Throwing bile into the esophagus: complications, diagnosis, treatment
If we turn to the moral and ethical characteristics of human nature, you can find such a definition as "a bilious person." It means an embittered and petty, tough and immoral character, as unpleasant as bile tastes. Everyone can imagine the taste of bile, even those who have never specially tasted it - a disgusting bitterness, which, moreover, has an unpresentable appearance. When bile, instead of performing its functions and moving in the prescribed way, is thrown from stomach into the esophagus, the patient experiences emotions that in no way contribute to the improvement of his well-being.

Bile
Content
- 1 Why bile is needed
-
2 Why does bile enter the esophagus?
- 2.1 Video - Vomiting, causes and symptoms
-
3 How to understand that bile is in the esophagus
- 3.1 Complications
-
4 Diagnosis of pathology
- 4.1 Video - Anamnesis
-
5 Treatment process
- 5.1 Lifestyle changes if necessary
Why bile is needed
Bile in the body is the most important element, without which the normal process of digestion is unthinkable. It is an emulsifier of fats and a stimulant of protein-digesting enzymes. That is, without bile, the human gastrointestinal tract will not be able to digest more than half of the foods that make up the diet.
The liver produces bile. The gallbladder is connected to the liver with the help of the bile ducts. One of its main functions is to collect bile from the liver and store it until the body needs it. As soon as food enters the duodenum, which needs bile for digestion, the gallbladder releases a certain amount of this bitter solution into it. Then everything goes to the rest of the intestine already in a digested state, and is excreted from the body in a natural way.

Physiology of bile
Important! Bile is needed to help the rest of the digestive juices digest food. If for some reason it does not come (for example, with congenital or acquired bending of the gallbladder), the duodenum cannot cope with digestion. But if it enters in excess, so much so that part of it rises from the intestine through the stomach into the esophagus, this is a pathology that leads to serious diseases.
Why does bile enter the esophagus?
There must be reasons for any phenomenon. To understand how bile masses rise from the duodenum, and why it is dangerous, it is necessary to trace the path of food movement along the gastrointestinal tract.
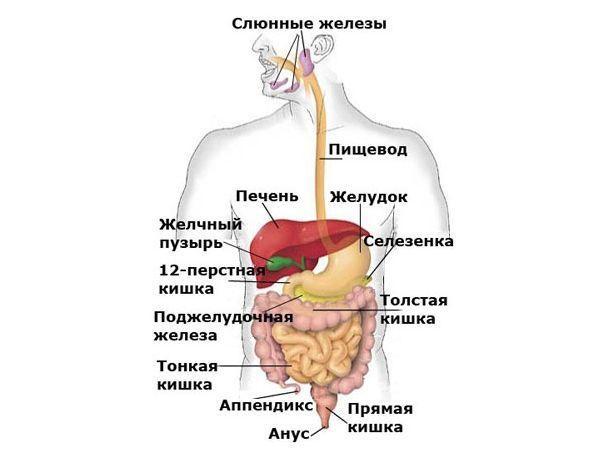
Gastrointestinal tract anatomy
Rule number one - food that has entered the body moves along the path to the anus. As with many rules, there is an exception to this - vomiting. It is necessary to rid the stomach of toxic substances trapped there for various reasons.
Video - Vomiting, causes and symptoms
The alimentary tract has “valves” (sphincters) between some sections that move food to its more distal sections - these “valves” cannot do otherwise. But this is if the muscles are normal, and not relaxed. When muscle tone is weakened, under pressure, the contents of the duodenum and stomach can move back up, "taking" with you gastric juice and bile, which is involved in the digestive process.

The composition of human bile
Important! Moving the contents of the stomach and duodenum 12 into the esophagus is dangerous for its mucous membrane. If the walls of the duodenum have protection from the irritating effect of bile, or rather, the salts and acids they contain, which help break down food into fragments, then the walls of the esophagus do not have such protection.
Getting into the esophagus, bile affects its mucous membrane, which can cause erosion and other pathologies to form. The process of moving this fluid in the wrong direction without the participation of gastrointestinal motility is called bile reflux.

Endoscopy of biliary reflux esophagitis
Why do muscle "valves" relax, and it becomes possible for bile to flow into the esophagus? There are several reasons.
- One of the first - pregnancy. The embryo exerts pressure on all internal organs, and the muscles of the "valves" do not fully withstand such pressure.
- Congenital pathology can also cause abandonment - muscle tissue is weakened genetically or due to a birth defect.
- Of the acquired pathologies, the formation of casting is promoted by hernial and tumor-like formations, as well as various happy trauma.
- Carrying out operations, which is complicated by damage to the muscle "valves", also becomes the cause.

Throwing bile into the esophagus
These are reasons of the first order, but there is also a second order, in conjunction with the first or with each other, creating the same effect - muscle relaxation, which makes it possible for bile to enter the esophagus.
- When patency is impaired in the digestive tract.
- If the meals are not regular and regular, the person overeats, especially before bed.

Overeating at night can lead to insufficiency of the sphincters responsible for bile reflux.
- Exercising immediately after a meal also causes bilious reflux.
- The cause may be any diseases of the gastrointestinal organs, which have an inflammatory nature.
Inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract can lead to insufficiency of the sphincters responsible for bile reflux
- The same will happen if you drink too much water during a meal.
- There are foods that reduce the contractile ability of muscle valves - chocolate and coffee, as well as raw tomatoes. If consumed in large quantities on a regular basis, muscles will weaken.

Eating a lot of chocolate can lead to a failure of the sphincters responsible for bile reflux
How to understand that bile is in the esophagus
Gastrointestinal tract - "darkness". Not every apparatus is capable of seeing what is happening there. How can a person know that bile is entering the esophagus? 7% of the bile substance in the bladder is acids. They aid in the digestion of protein and fats, and they also interact with gastric juices, which are also involved in the digestion process. The throwing of bile into the esophagus occurs along with the contents of the stomach, which leads to injury to the mucous tube, causing discomfort.
- Pulling pain may occur.
- Surely there will be a feeling of heaviness on the way from the esophagus to the stomach.
- An eructation will appear, in which there will be air and a certain amount of liquid components.

Belching
- The patient may experience heartburn.
- The discharge of bile is, of course, accompanied by the bitterness that the patient feels.
- Feelings of nausea may occur.

Nausea
- Spasmodic vomiting may begin, in the mass of which there will be an admixture of bile.
- Over time, a yellow-white coating forms on the tongue.
- At night, the patient will be tormented by thirst, and during the day there will be general weakness, combined with rapid fatigue.

General weakness
- Naturally, the appetite will change.
Important! If any of the symptoms of the presence of bile in the esophagus occur once or have been experienced several times, but with rare periodicity, this does not indicate a persistent pathology, but, most likely, only means indigestion from overeating or abundance fatty foods. But if the manifestations are regular, biliary reflux esophagitis is diagnosed.
Complications
The disease has not only a direct directional effect - the destruction of the esophageal mucosa, but also many complications. The tissues take on an atypical shape. Diseases such as Barrett's esophagus (a precancerous condition of the esophageal mucosa), biliary reflux esophagitis develop (chronic reflux of bile), bile reflux gastritis (reflux of bile into the stomach, accompanied by inflammation of its mucous membrane).

Barrett's esophagus - one of the possible complications of bile reflux esophagitis
Diagnosis of pathology
Like almost any examination, it all begins with the collection of anamnesis, carried out in the process of communication with the patient. The doctor listens to complaints, determines how long the problems that bother the patient last, how pronounced the symptoms are.
Video - Anamnesis
Then, to find out the reason for the ingress of bile into the upper parts of the stomach and esophagus, a number of instrumental and instrumental studies are carried out.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy shows the presence of bile in the lower esophagus.
- An ultrasound of the stomach helps to detect the presence of bile in it.

Ultrasound of the stomach
- On ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, you can see the abnormalities of the internal organs, which caused the formation of the cast.
- Analyzes of biological substances secreted by the body will help establish the presence of inflammatory and other pathological processes.
- Choledochoscintigraphy shows how normal the contraction of the muscle valves is.
- Additionally, the tone of the gallbladder can be examined.

To detect biliary reflux esophagitis, the tone of the gallbladder may be examined.
Based on all the data, a diagnosis is made and treatment is prescribed, which must be accompanied by a diet.
Treatment process
The goal of treatment is the ability to reduce the frequency of biliary reflux until it stops completely. The therapy is not instantaneous and takes several months. It consists not only in the selection of drugs, but in the whole complex, which has its own characteristics.
- Long-term treatment - at least (mild form) one and a half months.
- Only drugs are not able to destroy the disease, they only relieve its symptoms.
- Diet alone will not cure biliary reflux, but without it, therapy will not be successful.

Compliance with a special diet is a prerequisite for getting rid of bile reflux esophagitis
- In parallel with the treatment, it is necessary to raise the immune system.
- The lifestyle must be maintained healthy.

A healthy lifestyle is an important part in the treatment of biliary reflux esophagitis
- Physiotherapy will be needed.
- In the treatment process, you cannot do without gymnastics.
- Traditional methods will help make the treatment more effective.

The use of alternative methods of treating biliary reflux esophagitis is the key to increasing the effectiveness of therapy
Important! There are stages of bile reflux esophagitis in which it does not respond to therapeutic treatment. They are rarely diagnosed, since in most cases the diagnosis is made long before they occur, but if the patient has passed into this stage, the disease can only be treated surgically.
Table. Methods for the treatment of biliary reflux esophagitis.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
 Diet therapy |
The patient will be forced to change eating habits and develop the correct eating behavior, otherwise it will not be possible to get rid of bilious reflux. Culinary processing: cooking, steam, stewing. You can't fry. Meals - up to six times a day. Reducing the standard portion in half. Animal fat is reduced, and foods that weaken muscle tone (coffee, chocolate, tomatoes, and so on) are excluded. Alcohol is also absolutely excluded. |
 Drug treatment |
The drugs of the following groups are prescribed: anti-inflammatory, anti-acid, anti-reflux and pain relievers. The first ones relieve mucosal inflammation (Actovegin, Sucralfat, Likviriton). The latter reduce the acidity of the cast contents: (Omeprazole, Maalox, Cimetidine). Still others relieve nausea, heartburn, belching ("Ganaton", "Motilium"). The fourth reduce the pain syndrome, if any, and promote the healing of erosion ("Solcoseryl", "Tricardin", "Drotaverin"). |
 Physiotherapy |
Physiotherapeutic methods are used in parallel with drug treatment. They help to increase blood circulation in the esophageal and gastric walls, promote tissue regeneration and raise the immune level. This also includes special gymnastics. |
 Treatment with folk remedies |
From medicinal plants and other folk remedies, those are used that will help reduce the intensity of symptoms, promote healing of the mucous membrane and relieve inflammation. These are: chamomile, lemon balm, flaxseed, rose hips, aloe, as well as collections from these plant components. Decoctions and infusions are prepared, always water-based, but not alcohol-based. |
 Surgery |
If the disease is not diagnosed at the right time, or if the proper effect of treatment is not obtained, the disease enters an incurable stage that requires surgical intervention. Operate if the therapy did not give the expected effect within six months, if the disease progresses rapidly, affecting a large area of the mucous membrane, if there was a narrowing of the esophagus, or the esophageal-gastric bleeding. |
Lifestyle changes if necessary
As well as food, the patient may have to change their household habits.
- Getting enough sleep is important.
- It is necessary to do exercises or engage in a non-strength sport.
- Get hardened so that colds do not reduce immunity.

Hardening is a recommended part of life to improve the effectiveness of the treatment of biliary reflux esophagitis
- Less nervous.
- Take vitamin complexes.
- Do not overwork.

Overwork is a condition that should not be tolerated in the prevention of biliary reflux esophagitis
If you strictly follow all the recommendations, complete relief of symptoms occurs within one and a half to two months. A control endoscopy is done to ascertain the absence of lesions. If there are no relapses within six months from the end of therapy, the patient is considered completely cured. Nevertheless, in patients who have returned to their previous habits and unhealthy lifestyle, in 10% of cases, there is a relapse of the pathology within a year.