Benign brain tumor
The brain tumor, whether it is benign or malignant, is one of the most terrible diagnoses, capable of seriously destroying the fate of both the patient himself and his loved ones. Benign tumors are usually referred to as intracranial neoplasms. All possible types of tumors arising in the brain are divided into two types: primary, which are formed directly in the brain, and secondary, which are the result of the appearance of tumors of other organs.
Benign brain tumors are characterized by the fact that they do not spread to other organs, based only on the brain tissue. Usually they grow slowly enough, and the specific symptoms depend on the place of the brain in which the tumor is located.
Types of benign tumors
The group of benign brain tumors include:
- Meningioma. This type of tumors is considered the most frequent oncological disease of the brain( this disease is diagnosed in 20-30% of all brain tumors).Most often, meningioma is a benign tumor, but in some cases it can turn into a malignant form, affecting other organs, most often the skin and lungs. The most likely source of a tumor is the meningeal envelope, the tumor itself can appear in any part of the brain. Most often, tumors are diagnosed in the age groups of 30 to 40 years, in women this disease is twice as likely as in males, it is often possible to observe the rapid development of the tumor in pregnant women. There is a family type of meningioma associated with neurofibromatosis of the second type.
- Gliomes of the first stage. Gliomas are tumors formed from glial cells of the brain. They are also often referred to as oligodendrogliomas, astrocytomas, mixed gliomas and ependymomas.
- Hemangioblastoma. This type of tumors, most often diagnosed in the blood vessels of the brain.
- Neurinoma of the auditory nerve( Schwannoma).The auditory nerve strikes.
- Tumors of the spinal cord and pituitary gland.
Symptoms of a benign brain tumor
As noted above, the symptoms of the disease strongly depend on the location of the tumor in the brain. Such symptoms can be headaches( most of all in the morning), hearing or visual impairment, epileptic convulsions and seizures. Also, there may be a urge to vomit or nausea, coordination of movement and gait disorder, rapid and unexpected changes in mood, inability to concentrate on anything, severe absent-mindedness. Often there are memory disorders, tingling and numbness of the limbs. Of course, the presence of these symptoms is not a direct evidence of the presence of a brain tumor, but they can signal about it, so when they appear, it is worth examining for the presence of a tumor. Also, the symptoms may be completely absent - there are cases when the tumor was detected accidentally during the examination on a tomograph or another examination, while the patient did not complain of any of the above symptoms.
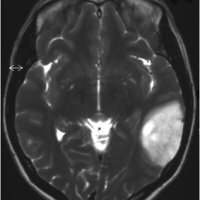
Diagnosis of a benign brain tumor
As indicated above, the most significant reason for carrying out the procedure for studying the brain is a gradual increase or a pronounced symptom of tumors. Most often for diagnosis, use magnetic resonance imaging, combined with computer tomography and neurological examinations of the patient.
Treatment of a benign brain tumor
In most cases, treatment of a benign tumor is not difficult. Nowadays, neurosurgical centers have the latest equipment and highly qualified doctors. Only in some cases there may be difficulties associated with the place where the tumor is located - if it is located so that the operation is fraught with the risk of damaging the important structures of the brain, which can lead to more serious problems. Also, sometimes relapses of certain types of tumors are possible. In this case, a specialist can prescribe a patient either a course of radiotherapy, or repeated resection.