Anthracosis of the lungs: what is it, causes, symptoms, treatment
Content
- What is lung anthracosis?
- Causes and risk factors
- Anthracosis symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of lung anthracosis
- Examination of incapacity for work
- Prophylaxis
What is lung anthracosis?
Lung anthracosis Is an occupational disease that occurs among workers in the coal industry and is associated with the inhalation of carbon-containing dust. The prevalence of the disease among miners is about 12%. Moreover, with a long experience (about 20 years) of work in mines with the extraction of hard or soft coking coal, the number of such patients increases dramatically and reaches 50%.
Considering that the dust of coal mines is mixed and contains not only coal dust, but also free dioxide silicon, people working in such enterprises often develop a mixed type of pneumoconiosis - anthracosilicosis. In its pure form, anthracosis is found in miners, bulk cutters, and cutter operators, since their work is associated with the inhalation of mainly coal dust.
Causes and risk factors

The main provoking factors for the development of the disease are:
- the amount of coal dust in the air;
- work experience in unfavorable conditions for more than 15 years;
- predisposing factors (smoking, chronic diseases of the bronchi and lungs, etc.).
As a rule, the disease earlier and more often affects miners who extract anthracite, less often workers in mines for the extraction of coal or brown coal. In most cases, silicosis and anthracosilicosis are added to the painful state, since there are impurities of silicon dioxide in the dust.
Coal dust penetrates into the upper respiratory tract of a person, and at high concentration - into the lungs. The lymph carries dust to the regional lymph nodes, the surface of the lungs becomes spotty, gray-black. A person first develops chronic bronchitis (catarrhal), over time - desquamative interstitial pneumoniaturning into cirrhosis.
Anthracosis symptoms
The disease is characterized by a relatively slow development and is often combined with dust bronchitis. Changes in the lungs occur after 15 or more years of work in harmful conditions. This is due to the properties of coal dust to increase the activity of phagocytosis (the process of absorption of foreign particles by cells), which promotes hypersecretion of mucous glands and increased excretion of sputum along with dust.
Read also:Symptoms and treatment of bronchitis in adults

Such patients complain about:
- persistent cough with dark sputum;
- shortness of breath;
- pain in the chest.
When examining patients with anthracosis, the pulmonologist detects weak or hard breathing with dry or moist wheezing, signs of emphysema:
- expansion of the chest;
- smoothness of intercostal spaces;
- displacement of the lower borders of the lungs downward;
- boxed percussion sound.
If a patient with anthracosis does not have concomitant dust bronchitis, then clinical signs of the disease may be absent or mild.
Anthracosilicosis combines the clinical manifestations of both anthracosis and silicosis. Symptoms of this pathology appear after 10 or more years of contact with mixed dust. Moreover, the nature and flow depends on the concentration of silicon dioxide in coal dust. pulmonary fibrosis.
With anthracosilicosis, the signs of emphysema are less pronounced, they develop against the background of already existing fibrosis.
- In the initial stages disease complaints are very scarce and the general condition of patients practically does not change. Only with careful questioning can it be revealed that they have a slight cough in the morning or slight shortness of breath during exercise.
- Over time the disease progresses, pneumofibrosis increases and all pathological symptoms become more pronounced. This is facilitated by the development of pulmonary and heart failure, as well as the addition of intercurrent infections.
In addition, the course of the disease is aggravated by the presence of chronic nonspecific lung diseases:
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- bronchial asthma;
- bronchiectasis (bronchiectasis).
Diagnostics
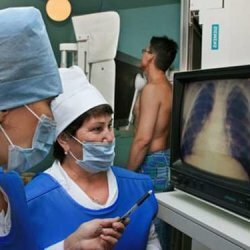
Timely detection of anthracosis is very important for the patient, as this allows you to stop contact with dust and stop the progression of the pathological process. For this purpose, the enterprises carry out preventive medical examinations with a frequency of 1 time per year. However, for the first time, only occupational pathologists can make a diagnosis, and those who have suspicious symptoms are sent to them.
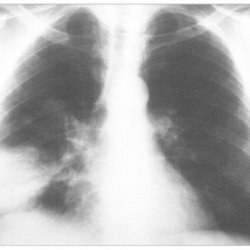
The doctor may suspect anthracosis of the lungs, having studied the complaints, the patient's medical history, taking into account his work experience in hazardous production. The data of objective and additional examination will complement the general picture. Such patients are necessarily assigned an X-ray examination of the chest organs, which reveals specific changes in the lung tissue:
- reticular change in pulmonary pattern;
- nodular shadows.
Read also:Bronchiolitis
Often, with anthracosis, a person has impairments to the function of external respiration in a restrictive manner.
During the course of the disease, three stages are distinguished according to the clinical and radiological symptoms:
- In the first of them, the symptoms are poorly expressed, a small mesh of the pattern appears in the lungs.
- In the second stage, dyspnea and coughing increase, signs of emphysema appear, and many nodular shadows appear on the x-ray.
- At the third stage of the disease in persons suffering from anthracosis, the structure of the lung tissue becomes cellular and takes on the appearance of a honeycomb. In this case, cor pulmonale is formed with the development of right ventricular failure. To identify these changes, the patient undergoes electrocardiography and ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the heart.
Treatment of lung anthracosis
Persons suffering from anthracosis are shown breathing exercises and physiotherapy exercises (LFK).
Treatment is carried out taking into account the stage of the disease, the severity of its course and the presence of complications. The first step is to stop contact with dust.
Anthracosis therapy includes:
- drug exposure;
- physiotherapy;
- Spa treatment.
Of the drugs are prescribed:
- Drugs that improve the drainage function of the bronchi (expectorant and thinning phlegm).
- Means that reduce pressure in the pulmonary circulation and improve the work of the heart muscle (nitrates, cardiac glycosides, metabolism).
- Bronchodilators (inhaled B2 agonists and anticholinergics).
- Vitamin complexes.
- Adaptogens.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics (in the presence of bacterial complications).
Of the physiotherapy techniques, the following will be useful:
- inhalation of essential oils, proteolytic enzymes;
- UFO;
- UHF;
- diathermy to the chest;
- laser therapy;
- vibration massage;
- aeroionotherapy.
In addition, breathing exercises and physiotherapy exercises are recommended for patients with anthracosis.
Examination of incapacity for work
All patients with anthracosis need to change their place of work without contact with dust and other irritants.
- With pronounced functional disorders, they may be contraindicated to work in unfavorable meteorological conditions and with great physical stress.
- The exception is patients with initial signs of the disease without functional disorders. Such persons can be left to work underground, but their condition is closely monitored. In case of progression of pneumoconiosis, they are transferred to superficial work.
- With severe respiratory and heart failure or severe complications (for example, pulmonary tuberculosis or severe emphysema) in patients with anthracosis, there is a complete permanent disability.
Read also:Fluid in the lungs
In these cases, the medical and social expertise (MSEC) deals with expert issues. It determines the degree of disability and the amount of compensation that the patient receives.
Prophylaxis
Reducing the incidence of anthracosis and anthracosilicosis is of great socio-economic and medical importance for the state.
At all enterprises of the coal industry, special attention is paid to the prevention of occupational diseases, the main activities of which are:
- The use of personal protective equipment (respirators).
- Carrying out preventive medical examinations.
- Annual rehabilitation of persons working in hazardous conditions.
- Correct operation of the supply and exhaust ventilation.
- Injection of water and special solutions into coal seams to reduce dust.
- Improvement of the irrigation system during the operation of coal miners.
- Development of new methods of destruction of coal and rock that are safe for workers.
Anthracosis, by the nature of the fibrotic process in the lung tissue, refers to pneumoconiosis with a relatively benign course that does not have a pronounced tendency to progression for a long time. An unfavorable course can have anthrosilicosis in miners working in deep mines with the presence of additional harmful factors (high temperature, excessive loads).