Schistosomiasis: what is it, causes, symptoms and treatment, types of schistosomiasis
For a long time, schistosomiasis was not an actual disease in the post-Soviet space. The parasite that causes the pathology can reproduce only in a tropical climate.
Recently, tourists are increasingly attracted to travel to unknown places for many. From there they bring such dangerous souvenirs.
In this simple way, cases of schistosomiasis now appear on the territory of almost the entire planet. The consequences of the disease are serious. Let's take a closer look at what it is, its symptoms and treatment.
Content
- What is schistosomiasis
- Epidemiology
- Causes of schistosomiasis
- Life cycle of a schistosoma
- Clinical picture
- What types of schistosomiasis do I have?
- Gastrointestinal schistosomiasis
- Genitourinary schistosomiasis
- Japanese schistosomiasis
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of schistosomiasis
- Drug treatment
- Surgical intervention
- Treatment of schistosomiasis with folk remedies
- Prevention
- Forecast
- Related Videos
What is schistosomiasis
Schistosomiasis (alternative names of the disease bilharziasis, schistosomiasis) - caused by parasites called blood flukes or trematodes (see. photo below). The disease begins with dermatitis in the place where
parasites enter the body through the skin.As the disease progresses, a person has a prolonged fever, rash, an increase spleen, eosinophilia. The clinical picture also affects the gastrointestinal tract and the genitourinary system, depending on the pathogen.

The basis of all clinical manifestations of the disease is not only the infectious nature of the helminth, but also the body's allergic reaction to the introduction of a foreign agent. This mechanism explains all the symptoms of schistosomiasis.
Epidemiology
The disease is more typical for countries with a tropical climate, in which access to suitable water is difficult, where unsanitary conditions flourish. Schistosomiasis is widespread in Africa, Asia and South America.
According to the WHO, the disease is observed in more than 300 million. people, and every year from 350-600 thousand people die from the disease. Human. There are much more real numbers, because there are many people who have not been correctly diagnosed due to a low standard of living.
Men get sick 5 times more often than women. Illness can lead to disability or death. In most cases, the parasite infects children. Any child loves to play near water bodies. It is very difficult for them to instill all the necessary hygiene rules. In countries without access to safe water and unsanitary conditions, such games often end up with this disease. Children often suffer from mental or physical retardation due to bilharziasis.
Causes of schistosomiasis
The cause is trematodes, helminths from the genus Shistosoma, class Trematoda. Trematodes are flatworms, measuring about 5-25 mm in length. The eggs are oval and about 0.1 mm in diameter. The most common representatives are S.haematobium, S.mansoni, S.japonicum. The first causes genitourinary schistosomiasis, the second intestinal, and the third Japanese.
The life cycle is characteristic for parasites. They pass the initial part of their development in body of gastropods, for example, snails, and the final one - in the body of mammals, including humans.
Between these stages, intermediate forms are in free swimming in water bodies. Infection most often occurs through water, namely: in the process of bathing, fishing, and chores. Recently, cases of infection of tourists who love unusual places have become more frequent.
Pathogens are most often affected by the veins of the intestine, abdominal cavity, uterus, small pelvis and bladder. They feed on blood, from which they receive the necessary nutrients. During normal life, the parasites lay eggs, which settle in the intestines or the genitourinary system, depending on the pathogen.
Life cycle of a schistosoma
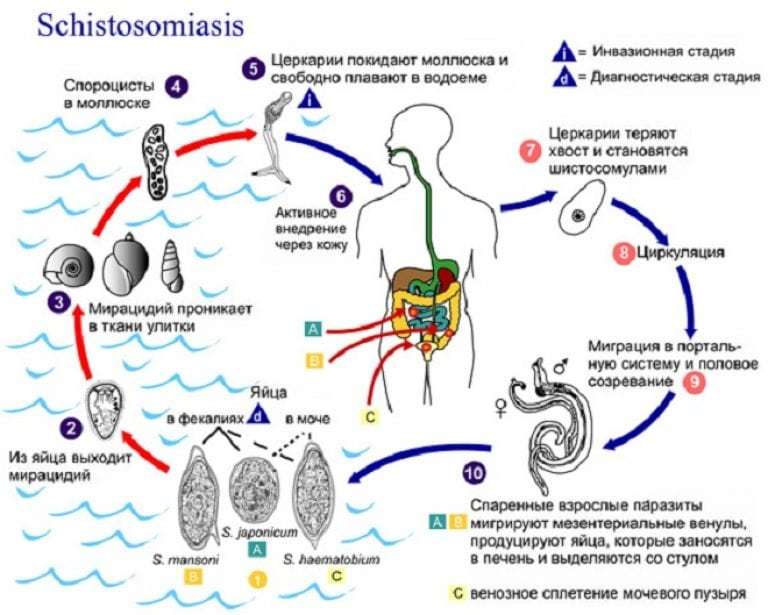
All parasites have complex life cycles with changing hosts for their successful development and reproduction. Schistosomes are no exception.
Schistosom eggs, along with urine and feces, enter fresh water. From them special life forms hatch - miracidia. Their body surface is all covered with cilia, which are a way of locomotion. Miracidia float in water, then enter the bodies of snails or molluscs, which are called the intermediate hosts of schistosomes.
Read also:Anthelmintic drugs for humans with a wide spectrum of action
In the body of the molluscs, they no longer need cilia, so they disappear. Thus, miracidia pass into sporocysts. They fully develop in the body of molluscs within a few weeks through asexual reproduction to the next life form - cercariae.
Cercariae float freely in contaminated water. It is this form of life that infects the main host - a person or another mammal. Their body surface secretes specific enzymes that help easily penetrate the skin, causing only a local allergic reaction.
Penetrating into the host organism, cercariae lose their tails, which makes them the larval stage - schistosomes. Once in the bloodstream, they first pass through the lungs, then the left heart, and then settle in the gastrointestinal tract or genitourinary system. After a few weeks, they reach their sexual maturity, which allows them to start laying eggs in the body, and this process starts the life cycle from the very beginning.
Clinical picture



The first symptoms of schistosomiasis appear instantly. Already in 10-20 minutes in the place where the parasite has entered the body, a local allergic reaction appears - hives.
During the first day, a migratory rash will develop in the form red spots on the body.
There is a likelihood of coughing, hemoptysis, enlargement of lymph nodes and size liver. The appearance of nonspecific symptoms of intoxication of the body is not excluded:
- fever;
- muscle and joint pain;
- chills;
- sweating;
- diarrhea;
- headache.
The complete picture of the disease appears a month or two after infection. Mild, moderate, or severe schistosomiasis develops. Typical symptoms:
- prolonged fever;
- dry cough;
- hives;
- hepatosplenomegaly;
- leukocytosis and eosinophilia, increased ESR;
- the presence of eosinophilic accumulations in the lungs;
When the structures of the brain are involved in the process, paresis and paralysis are observed, as well as epileptic seizures. With blood flow, schistosomes can settle in the appendicular process cecumthat will cause an acute attack appendicitis.
What types of schistosomiasis do I have?
There are a great many species of this genus of parasite, not all of them have even been discovered and fully studied. This division into types of diseases is only conditional. Because several species can cause the same pathology. Conversely, one type of helminth can cause different pathologies.
Diseases can be of three types: intestinal, Japanese and genitourinary schistosomiasis.
The most common is genitourinary.
Gastrointestinal schistosomiasis

This type of disease is caused by the Manson schistosome (S.mansoni). It develops in the circulatory system of the gastrointestinal tract.
Initially, inflammation of the intestines and liver prevails, and then a violation of the blood supply causes complications, for example, intestinal obstruction, impaired absorption of substances.
In the acute stage, the following symptoms are observed:
- severe abdominal pain;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- colitis;
- cholecystitis;
- intestinal polyposis;
- intestinal obstruction;
- cachexia, or wasting.
The main problem with gastrointestinal schistosomiasis is that this pathology is often confused with oncology. It should be remembered that complications of this type of disease are fatal without treatment.
Genitourinary schistosomiasis
The causative agent of this type of pathology is a blood schistosome (S.haematobium). The most common type of disease in which any part of the genitourinary system can be damaged. Usually the first target is the bladder, which causes the clinical picture of cystitis.
Often, the infection reaches the kidneys, disrupting the correct outflow of urine from it. Due to stagnation, the formation of calculi in the kidneys may begin. The medical term for this complication is nephrolithiasis. At the exit from the kidney, stones usually give a very severe pain syndrome - renal colic. This situation urgently requires the introduction of painkillers and surgery.
The main symptom of genitourinary schistosomiasis is considered hematuria, or the appearance of blood in the urine. Also, patients are worried about:
- lumbar pain;
- night urinary incontinence;
- disorders of urination;
- allergic reactions;
- weakness, increased fatigue;
- women experience menstrual disorders and miscarriages;
- men develop erectile disfunction and spermogram indices decrease;
- accession of infection to the genitourinary organs;
- fibrosis of the genitourinary system;
- the formation of stones in the urinary tract;
- hydronephrosis;
- infertility.
Read also:What do bedbug bites look like and how to treat on the human body
With damage to the reproductive system, schistosomiasis almost always leads to infertility. Such a formidable complication is practically not amenable to treatment. The changes caused by the parasite are irreversible.
Japanese schistosomiasis
Caused by the Japanese schistosoma (S. japonicum). According to the clinical picture, it is very similar to intestinal bilharziasis, only it has a more rapid development of the disease. Therefore, the course of the disease is more severe. Because this parasite lays eggs 10 times more than others. Differs in the place of spread of the pathogen. Japanese schistosomiasis occurs primarily in Taiwan, southern China, southern Japan, and the Philippine Islands.
That is, Japanese schistosomiasis manifests itself with all clinical signs of the gastrointestinal type, as well as:
- portal hypertension;
- ascites (accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity);
- bleeding from the veins of the esophagus, hemorrhoids;
- tubular-inductive liver fibrosis;
- complications are associated with the central nervous system, helminth eggs can get there.
A distinctive feature of the Japanese type is the defeat of the central nervous system. With such a complication, patients have epileptic seizures, all types of seizures, paresis and paralysis. Considering that usually the course of this type is lightning-fast and heavy, then this type can be called the most dangerous of the existing ones.
Diagnostics
It is always advisable to start diagnostics with the collection general tests of blood, urine, feces and tissue samples of the genitourinary tract. It is in these biological materials that the parasite can be found. And also see blood counts. In the presence of schistosomiasis, leukocytosis is noted with a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left. Sharp increased eosinophil countthat react to helminthic invasion and allergens. And also the ESR can be increased.
In order to detect the presence of intestinal schistosomiasis eggs in feces, it is recommended to use glass slides or cellophane stained with methylene blue, with glycerin impregnation. A filtration method is used to diagnose genitourinary schistosomiasis. Nylon, paper or polycarbonate filter systems are used. Blood in urine can be determined both under a microscope and with test strips.
In more developed countries, it is used immunofluorescence reaction with schistosome antigens. But these methods cannot distinguish the active form of the disease from the transferred one. There are also false positives due to cross-sensitivity to other parasites.
With genitourinary schistosomiasis, it is advisable to carry out cystoscopy to detect granulomas or ulcers, growths of polyps, accumulations of eggs. It also allows you to take a biopsy from a suspicious or affected area of the bladder mucosa. Excretory urography method will help to detect stones in the genitourinary system, strictures of the ureters, foci of calcification, hydronephrosis. With intestinal bilharziasis, they are used for the same purposes diagnostic laparoscopy and liver biopsy.
From simple research methods, you can also apply chest x-ray, on which you can observe the accumulation of eosinophils. With help Ultrasound you can assess the condition of the liver, lymph nodes, genitourinary system.
Treatment of schistosomiasis
Treatment will be most effective when the disease is mild, especially in the absence of complications. The main method is considered to be medication.
Symptoms and treatment are closely related. For example, therapy is always prescribed not only taking into account the presence of a parasite in the body, but also the presence of certain symptoms. They may require additional treatment. In severe forms or complications, it is necessary to resort to surgical methods.
Drug treatment

Are applied antiparasitic drugs: Praziquantel and Oksamnihin. Drugs in this group are usually extremely toxic to the human body. These two examples are the most acceptable in terms of the prevalence of positive effects over negative ones.
- Praziquantel. Tablets with a dose of 600 mg are used for children under 14 years old in an amount of 1 to 5 per day. In adults, the required dose is 40 mg / kg body weight.
- Oksamnikhin. Pediatric doses - 20 mg / kg, adult - 15 mg / kg body weight.
Read also:Trichocephalosis
The goal of conservative therapy is to cure the disease and prevent the transition of an acute form to a chronic one. The effectiveness of the combination of various drugs is also noted. For example, Praziquantel with Metriphonate or Artesunate.
Surgical intervention
The presence of severe forms and complications of the disease always implies surgical treatment. In such cases, irreversible processes have already been launched that cannot be eliminated with drugs.
For example, in genitourinary schistosomiasis, ureteral strictures and nephrolithiasis are often observed. The operation to crush and remove calculi is called lithotripsy. With good equipment of the urological department, it is better to resort to ESWL - extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy. This is a device that crushes kidney stones by the wave method without violating the integrity of human tissues.
If it is impossible to carry out such a manipulation and with small stones, they resort to catheterization. This operation is performed through the urethra through a catheter, which also does not violate the integrity of the patient's tissues. However, if all these methods are impossible, surgeons use open or laparoscopic methods of surgery to remove stones. Ureteral strictures are also removed using the latter methods.
In the case of gastrointestinal schistosomiasis, surgery is usually used to eliminate intestinal obstruction. This operation is usually performed in an open, rather than laparoscopic, method.
As for the liver, more often vascular or general surgeons perform operations on the venous system of the liver. This does not correct the situation, but improves the course of the disease. With advanced complications from the liver, sometimes its parts are removed or transplanted.
Treatment of schistosomiasis with folk remedies

It is advisable to combine treatment with folk remedies with therapy prescribed by a medical specialist.
You should also consult with him in advance about the compatibility of drugs with some herbs.
Given the severity of the disease, self-medication is not recommended.
The most common options for treating schistosomes are:
- Nettle root decoction. It is necessary to boil 20 mg of crushed roots in 250 ml of water. After 15 minutes, strain and take 2 tablespoons 4 times a day. The duration of therapy is no more than a week.
- Make the following mixture: 20 mg beet juice and 20 mg mustard oil. Consume in the morning, 20-40 minutes before breakfast. The duration of the course is one week. Then, after a week's rest, it is recommended to repeat the course.
- It is also possible to use chopped cloves 10-15 minutes after eating. Every day it is necessary to gradually increase the dose to a maximum of 1.5 g. the duration of therapy is a week.
There is also evidence that carrots, peppers, garlic and pumpkin, especially its seeds, have anthelmintic properties.
Prevention
WHO is actively trying to solve the problem of the incidence of schistosomiasis through preventive measures:
- purification of reservoirs;
- work on the destruction of the population of gastropods and snails;
- creation of effective work of water supply of endemic areas;
- carry out sanitary and educational activities for residents who are at risk;
- ensuring the possibility of early detection of the disease and its treatment;
Residents of areas that are at risk for this disease, need to treat water. Use it for any purpose only after boiling and high-quality filtration. It is also recommended to put into use protective equipment for any contact with water, for example, rubber gloves and boots.
Forecast
With timely treatment, the prognosis of bilharziasis is favorable. Timely specific therapy, which is individually selected by an infectious disease doctor or parasitologist, gives many positive results.
Chronic schistosomiasis without treatment leads to disability, disability and even death from developing complications.