Disease of mastocytosis
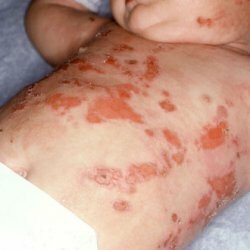
Since mastocytosis is directly associated with mast cells, it is also called fat-cell leukemia. The disease is quite rare, and the exact causes of its occurrence are not yet known. According to research centers, the disease most often affects children who are not yet 2 years old. Most of these diseases go away on their own at a time when the sexual maturation of a person.
Mastocytosis is a group of diseases. The pathogenesis of the disease is based on the release of mediators, the so-called mast cells, among which histamine, leukotrienes and heparin can be isolated. The involvement of histamine in pathogenesis is manifested in many symptoms, including the stomach. With a significant infiltration of the body, a violation of his work occurs, which is dangerous for human health.
To date, there are several reasons for the selection of mediators:
- Physical load.
- Physical contact.
- Bite stinging insect.
- Food.
- Apioids.
- NSAIDs.
Classification of the disease
There are two types of mastocytosis: systemic and cutaneous. Most often, cutaneous mastocytosis affects children. Symptoms of this type of mastocytosis are pigmentary urticaria and rash. The rash may have a different shade. Diffuse and local rash has an orange-pink hue, and maculopapular - brown. Diffuse rash is the least common.
What swings the systemic mastocytosis, then they are most often sick adults. A characteristic feature of the disease is the multifocal lesion of the bone marrow, but sometimes the spleen, skin, liver and lymph nodes get under attack. Systemic mastocytosis proceeds painlessly, and doctors' forecasts are encouraging. With such a disease, the internal organs are practically not damaged. In addition, there is an aggressive type of mastocytosis, which proceeds quite differently. With this option, the forecasts of doctors are not encouraging. The skin in this case is not affected, which can not be said about internal organs.
The main symptoms of the disease
The main and most common symptom of mastocytosis is itchy skin. Struck skin is extremely not desirable to rub and stroke. Otherwise, this action can lead to the appearance of urticaria, as well as erythema, which manifests itself around the affected area of the skin.
Actually, the disease can manifest in different forms. In addition to skin itching, people may have fever, as well as anaphylactoid reaction, which is accompanied by shock and syncope. The patient may experience epigastric pains, which are a sign of peptic ulcer, chronic diarrhea and bone pain. If there is infiltration of the liver or spleen, portal hypertension may occur, which later can develop into ascites. During illness, a person may experience vomiting or nausea. Also, the disease can be accompanied by a drop in blood pressure.
Mastocytosis can also cause neuropsychiatric changes, such as irritability, frequent mood changes and depression.
Diagnosis of the disease
Initial diagnosis is carried out according to clinical signs. But this is not enough, since the symptoms that are manifested in mastocytosis are similar in symptom with pheochromocytosis, anaphylaxis and some other diseases. In this regard, in order to establish an accurate diagnosis, a bone marrow biopsy or an affected area of the skin should be performed. If a person has symptoms of peptic ulcer, then it is necessary to measure the level of gastrin in the blood plasma. Such an analysis would rule out the possibility of the disease on Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Also, special tests are performed in the presence of fever in the patient. The disease can be detected by blood and urine tests, but their results are not enough to determine the exact diagnosis.
If internal organs are affected during the disease, then it can be checked by ultrasound. Using ultrasound of organs that are in the abdominal cavity, you can detect an increase in the spleen or liver. With this following, it is possible to determine the violation of bone tissue, since mastocytosis can lead to osteosclerosis or osteoporosis.
Treatment of the disease
For the treatment of mastocytosis of the skin, so-called H2-blockers are used. Children who have a manifestation of cutaneous mastocytosis do not need additional treatment, since such variants of the disease most often pass without the use of medications. As for adults, they need to undergo treatment. Most often, doctors prescribe psoralen, as well as ultraviolet irradiation. For treatment also use glucocorticoids, which take one or two times a day. Sometimes the mastocytosis of the skin passes without the intervention of doctors. This form of illness is not threatened by children. In rare cases, the dermal form of mastocytosis can develop into systemic mastocytosis.
People who have systemic mastocytosis, in addition to the H2-blocker, also prescribe the H1-blocker. When the temperature rises, it is necessary to take aspirin. But it must be taken cautiously, as it promotes the development of those symptoms that are associated with mast cells. In connection with such a risk, aspirin is strictly forbidden to children. The use of aspirin by children can cause the onset and development of Reye's syndrome. For the treatment of mastocytosis, cromolin is widely used. Apply the drug to 200 mg 4 times a day. As for children, for them, the dose is half that, that is, 100 mg. No matter how scientists tried, the way by which it is possible to reduce the amounts of mast cells formed has not yet been found. Ketotifen is also used in the amount of 4 mg twice a day. But this drug is not as effective as cromolyn.
A patient who is ill with severe form is prescribed for treatment of interferon. With the help of this drug, you can block the symptoms that are associated with bone marrow damage. Glucocorticoids are also used. So, for example, prednisolone is prescribed in an amount of 60 mg once a day. The course of treatment lasts several weeks. People with severe form are sometimes prescribed splenectomy, which can improve the patient's condition.
Cytotoxic drugs such as etopizod and daunomycin are also sometimes used to treat mastocytosis, but their effectiveness in treatment has not been proven. To date, consider the use of imatinide. Surgical methods are used to remove individual mast cells.



