mobility is limited, as a result - there is a chronic pulmonary heart:
- kyphoscoliosis of the thoracic spine( curvature in the anterior-posterior and lateral projections);
- polycystic lung disease( multiple cysts due to lung underdevelopment);
- chest deformation ;
- pleural moorings( connective tissue lintels in the pleural cavity, which do not allow the easy to straighten to the fullest extent);
- the so-called Pickwick syndrome, provoked by obesity - the inability to do deep and frequent breaths and exhalations;
- paresis( partial paralysis) of the diaphragm;
- neuromuscular lesions - in particular, poliomyelitis;
- Bechterew's disease( chronic inflammation of the joints of the spine);
- violations of the chest excursion after unsuccessful thoracoplasty( surgical manipulations leading to a change in the shape of the chest).
In recent years, the clinic has been experiencing an increase in cases of chronic heart disease, which is explained by the increase in obstructive diseases in the population.
Development of the disease
The acute pulmonary heart develops as follows.Diseases of the small circle of blood circulation lead to a narrowing of the pulmonary vessels over a long distance and the appearance of persistent bronchospasm.Because of this, the pressure in the great circle of blood circulation decreases, ventilation of lungs and gas exchange worsen( carbon dioxide does not leave the lung tissue, and oxygen does not saturate it). A vicious circle is formed: due to these phenomena in the small circle of blood circulation, blood pressure rises, which causes the right heart( atrial and ventricle) to overload and gradually expand due to stagnant blood phenomena in them . In far-reaching cases, due to the fact that the blood does not hurry to leave the right heart, it presses on the surrounding tissues, as a result, the permeability of the pulmonary capillaries increases, the fluid gets easy access and exits into the alveoli - lung swelling occurs.
In the development of chronic pulmonary heart, the role of increased pressure in a small circle of blood circulation due to pathological changes in the lungs. In obstructive processes, the permeability of the bronchi is impaired, as a result - the lungs are ventilated( aerated) unevenly.Because of this, gas exchange is interrupted - getting rid of carbon dioxide and oxygen saturation, naturally patients suffer from the fact that oxygen supply to tissues is disrupted.
Both acute and chronic heart, as progression occurs, there is a violation of the acid-base state of the tissues. First they are compensated for by internal reserves of the body, but decompensation comes quickly enough.
In an acute or prolonged chronic pulmonary heart in a myocardium that suffers an exorbitant load, dystrophic changes( disruption of nutrition) and then necrosis( necrosis) eventually develop, which can provoke myocardial infarction .
Symptoms
An acute pulmonary heart with severe course develops most often during 4-5 hours( less often 1-2 hours or several days). Its main manifestations:
- sharp deterioration of state of health on the background of complete physiological well-being;
- chest pain pressing, medium intensity;
- excited state( due to sudden onset of hypoxia);
- signs of acute onset of heart failure.
Signs of acute cardiac failure are:
-
 severe dyspnea;
severe dyspnea; - abruptly cyanosis of the skin and visible mucous membranes;Especially pronounced acrocyanosis - cyanosis of the tips of the fingers and nose, ears;
- swelling of veins on the neck ;
- increase and soreness of the liver;
- inability to perform physical actions;
- may be swelling of the extremities.
If the cause of the acute pulmonary heart is the thromboembolism of the main pulmonary artery trunk, then all these symptoms can develop from a few minutes to half an hour.In this case very quickly come:
- shock due to severe cardiovascular abnormalities;
- pulmonary edema.
If you do not take any action, the development of necrosis of the lungs will begin. Symptoms of a heart attack( necrosis) of the lungs with an acute cardiac heart:
- The increase in chest pain associated with the act of breathing, dyspnea and cyanosis( cyanosis) of the skin and mucous membranes;
- The appearance of a cough is mostly dry, but there may be a separation of a small amount of sputum;
- in about half of patients - the appearance of hemoptysis;
- increase in body temperature - this is due to aseptic necrosis, in this case the characteristic resistance( stability) of hyperthermia to the use of antibiotics is manifested;
- weakened breathing.
Acute pulmonary heart with subacute flow manifested by acute symptoms, but more moderate in comparison with acute course. These are the following features:
- average intensity of pain in the chest at the act of breathing;
- dyspnea, which can pass fairly quickly;
- increased heart rate and pulse;
- faintness.
The chronic pulmonary heart can be:
- compensated;
- decompensated.
This also determines the clinical symptoms of the pathology.
At the compensation stage, there are signs of a major pathology that provoked the emergence of a chronic pulmonary heart - the symptoms of the expansion of the right half of the heart begin to develop gradually, at later stages.These are signs such as:
- dyspnea, which is aggravated in some conditions - during physical exertion, in a recumbent position, by inhalation of cold air.Dyspnoea in this case has a dual origin - arises through respiratory and heart failure;
- pains in the heart area - they appear due to the fact that its right half due to overload perform more than usual, work, and the food remains the same . Painful sensations can also occur due to the stretching of the pulmonary artery;
- cyanosis of the skin and visible mucous membranes;
- arterial hypertension;
- reduced body temperature.
It is noteworthy that all these symptoms manifest themselves more intensively if inflammation occurs in the lungs. Characteristic sign - with even expressed pneumonia in patients with pulmonary heart, body temperature becomes normal or at the extreme reaches a mark of 37 degrees Celsius.
Some patients may have signs of a stomach ulcer that occurs due to a violation of the gas composition of the blood.
If the decompensation stage comes, the following clinical picture is observed:
- persistent build-up of edema;
- progressive increase and soreness of the liver;
- worsening of urine production;
- disorders from the central nervous system - headache, attacks of dizziness, tinnitus, a feeling of drowsiness, apathy.Such signs appear because the CNS structures lack oxygen in the required quantity and are affected by under-oxidized products.
Diagnosis of pulmonary heart
The diagnosis of pulmonary heart disease is based on the history of the disease, developing symptoms and data obtained by using additional survey methods.In the diagnosis, the doctor also focuses on the presence of diseases that can trigger the development of the pulmonary heart.
Additional instrumental and laboratory research methods that are used in the diagnosis of pulmonary heart:
-
 chest X-ray - in the picture in chronic, far-reaching cases, the right heart is enlarged, and the pulmonary artery swells.Radiography is informative in the late stages of the disease, since the thickening of the walls of the heart at the initial stages is not so significant as to manifest itself on the X-ray image;
chest X-ray - in the picture in chronic, far-reaching cases, the right heart is enlarged, and the pulmonary artery swells.Radiography is informative in the late stages of the disease, since the thickening of the walls of the heart at the initial stages is not so significant as to manifest itself on the X-ray image; - Ultrasound of the heart - with his help determine the thickening of the right heart;
- electrocardiography - signs of right heart ischemia will be revealed, in some cases - rhythm disturbance;
- pulmonary angiography - it is used to diagnose thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery;
- spirometry - during it determine the degree of respiratory failure and by these signs indirectly draw conclusions about the degree of development of the pulmonary heart;
- coagulogram and prothrombin index - determine the state of the blood coagulation system.
Treatment of pulmonary heart
The therapeutic measures for the pulmonary heart should first of all be directed to the treatment of the disease causing it . Applicable:
- broad-spectrum antibiotics for massive pneumonia;
- antihypertensive drugs for hypertension;
- cardiac glycosides for heart disease;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in vasculitis;
- oxygen therapy for chronic obstructive diseases( in a number of cases, long night oxygen therapy is used)
and so on.
Symptomatic therapy is shown depending on the emerging conditions and symptomatic complexes:
- with increased blood viscosity - anticoagulants to prevent the formation of blood clots.Http://www.f-med.ru /nevrologia/img/ hart15.jpg In some cases, an old but effective method is used as an alternative: bloodletting( it is used in case the ratio of erythrocytes to plasma exceeds the norm);
- for the purpose of facilitating the removal of sputum from the respiratory tract - mucolytic( thinning liquor) preparations
and so on.
It should be noted that the development of heart failure in patients with pulmonary heart disease is a poor prognostic sign that can result in death. Therefore, in the development of signs of heart failure urgent intensive therapy is necessary:
- diuretics( due to their diuretic effect, the burden on the heart will decrease);
- nitrates( used to improve the blood supply to the right heart, which suffers from increased stress on them);
- inhibitors of phosphodiesterase( used for bronchial obstruction);
- inotropes( they are used in the deterioration of the contractility of the heart).
With an acute pulmonary heart with a sharp current and its chronic neglected form, a shock condition can develop which leads to clinical death due to cardiac arrest. In this case, resuscitation is carried out:
- indirect cardiac massage;
- intubation of the respiratory tract with artificial ventilation.
If this condition was due to pulmonary embolism, an emergency operation is required, during which a thrombus is extracted from the pulmonary artery and thrombolytic agents are administered.
If the patient has a chronic pulmonary heart, and conservative therapy is ineffective, then surgical treatment is needed - heart transplant( often combined with lung transplantation).Such surgical intervention is extremely rare due to the lack of donors( for example, in North America - 10-15 per year), but it is a chance to continue the life of the patient.After heart and lung transplantation, the life span of about half of the operated ones is 5 years.
Prevention
Prevention of pulmonary heart disease is the prevention and treatment of diseases that cause its appearance.Particular caution should be exercised with regard to pulmonary embolism.
Emphysema of the lungs and obstructive diseases of the respiratory system at the advanced stages always lead to the development of the pulmonary heart.
Pulmonary heart: how many live with it?
The prognosis for acute pulmonary heart disease with acute course and chronic form at the stage of decompensation is complex, more favorable in acute form with subacute flow and chronic at the stage of compensation. The prognosis and course depend on:
- the severity of the underlying disease;
- degree of pulmonary hypertension.
According to different data, 10 to 50% of patients with this pathology live more than 5 years( this figure increases with regular inhalation of oxygen).
Even with timely diagnostics and adequately selected therapy of complete cure, does not occur, as the pulmonary heart is essentially the result of urgent conditions( pulmonary embolism) or prolonged course of many chronic diseases.
Mortality due to pulmonary heart remains high.Annually in the world because of a pulmonary heart about 20 thousand people die, about 300 thousand are hospitalized in a hospital about this disease.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, consulting physician