Internal hemorrhoids: symptoms and treatment
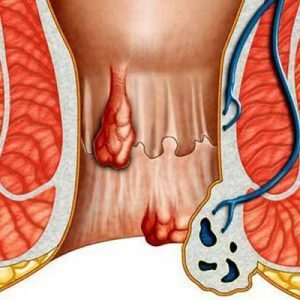
Hemorrhoids are a pathology of the veins of the rectum, which is accompanied by their expansion to the formation of varicose nodules.Internal hemorrhoids are characterized by the fact that these nodes are localized under the mucosa of the intestinal walls inside its lumen.According to medical statistics, its prevalence in the population is about 4%( taking into account mixed forms, the figures are 1.5 times higher).
Important: hemorrhoids develops in almost 80% of women giving birth.The probability of development of the pathology of the veins of the rectal region increases with each repeated birth.
Contents: Why does internal hemorrhoids develop?Symptoms of internal hemorrhoids Complications Diagnosis Treatment of internal hemorrhoids and preventionThe disease is accompanied by a pain syndrome, the intensity of which increases during the evacuation of the intestine.Nodes have the ability to bleed and fall out.At laboratory research of blood at the patient signs of an anemia quite often are taped.
Pathology in most cases occurs chronically with a slow progression. In the early stages, it may not manifest itself clinically, since there are relatively few nerve endings in the rectal intestine.Vascular changes can not be determined visually.In this regard, the proctologist is often treated by patients with already quite neglected internal hemorrhoids.
Why does internal hemorrhoids develop?
Important: requires the combination of two conditions - the relative weakness of the vascular( venous) walls and the increase in intramuscular( rectal) pressure - to form internal hemorrhoids.
Among the causes of the disease are:
- hereditary predisposition;
- physical inactivity;
- sedentary work;
- excessive physical activity;
- non-compliance with drinking regimen( low water consumption leads to blood thickening);
- alcohol abuse;
- chronic constipation;
- frequent diarrhea( incl. Against the background of abuse of laxatives);
- improper power supply;
- overweight( obesity);
- delivery;
- neoplasms of the pelvic organs;
- intestinal infections;
- age factor;
- psychoemotional factors( stresses).
One of the main factors predisposing to the disease experts consider the hereditary predisposition of .Even in the intrauterine period of development, enlarged cavernous( cavernous) formations are laid in the distal part of the intestine.In the future, they increase and shift, forming nodes.
Frequent lifting of weights also provokes the formation of pathological nodes of the venous plexus.
Low fluid intake( less than 1.5 liters per day) causes condensation of fecal matter, which often leads to constipation. In addition, against the background of the dehydration of the body, the rheological properties of the blood deteriorate, and this in turn provokes thrombosis of the veins.
 Snacks "on the run," low fiber intake and addiction to acute and salty foods disrupt intestinal motility.
Snacks "on the run," low fiber intake and addiction to acute and salty foods disrupt intestinal motility.
Circulation in the intestinal wall is significantly impaired if there is a compression of the vessels with a tumor or fat deposits.
Intestinal infections often contribute to the appearance of microscopic lesions on the surface of the intestinal mucosa, which also contributes to the development of internal hemorrhoids.
In elderly patients, as a result of natural age-related changes, muscle fibers are atrophy, and this often leads to the formation of internal nodes.
Frequent stresses negatively affect many functions of the body, including - and on the activity of the intestine.
Symptoms of internal hemorrhoids
The most important difference between the internal form of hemorrhoids from the external or mixed is the absence of changes that are noticeable during external examination.Pathological formations( nodes) are localized in the lumen in the immediate vicinity of the anal sphincter or at some distance from it.
Severity of symptoms directly depends on the size of varicose extensions. Hemorrhoids are characterized by stage progression;In clinical proctology, it is common to distinguish 4 stages of development of this pathology:
-
 At an early stage, the nodes are small;They do not cause the patient any inconvenience.In rare cases, varicose enlargement may be damaged by dense fecal masses, which provokes an inflammatory process.Due to the release of exudate, the perianal zone is constantly moistened, which causes itching( or burning sensation).Slight bloody traces are sometimes found on toilet paper after the act of defecation, but in the vast majority of cases, blood is detected only in the laboratory examination of stool tests.Patients complain of vague unpleasant sensations in the rectal area after bowel movement.
At an early stage, the nodes are small;They do not cause the patient any inconvenience.In rare cases, varicose enlargement may be damaged by dense fecal masses, which provokes an inflammatory process.Due to the release of exudate, the perianal zone is constantly moistened, which causes itching( or burning sensation).Slight bloody traces are sometimes found on toilet paper after the act of defecation, but in the vast majority of cases, blood is detected only in the laboratory examination of stool tests.Patients complain of vague unpleasant sensations in the rectal area after bowel movement. - If therapy is not initiated at an early stage, then the process progresses.Varicose enlargement increases in size, which causes the sensation of a foreign body and gravity in the intestine.After physical exertion, coughing or straining, the nodes go out from the anus, but then spontaneously "retract" back.Bloody discharge becomes easily visible on toilet paper and the surface of fecal matter.Each release of the intestine is accompanied by a pain syndrome of moderate intensity.At laboratory analysis of blood signs of anemia are revealed.Clinical manifestations can weaken for a while, that is, remission is possible.At this stage, the pain becomes acute, and the patient worries almost constantly.Hemorrhoidal enlargements increase so much that they come out even against very small loads.They can no longer self-retract, and the patient has to correct them.A pronounced inflammatory reaction and development of complications in the form of rectal bleeding and anal fissures are characteristic.
- The heaviest( neglected) stage is characterized by the protrusion of the nodes, which it is almost impossible to fix independently.Acute pain is a constant concern;They have the property of increasing with sitting or walking.The periods of exacerbation become more frequent.The likelihood of such a complication, as infringement of nodes with tissue necrosis, is high.
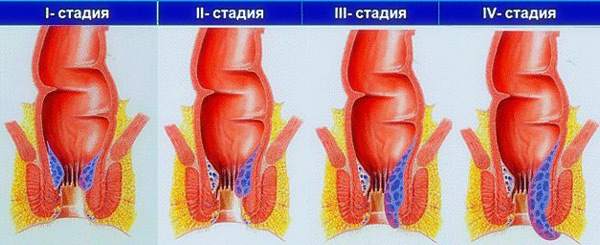
Depending on the individual characteristics of the body and the presence of provoking factors, the rate of progression of internal hemorrhoids depends.
Complications
Complications of internal hemorrhoids include:
-
 vein thrombosis;
vein thrombosis; - infringement of hemorrhoids;
- loss of varices ;
- intestinal bleeding;
- anal sphincter failure.
Hemorrhoids lead to stagnation of blood in the veins, and this causes a thrombosis. Symptoms of this complication are an increase in the nodes, the acquisition of a bluish-purple hue and sharp pains in the perianal region, which increase with palpation.
Infringement is usually caused by lifting weights and straining for problems with bowel movement. In the weakened nodes, thrombosis develops;A sharp lack of local circulation leads to necrosis( necrosis of tissues). Typical signs of infringement are intense raspiruyuschie pain and sensation of a foreign body in the rectum.In the course of a proctologic examination, prominent nodes that are very dark( up to black) are detected.
Frequent complication of III - IV of internal hemorrhoids is a constant bleeding from cavernous bodies .With him, the patient complains of general weakness( which is due to increasing anemia).Analyzes show a drop in hemoglobin of blood to 40-50 g / l.
In elderly patients, frequent prolapse of nodes on the background of progressive hemorrhoids in some cases leads to weakness of the anal sphincter .This complication is manifested by incontinence of gases and even the contents of the rectum( liquid fecal masses).
Diagnostics
 Note: pathomorphologically with internal hemorrhoids reveals a mucosa-covered node, the vascular structures of which consist of pathological( cavernous) bodies.They in turn consist of a large number of cavities, separated by walls of connective and muscle tissue.
Note: pathomorphologically with internal hemorrhoids reveals a mucosa-covered node, the vascular structures of which consist of pathological( cavernous) bodies.They in turn consist of a large number of cavities, separated by walls of connective and muscle tissue.
Early diagnosis is often difficult, because external varicose extensions are not identified, and the patient's complaints are rather vague( often asymptomatic).
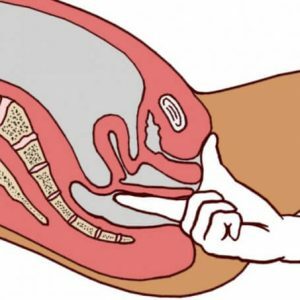
Characteristic nodes are identified in finger research.Manual study allows you to assess their localization, consistency, size and degree of soreness. Cavernous bodies can be grouped or distributed across different parts of the intestinal wall.If the disease develops for a long time, a decreased tone of the musculature of the rectal region is revealed.
To clarify the diagnosis proctologists resort to endoscopic methods of diagnosis - anoscopy and sigmoidoscopy .Anskopia gives an opportunity to examine the rectum to a depth of no more than 10 cm;With a higher localization of varicose extensions, a sigmoidoscope is required - a tube up to 25 cm long, equipped with optics and a backlight system.
In the course of endoscopy, a physician can draw a biopsy specimen - a tissue sample for cytological and histological examination.This is necessary for differential diagnosis of hemorrhoids from neoplasms.
Additionally, an irrigoscopy is used - X-ray examination of the large intestine with a retrograde introduction of a contrast agent( barium sulphate ) into its lumen.Fluoroscopy helps visualize any convexity( including cavernous enlargement) and anal fistulas.
Note : when examining children, irrigoscopy often replaces all other types of proctologic examination.
The process of preparation for any kinds of instrumental diagnostics in proctological practice presupposes compliance with the diet for 1-2 days.In this case, the ration excludes rough food .Immediately before the examination, the patient is treated with a cleansing enema( in some cases, laxatives can be dispensed with).
Additional methods of investigation include analysis of feces for latent blood, lamblia and helminth eggs.Often the presence of parasites, rather than hemorrhoids, causes the appearance of such a symptom as anal itching.
Important: necessarily conducts differential diagnosis of internal varicose veins with diverticula, condylomata, malformations, malignant neoplasms and prolapse of the rectum.
Treatment of internal hemorrhoids and prevention
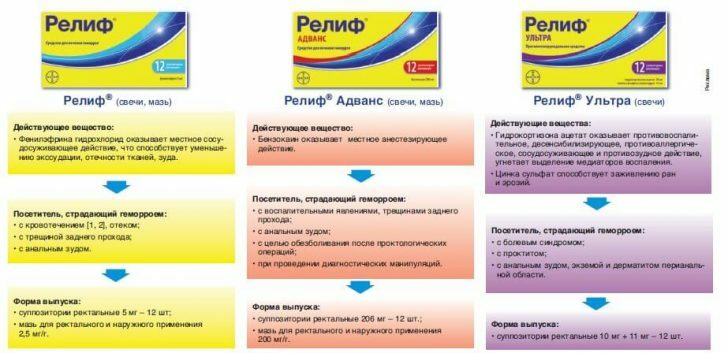
With early diagnosis of the disease in the acute phase, conservative treatment is possible. Symptomatic therapy includes normalization of the functional activity of the intestine( diet and administration of drugs that stimulate motor activity) and the appointment of analgesic agents for topical application. One of the most important tasks of internal hemorrhoid therapy is prevention of venous thrombosis.Locally applied Gepatrombin G and Proctosedil, and orally - preparations for improving the tone of the veins - Detraleks and Troxevasin.
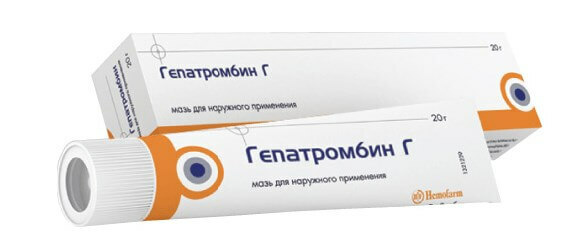
Means for ingestion are given in repeated courses;The duration of each of them is 3 months.
The effectiveness of such techniques as sclerotherapy, as well as electrocoagulation and infrared coagulation has been clinically proven.
 Note: sclerotherapy is the introduction of a sclerosing agent into the veins that causes the vessel to collapse and close the lumen of the vessels.In a fairly short time, veins start to desolate and then be resorbed.
Note: sclerotherapy is the introduction of a sclerosing agent into the veins that causes the vessel to collapse and close the lumen of the vessels.In a fairly short time, veins start to desolate and then be resorbed.
I cryodestruction is shown on I I-II I stage( action on the nodes with ultralow temperatures by means of liquid nitrogen).
In severe situations, physicians have to resort to ligation of the arteries of nodes by means of rings made of latex( under the control of Dopplerography).Surgical intervention may involve bandaging or excision of pathological nodes.An alternative is hemorrhoidectomy.
With diagnosed thrombosis, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.Often, surgery is required, the purpose of which is to remove blood clots and affected areas of the venous plexus.
Nodal drop is an indication for manual repositioning.If the technique is ineffective, they resort to surgery, but only in the remission phase.
With timely and adequate therapy, the prognosis for a complete cure is favorable.
The most important measures for the prevention of internal hemorrhoids:
- fight against chronic constipation and frequent diarrhea;
- normalization of power;
- compliance with drinking regimen;
- exclusion of significant physical exertion;
- active lifestyle management;
- rejection of alcohol and nicotine.
To reduce the frequency of exacerbations, it is advisable to designate venotonic therapy( orally and topically in the form of rectal suppositories).
Vladimir Plisov, medical reviewer