Noonan syndrome: what is it, symptoms, photos, treatment, prognosis
Content
- What is Noonan Syndrome?
- Typical manifestations of the syndrome
- Symptoms of Noonan's syndrome
- Causes of Noonan's syndrome
- Genes and heredity
- Diagnostics
- Treatment for Noonan's syndrome
- Prognosis and complications
What is Noonan Syndrome?
Noonan syndrome (Ulrich-Noonan syndrome, turneroid syndrome with normal karyotype) - this state, causing both characteristic changes in appearance and physiological changes that affect the functioning of the body in several ways. The disease is considered rare and is estimated to affect approximately 1 in 1,000-2,500 people. Noonan syndrome is not associated with any particular geographic region or ethnic group.
Although Noonan's syndrome is not life-threatening, if a person has it, they may develop comorbidities, including heart diseases, bleeding disorders and some cancers at some point in life. These concomitant health problems are expected with Noonan syndrome.
The prognosis will be much better if you periodically visit your doctor to monitor your health and get timely treatment of any emerging diseases and disorders, before they begin to cause serious effects.
The identification of this syndrome is based on the recognition of several associated symptoms. The severity of the disease can vary, and some people may have more obvious physical features or more significant health effects than others. If you already know that you have relatives diagnosed with Ulrich-Noonan Syndrome, this may be the reason for identifying signs that you or your child may be suffering from this syndrome.
Typical manifestations of the syndrome
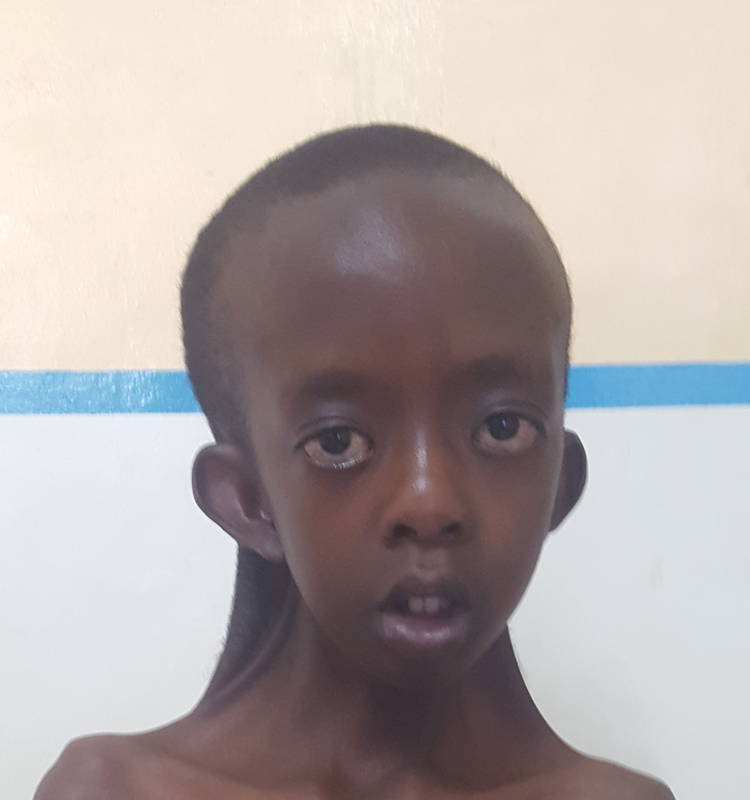
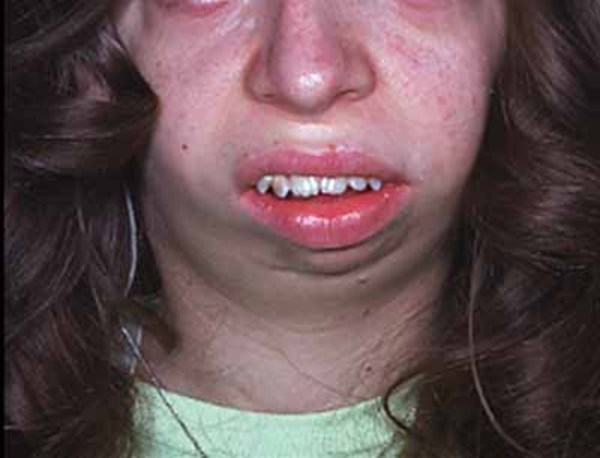
Noonan syndrome manifests itself both inside and outside the body, resulting in a characteristic appearance, marked by physical features of the condition, as well as medical problems caused by disease.
- Appearance: The facial and body features of a person with Noonan Syndrome may appear rather unusual or may appear completely normal. The most obvious physical signs associated with this condition are oversize head, wide-set eyes, and slightly shorter than average height (see picture). Photo).
- Head: The face and head of a person with the syndrome is often described as triangular in shape because the forehead is proportionally larger than the small jaw and chin.
- Eyes: It is noted that the eyes are tilted down, sometimes it seems that they are tilted to the sides of the face. The eyelids can be thick, creating deep skin folds.
- Neck: Ulrich-Noonan syndrome is also associated with a webbed neck, which means that people affected by the condition may have a thicker-than-usual neck with folds of skin that appear to form a web between the upper chest and jaw (see. Photo).
- Edema: Some people with the syndrome may have swelling of the body, hands, feet, or fingers. It has been found in both infants and adults with Noonan's syndrome and is caused by swelling as a result of fluid accumulation.
- Short stature and toes: Across cultures, people with Noonan syndrome are below average and may also have short fingers. Babies with this condition are usually at least the average at birth, but grow up slowly in infancy, and, therefore, short stature is what is first noticed in infancy or in early childhood.
Read also:Hydrocephalus (dropsy) of the brain in children: causes, consequences and methods of treatment
Although Noonan syndrome is usually associated with certain facial features and body type, there is a wide range of how these features will manifest. Therefore, the appearance of the face and body cannot reliably determine whether someone has this disease or not.
Symptoms of Noonan's syndrome

There are several symptoms of this condition, and they may or may not affect all patients with Noonan syndrome.
- Power problems: Some children with the disease may not eat like all normal children of the same age, and this can cause problems with weight gain and stunted growth.
- Heart problems: The most common health problem associated with Noonan syndrome is a cardiovascular problem called pulmonary valve stenosis. This problem interferes with the flow of blood from the heart to the lungs, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, dyspnea or bluish color of lips or fingers (cyanosis). Over time, people with untreated pulmonary valve stenosis may develop increased heart, which also causes fatigue and can over time lead to serious heart problems such how heart failure. There are other heart defects associated with Noonan's syndrome, including hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, atrial septal defect and ventricular septal defect.
- Bruising or bleeding: Ulrich-Noonan syndrome can cause blood clotting problems, resulting in excessive bruising as well as bleeding for a longer than usual period of time after injury.
- Vision changes: At least half of children with the disorder have vision and eye movement problems such as amblyopia (lazy eye).
- Weak bones: Children and adults with Noonan syndrome may have problems with bone formation and strength. as a result of which fragile bones can easily break or lead to unusual body deformations, especially breasts. An example of an unusual bone structure that can occur with Noonan syndrome is a deep "pit" in the upper chest. It is unclear why this is happening, and does not apply to everyone with the syndrome.
- Puberty: Boys and girls with the disorder may experience delayed puberty. Some boys have non-descended testes and may experience decreased fertility at a later age.
- Learning delay: There is a link between learning disorders and Noonan's syndrome, although the link is not strong. Overall, current information on the cognitive development of individuals with the disorder suggests that children with this syndrome are likely to have higher than secondary education, although most often children and adults with Noonan syndrome have average intellectual capabilities.
Read also:Acetone in the urine of a child (acetonuria in children): what to do, causes, symptoms, treatment
Causes of Noonan's syndrome
Noonan syndrome results from a protein defect that is often caused by a genetic abnormality. A genetic abnormality alters a protein that is involved in altering the growth rate of the body.
This protein specifically functions in the RAS-MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) signaling pathway, which is a key part of cell division. This is important because the human body grows through the process of cell division, which is the production of new human cells from existing cells. Cell division essentially results in two cells instead of one, causing body parts to grow. This is especially important in infancy and childhood when a person grows in size. But cell division continues throughout life as the body recovers and renews itself. This means that problems with cell division can affect many organs throughout the body. This is why Ulrich-Noonan syndrome has so many associated physical and cosmetic manifestations.
Because Noonan's syndrome is caused by changes in RAS-MAPK, it is specifically called RASopathy. There are several RAS diseases, and they are all relatively rare disorders.
Genes and heredity

Protein dysfunction in Noonan syndrome is caused by a genetic defect. This means that the genes in the body that code for the protein responsible for the syndrome have an erroneous code, commonly called a mutation. The mutation is usually hereditary, but it can be spontaneous, which means that it happened without inheriting from the parent.
It turns out that there are four different gene disorders that can cause this disease. These genes are the PTPN11 gene, SOS1, RAF1 and the RIT1 gene, with defects in the PTPN11 gene accounting for approximately 50% of cases of the syndrome. If a person inherits or develops any of these 4 gene abnormalities, Noonan syndrome is expected.
This syndrome is inherited as an autosomal dominant disease, which means that if one of the parents has the disease, then the child will have it. This is because inheriting this particular genetic abnormality from one of the parents causes the defect in the production of the RAS-MAPK protein, which cannot be compensated even if the individual also inherits the normal gene protein production.
There are cases of sporadic Noonan's syndrome, which means that the genetic abnormality was not inherited by the child from the parents. A person with sporadic syndrome may have a child with the disease in the future, because the patient's children may inherit a new genetic abnormality.
Diagnostics
The most compelling evidence for Noonan syndrome is a genetic test. However, it is estimated that 20 to 40 percent of people diagnosed with the syndrome do not have family history of the condition or do not have characteristic abnormalities found with genetic testing. Sometimes other tests and observations can confirm the diagnosis.
- Laboratory tests: A blood test to assess blood clotting function may be normal or abnormal in people with Noonan syndrome. There is no strong correlation between blood tests that measure blood clotting and symptoms of bruising or bleeding.
- Heart function tests: Diagnosis pulmonary hypertensionas well as other heart defects associated with the syndrome can confirm the diagnosis of this condition. However, all heart diseases associated with this syndrome can occur in other circumstances; the identification of one of the conditions of the heart does not confirm the syndrome, and the absence of a heart problem does not mean that the person does not have Noonan's syndrome.
- Genetic testing: There are several genes that have been associated with the disease, and if these genes are identified, especially among family members, this could be diagnostic confirmation of the syndrome.
Read also:Amniotic fluid embolism
Treatment for Noonan's syndrome
Treatment for Ulrich-Noonan syndrome focuses on several aspects of the disease.
- Preventing Serious Heart Problems: Early diagnosis and treatment of heart problems can prevent long-term health consequences. Depending on the severity and type of heart disease, treatment or close monitoring of these conditions may be the best option.
- Identifying and treating medical complications: Noonan's syndrome is associated with a variety of health complications ranging from bleeding to infertility and cancer. There is no test yet that can predict if you will develop one of these problems. Thorough medical care includes regular doctor visits so that the doctor can identify emerging problems with medical history and physical examinations while they are still amenable treatment.
- Stimulating Normal Growth: Some children with Noonan syndrome use growth hormone to stimulate growth to help them achieve optimal bone growth, shape, and structure. Although growth hormone has been used as a successful strategy for treating children with this condition, levels of growth hormone, as well as other hormones, are not abnormal in people with this disease.
Prognosis and complications
Life expectancy with Noonan syndrome is generally normal, but health complications can occur that need to be addressed with medical or surgical care.
- Bleeding can lead to bleeding, which can cause fatigue symptoms. Less commonly, excessive bleeding can lead to unconsciousness or an urgent need for a blood transfusion.
- Heart disease are the most common health consequences of patients with the syndrome. Heart disease can lead to heart failure and it is therefore important to maintain regular follow-up with a cardiologist.
- If you have Noonan syndrome, there is an increased likelihood of certain cancers, especially blood cancersuch as juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia and neuroblastoma.



