Diseases of the kidneys and urinary system in humans: a list
Content
- Description of the human urinary system
- Diseases and conditions of the kidneys
- Urinary tract obstruction
- Urinary tract infection
- Diseases of the glomeruli of the kidneys
- Other kidney diseases
- Signs and symptoms of kidney disease
- What examinations do you need to undergo?
- Kidney treatment
Description of the human urinary system
Urinary system (genitourinary system) or renal system maintains the balance of various substances and water in the body.
The human urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters (one from each kidney), tubes, which drain urine from the kidneys into the bladder (a storage bag) and the urethra (the tube that drains urine from organism). Muscles help control the flow of urine from the bladder.

The kidneys, a pair of bean-shaped organs, are located in the lower chest on the right and left sides of the back. Although the body is equipped with two kidneys, a person can function with one reasonably healthy kidneyif the other is damaged or removed.
The kidneys receive blood from the aorta, filter it, and send it back to the heart with the right balance of chemicals and fluids for use throughout the body. Urine produced by the kidneys is excreted from the body through the urinary tract.
The kidneys are in control the quantity and quality of fluid in the body. They also produce hormones and vitamins that direct the activity of cells in many organs; the hormone renin, for example, helps control blood pressure.
When the kidneys don't work properly, waste and liquid can accumulate to a hazardous level, creating a life-threatening situation. Important substances that the kidneys help control include sodium, potassium, chloride, bicarbonate, pH, calcium, phosphate, and magnesium.
Diseases and conditions of the kidneys
Any disease that affects the blood vessels, including diabetes, high blood pressure (arterial hypertension) and atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) can impair the kidneys' ability to filter blood and regulate body fluids.
Illness and infection in other parts of the body can also cause kidney upset. Because kidney damage can be life-threatening, disorders and diseases that can affect the kidney deserve immediate attention.
Kidney disease often causes no symptoms until late and can lead to end-stage renal failurewhich is fatal to a person unless a dialysis machine is used or a kidney transplant is not performed.
There are over 100 disorders, diseases and conditionswhich can lead to progressive kidney damage. Some of the most common problems are described in the article below for a list. Warning signs that should not be ignored are also listed in the next section "Symptoms".
Urinary tract obstruction

The urinary tract may become partially blocked (for example, due to kidney stones, tumors, enlargement of the uterus during pregnancy, or enlargement of the prostate gland).
Increased pressure can lead to infection and kidney damage. With a kidney stone, the blockage is often painful. Other obstacles may not cause any symptoms and only be detected if abnormal blood and urine tests or imaging techniques such as x-rays or ultrasounds, discovers it.
Urinary tract infection

Infections — urinary tract infections, such as cystitis (bladder infection) can lead to more serious infections further down the urinary tract.
Symptoms include fever, frequent urination, a sudden and urgent need to urinate, and pain or burning sensation while urinating. Pressure or pain in the lower abdomen or back often occurs. Sometimes urine has a strong and unpleasant odor.
Read also:Renal failure
PyelonephritisIs the name for a kidney tissue infection; most often it is the result of cystitis that has spread to the kidney. An obstruction in the urinary tract can make a kidney infection more likely.
Infections in other parts of the body, including, for example, streptococcal infections impetigo (skin infections) or a bacterial infection of the heart (endocarditis) can also be passed through the bloodstream to the kidney and cause a problem there.
Diseases of the glomeruli of the kidneys
Glomerular kidney disease is a disease of the kidney filter called glomeruli. Diabetes and high blood pressure can lead to glomerular disease. Diseases of this type cause more cases of chronic renal failurethan any other reason.
Blood is constantly filtered through microscopic clumps of looped blood vessels called glomeruli. Attached to each glomerulus is a tiny tube that collects the filtered waste. The filtering device (glomerulus plus tubule) is called a nephron.
Often, glomerular disease is caused by an abnormal response from the immune system. In this case, the body's own infection fighters mistakenly attack the kidney tissue.
Sometimes the reason is autoimmune disorder, such as systemic lupus erythematosus or Goodpasture syndrome.
An attack on the glomerulus can be the result of a hereditary disease, as well as occur after a bacterial infections in another part of the body, such as strep throat or skin infection, impetigo, or an infection inside hearts.
Viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which can lead to progressive HIV disease, can also cause glomerular disease.
For diseases and conditions classified as glomerulonephritis (also called jade), the glomeruli become inflamed. As blood filtration is impaired, urine output decreases, water and waste accumulates in the blood, and blood appears in the urine (hematuria).
As blood cells break down, the urine often turns brown rather than red. Some body tissues swell from excess water (a condition called edema). Results may vary: the condition may disappear after a few weeks, permanently reduce kidney function, or progress to end-stage renal disease.
With nephrotic syndrome blood loses protein in the urine due to damage to the membrane between the glomeruli and tubules. When the amount of albumin (a major protein) in the blood decreases, parts of the body become swollen with fluid (often around the eyes, abdomen, or legs).
Other illnesses and illnesses can also lead to this syndrome, and complications such as blood clots and high cholesterol levels can develop. Childhood nephrotic syndrome usually responds well to treatment and usually does not result in permanent kidney damage.
Other kidney diseases
Any situation in which severe blood loss or decreased blood flow occurs can interfere with the proper functioning of the kidneys. Heavy dehydration, some operations on the aorta and heart, severe infection in the blood (sepsis) or heart and heavy heart failure are examples of diseases that can lead to sudden kidney problems.
The damage is usually reversible; although with shock or severe infection, the damage can be permanent. Certain medications and diagnostics can be toxic to the genitourinary system.
In some cases non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs such as over-the-counter ibuprofen and various prescription drugs), x-ray dye, ACE inhibitors, and some antibiotics can damage the kidneys.
Acute (sudden) kidney failure, a condition that requires urgent medical attention to prevent death, may even occur.
Cancer of the urinary system not as common as in other parts of the body. Kidney cancers are of two main types. One of them is called Wilma's tumor, occurs in young children and is often defined as severe abdominal swelling. Renal cell carcinoma, which occurs in middle-aged and older people, can cause blood to form in the urine, but is often not found until it has spread to other parts of the body.
Read also:Hydronephrosis of the kidneys: what is it, causes, symptoms and treatment
Bladder cancer more common and often accompanied by painless, bloody urine. In many cases, blood is only detected by a urinalysis. Because the bladder cancer can be monitored with early detection, the doctor should, as soon as possible, conduct urine tests in adults (except for the period of menstruation in a woman).
Signs and symptoms of kidney disease

Kidney disease is common runs silently for many years, without signs or symptoms that the patient can recognize, or with signs that are too general for the patient to suspect kidney disease.
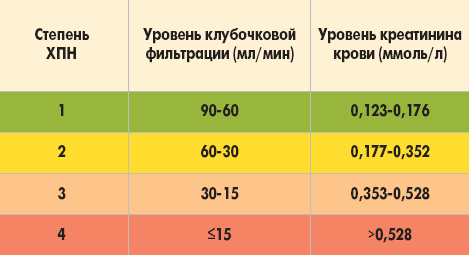
For this reason, routine blood and urine tests are particularly important: they detect blood or protein in the urine, and abnormal levels of chemicals in the blood, such as elevated creatinine level and urea, which indicate early signs of kidney failure and failure.
However, the following list of problems can be warning signs of kidney disease in humans and should not be ignored. Immediate medical attention is required if any of these conditions are present.
- Swelling or puffiness, especially around the eyes or face, wrists, abdomen, thighs, or ankles.
- Foamy, bloody, or coffee-colored urine.
- Decreased amount of urine.
- Problems with urination, such as a burning sensation or abnormal discharge while urinating, or changes in the frequency of urination, especially at night.
- Back pain (on the sides), below the ribs, near the location of the kidneys.
- High blood pressure.
What examinations do you need to undergo?
Analyzes of your samples blood and urineare the first step in the study of kidney problems. Studies of these types can show how well the kidneys are at removing excess fluid and waste. If you suspect a change in the shape or size of the kidneys, bladder, or urinary tract, various imaging techniques. Kidney tissue sample, biopsysometimes helps diagnose the specific cause of the problem.
Tests commonly used for screening and diagnosis. There are several examination methods that are commonly used by a healthcare professional. to identify kidney or urinary tract disease. A blood sample can be analyzed for creatinine (and estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR]) and urea.
The level of these waste products in the blood increases as kidney filtration decreases. Abnormal results are usually the first sign of kidney disease.
A urine sample is usually also examined and analyzed (urinalysis) as part of routine screening. This set of tests looks for signs of kidney and urinary disease, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and protein in the urine.
If you have diabetes or high blood pressure, you should check GFR and albumin ratio, and urine creatinine annually to detect early kidney disease. If you are a current smoker, obese, have cardiovascular disease, a family history of chronic kidney disease, and are 35 years of age or older, you should check GFR and creatinine ratio in urine every two years.
If you have symptoms that indicate an infection, urine culture can confirm the presence of a bacterial infection.
Tests to monitor kidney function - If you have been diagnosed with kidney disease, your doctor will ask you for laboratory tests to help monitor your kidney function. Levels of urea, creatinine, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in the blood are measured from time to time to see if kidney disease is getting worse.
Read also:Angiomyolipoma of the kidney: what is it, causes, symptoms, how to treat
The amount of calcium and phosphate in the blood, as well as the balance of electrolytes in serum and urine, can also be measured, as they are often affected by kidney disease.
Hemoglobin analysisas part of complete blood count (CBC)can also be performed (the kidneys produce a hormone, erythropoietin, which controls the production of red blood cells). Urine albumin / creatinine ratio can be used to test the effectiveness of treatment for diabetes and total urine protein in nephrotic syndrome (a condition in which the kidneys pass large amounts of protein into the urine).
The parathyroid hormone, which controls calcium levels, is often elevated in diseases kidney, and it can be tested to see if bone damage develops that requires treatment.
| Diseases | Analyzes used in diagnostics |
|---|---|
| Chronic kidney disease (chronic kidney failure) | Estimated GFR, urine albumin to creatinine ratio, general urine analysis |
| Urethral infection | General urine analysisurine culture |
| Stones in the kidneys | Imaging techniques (see. below), urinalysis |
| Nephrotic syndrome | Urine test, serum albumin, total cholesterol protein, total urine protein, antinuclear antibody (ANA) test, hepatitis B, hepatitis C test |
| Nephritis | Urinalysis, estimated GFR, albumin, total urine protein, antinuclear antibody test (ANA), antistreptolysin O, antiglomerular basement membrane antibody, antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies, biopsy |
| Kidney disease due to diabetes or high blood pressure | Urine albumin-creatinine ratio (ACRU), estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) |
Imaging techniques - If there is a suspicion of blockage of urine flow or kidney damage that can change the shape or size of the kidneys or urinary tract, imaging tests of the kidneys may be helpful.
Rendering techniques such as ultrasound examination (ultrasound), computed tomography (CT), isotope scan or intravenous pyelogram (IVP). Various X-ray procedures can also be used, such as: intravenous urogram, cystogram during urination (image when urinating) or renal arteriogram (which analyzes the blood flow in the kidney).
Kidney biopsy - a biopsy can determine the cause of the appearance of protein or blood in the urine. Analysis of a small piece of kidney tissue can reveal the nature and extent of structural damage to the kidney. A biopsy obtained using a biopsy needle and diagnostic equipment is often helpful if a glomerular filter disorder is suspected.
Kidney treatment
Treatment varies depending on the type of kidney or urinary tract disease. In general, the sooner kidney or urinary tract disease is diagnosed, the more likely it is to be cured. Diet restrictions, drug therapy, and surgical procedures may be appropriate.
If the kidneys can no longer effectively remove waste and water from the body, dialysis machineused several times a week can take over kidney filtration.
Transplant operation kidney is another option when kidneys fail. If you have diabetes or high blood pressure, controlling your blood pressure and blood sugar is extremely important to prevent or minimize kidney damage.