Muscle atrophy: what is it, causes, symptoms, how to treat
Muscle atrophy - This is a loss of muscle mass that can cause serious health problems, including difficulty walking and even breathing correctly. Often, muscle wasting occurs due to extremely sedentary lifestyles and other health problems that can lead to muscle loss.
In addition to what muscular atrophy is, let's look at the main symptoms of this condition and discuss what treatments are currently available.
Content
- What is Muscle Atrophy?
- Types of muscle atrophy
- Causes of muscle atrophy
- Causes of atrophy due to lack of movement
- Causes of neurogenic atrophy
- Other reasons
- Symptoms
- Complications of the condition
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- How to prevent atrophy
- Final tips
What is Muscle Atrophy?

According to scientific work “Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Muscle Atrophy ", published in the journal Disease Models & Mechanisms in 2013, atrophy is a term used to define a reduction in the size of a tissue or organ due to cell contraction, which can occur through the loss of organelles, cytoplasm and proteins. Thus, the loss of proteins in muscle cells causes muscle atrophy, which can interfere with some vital metabolic functions.
Muscle - this is a large supply of protein in our body. Muscle mass isn't just about keeping your body in shape. The main physiological muscle function is to stock up on energy sources for the body to use when needed. That is, if a person is deprived of nutrients or prone to a serious and debilitating medical condition (such as cancer, severe burns, autoimmune diseases and heart failure), the body looks for other available energy sources, such as protein stored in muscles.
It is very useful in emergencies, but not as a permanent source of energy.
Thus, the presence of a reserve of protein in the body useful for promoting healthy aging, preventing the occurrence of metabolic disorders and providing energy in stressful conditions of vital organs, such as, for example, the heart, brain and liver.
Thus, muscle atrophy is characterized by excessive degradation of proteins in the body, which impairs muscle functionand can also disrupt other metabolic functions. Excessive loss of muscle mass can impair the body's supply of energy in the medium to long term and lead to death.
Types of muscle atrophy
There are 2 main types of muscle atrophy, which differ in their causes. In addition, atrophy can affect one or more muscles, depending on the severity and cause.
1. Atrophy due to lack of movement.
This is a type of muscle atrophy in which the loss of muscle mass occurs due to a lack of muscle mass.
It can be due to an extremely sedentary lifestyle or some medical or medical conditions that prevent someone from exercising or even doing simple moves.
For example, people with rheumatoid arthritis or osteoarthritis have a greater risk of developing muscle atrophy, especially if they never exercise. Other medical conditions such as broken bone or severe burns (whose recovery is slow) and people with body paralysis can become victims of type 1 muscle atrophy.
Read also:Cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy)
2. Neurogenic atrophy.
Neurogenic atrophy is a type of atrophy caused by problems in the nervous system. The main reasons are neuromuscular diseasessuch as spinal muscular atrophy, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Guillain-Barré syndrome. Another health problem that can cause atrophy is diabetic neuropathy.
In such cases, the nerve signals of the muscle are interrupted, disrupting its normal functioning.
Causes of muscle atrophy
In addition to physical inactivity that leads to muscle wasting and the ailments mentioned above, there are other causes that can impair muscle health.
Certain other illnesses and injuries that interfere with or restrict movement can cause atrophy. There are even cases where muscle wasting is a symptom of severe malnutrition or muscle disease associated with alcohol abuse. Even astronauts who spend a lot of time in space travel can also develop muscle wasting due to lack of gravity.
Causes of atrophy due to lack of movement
Possible causes of muscle atrophy due to lack of movement:
- hospitalization or extended rest due to illness or surgery;
- temporary injuries such as a broken arm or leg;
- malnutrition, in which the muscles lack nutrients, which leads to gradual weakening and inability to use the muscles properly;
- dermatomyositis, in which muscle inflammation occurs, manifested by a rash;
- muscular dystrophy, an inherited disorder that causes progressive loss of muscle tissue and causes muscle weakness;
- osteoarthritis, a type of arthritis that causes pain and difficulty moving;
- rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic autoimmune disease in which there is inflammation in the joints;
- polymyositis, a generalized inflammation that causes muscle weakness;
- lack of physical activity;
- severe burns.
Causes of neurogenic atrophy
Possible causes of neurogenic muscle atrophy:
- alcohol-related myopathy;
- multiple sclerosisthat affects the nervous system, brain and spinal cord, causing imbalance, poor coordination, weakness and other symptoms;
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or Lou Gehrig's disease, a severe neuromuscular condition that leads to muscle weakness and difficulty in controlling voluntary muscle movement;
- diabetic neuropathy, a complication of diabetes associated with high blood sugar;
- damage to the neck, peripheral nerves, or spinal cord;
- spinal cord atrophy, a genetic disorder that causes decreased muscle function;
- exposure to toxins or compounds harmful to the body in the form of poisons;
- Guillain-Barré syndrome, an autoimmune nervous disorder that causes nerve inflammation and muscle weakness;
- spinal muscular atrophy or Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, a genetic disorder that weakens and atrophies muscles and impairs movement.
Other reasons
- natural aging process;
- long-term use of corticosteroids;
- vascular brain damage;
- trouble swallowing;
- neuropathy, a disease that causes damage to one or more nerves;
- polio, a viral disease that affects muscle tissue and causes paralysis.
Symptoms
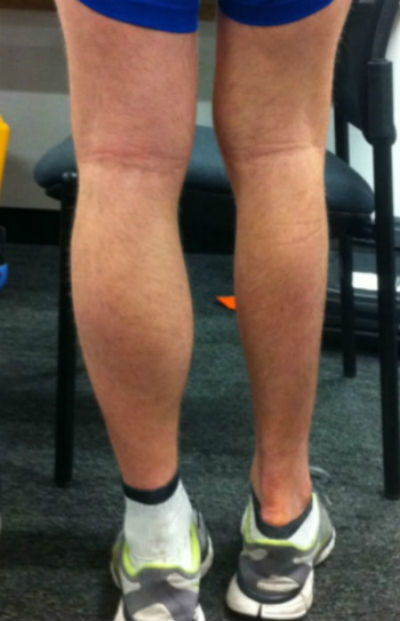
The symptoms of muscle wasting can vary depending on the cause. However, the most commonly observed symptoms are:
- pain;
- feeling that one limb is smaller than the other, for example, one arm looks thinner than the other;
- insensitivity;
- edema;
- muscle weakness in any limb of the body;
- Difficulty performing simple movements such as sitting or walking
- problems with swallowing and speaking;
- respiratory distress;
- muscle cramps or tremors;
- bone and joint problems such as scoliosis;
- coordination problems;
- fatigue;
- muscle stiffness.
Read also:Myasthenia gravis - what kind of disease, causes, symptoms and treatment
Some symptoms may indicate other more serious health problems. That's why, if you notice any of the following symptoms, seek medical attention as soon as possible:
- change in the level of consciousness, for example, fainting;
- distorted and protracted speech;
- inability to speak;
- vision changes, such as loss of vision or eye pain;
- sudden weakness or numbness on only one side of the body;
- inability to move a part of the body.
These more serious symptoms may indicate, for example, multiple sclerosis or stroke. When addressing any of these deviations, you need to seek help.
Complications of the condition
Muscle atrophy can be a sign of a more serious medical condition. Thus, lack of proper treatment can lead to serious complications and irreversible damage to the body.
Some of the complications of atrophy - This is a decrease in mobility, decreased physical performance, persistent problems with posture, loss of strength and paralysis.
Thus, the patient should know that as soon as he has a diagnosis on his hands, he should immediately begin treatment in order to stop the disease.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis consists of assessing symptoms, medical history, and requesting additional tests. It's also important to mention any type of old or recent injury and tell your doctor about any medications or supplements you are taking.
The doctor may request some tests, such as a blood test, X-ray, MRI, computed tomography, electromyography, muscle and nerve biopsy, and nerve conduction studies to rule out possible causes and complete the diagnosis.
Treatment
In some cases, for example, in those who have muscle atrophy due to low mobility, the condition can be change by treatment that includes a balanced diet combined with exercise and / or physical therapy.
People with neurogenic muscle wasting cannot be completely cured, but can follow specially formulated treatments to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment of muscle atrophy due to lack of mobility.
Treatments are available as part of a full course or as separate therapies:
Physical exercise and physiotherapy.

You are encouraged to move as much as possible. In addition to simple exercises such as walking, bodybuilding is recommended if possible, and aquatic exercises such as water aerobicswhich have less impact on the joints.
If you find it very difficult to exercise, seek the help of a physical therapist who can help determine their physical limitations and will teach the correct implementation of physical exercises, making physical activity easier and pleasant.
In cases where a person cannot move alone, physical therapy is needed to prevent the muscles from atrophy even more and even repair some damage.
Diet changes.
Eating well is essential to avoiding and treating atrophy caused by low mobility. In addition to using healthy foods, it is important to provide a good amount of protein so that the body can repair atrophied muscles. In some cases, supplements may be prescribed, but usually changes in food will already help replenish what the body needs.
Read also:Nervous tics
Other treatment options:
- Ultrasound therapy. This is a non-invasive therapy that uses sound waves to treat injuries that cause muscle wasting.
- Alternative treatments. Alternative treatments such as osteopathy and chiropractic can help reduce symptoms.
- Electrical stimuli. With prolonged hospitalizations, when a person cannot get out of bed, it is necessary that the muscles work artificially with using electrical stimuli and / or with the help of nurses, a professional therapist or physical therapist to maintain muscle mass. In such cases, the device generates an electrical current that, when applied to the skin, causes involuntary muscle contraction.
- Surgery: In cases where surgery can help, surgery is scheduled after considering the pros and cons of the intervention.
Treatment of neurogenic muscle atrophy.
In cases of neurogenic muscle atrophy, the condition must also be treated with medication. This is because with this type of atrophy, nerve damage cannot be reversed. Often these people are unable to perform physical activity or have great difficulty in controlling movements.
Thus, treatment with physical therapists is essential to help with exercise. In addition, it is possible to stimulate muscles and generate involuntary contractions using techniques such as neuromuscular electrical stimulation, which, using electrical impulses acting on nerves and muscles, causes involuntary muscle contractions that help muscle movement and treat muscle atrophy in a specific area.
Because there are several types of neurogenic atrophy, it is important to get the correct diagnosis and treat the condition according to medical guidelines. Usually, in addition to physiotherapy, doctors indicate the use anti-inflammatory corticosteroidsto reduce inflammation and pain and reduce compression of the affected nerves.
How to prevent atrophy
Because muscle wasting can also occur in old age, it is important to know how to prevent muscle wasting.
The best advice is to lead an active life. Lack of physical activity is one of the main contributors to muscle wasting. Therefore, do more sports, do strength training at least 2 times a week, swim, dance, run, walk with your pet in the park. It is important to move more often!
Another important tip is to eat right. Eat organic foods. This will help not only keep your muscles healthy, but the rest of your body as well.
Final tips
Except where you really can't, the rule is - get up and move. These can be simple movements, but it is important not to succumb to the difficulties associated with muscle wasting.
Even if your atrophy cannot be reversed, it is important to follow the progress of your treatment and try to stay active for as long as possible. This will help boost your self-esteem and quality of life. Treatment is very important, and with the increase in the resources available in medicine, it is possible to live well with muscle atrophy.