Jaundice of newborns: causes, treatment and consequences

Almost 70% of newborns in the first week of life are diagnosed with jaundice.But in 90% of cases it is physiological and only 10% - pathological.Let's try to understand what jaundice is, why it appears in a child who has just seen the light, how doctors diagnose and treat jaundice of newborns( neonatal jaundice).
Table of contents: Jaundice: general information Classification of neonatal jaundice Causes of pathological jaundice in newborns Principles of diagnosis of jaundice in newborns Jaundice of newborns: consequences Methods for treating jaundice in newbornsYELLOW: GENERAL INFORMATION
 Jaundice is not a disease, it isSyndrome( complex of symptoms), which manifests itself by yellowing the mucous membranes, skin and sclera.There are many diseases( congenital and acquired), in the clinical picture of which there is icterus of the skin and mucous membranes.
Jaundice is not a disease, it isSyndrome( complex of symptoms), which manifests itself by yellowing the mucous membranes, skin and sclera.There are many diseases( congenital and acquired), in the clinical picture of which there is icterus of the skin and mucous membranes.
It appears due to the accumulation of bile yellow pigment bilirubin in the blood( hyperbilirubinemia), and then in the tissues.The higher its level, the more intense the icteric staining.In this case, greenish and olive-yellow shades of mucous and skin indicate an increase in the concentration of direct bilirubin, and all shades from light-lemon to saturated saffron - about the increase in the amount of indirect bilirubin.
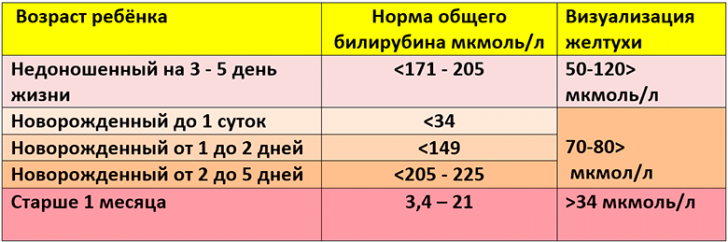
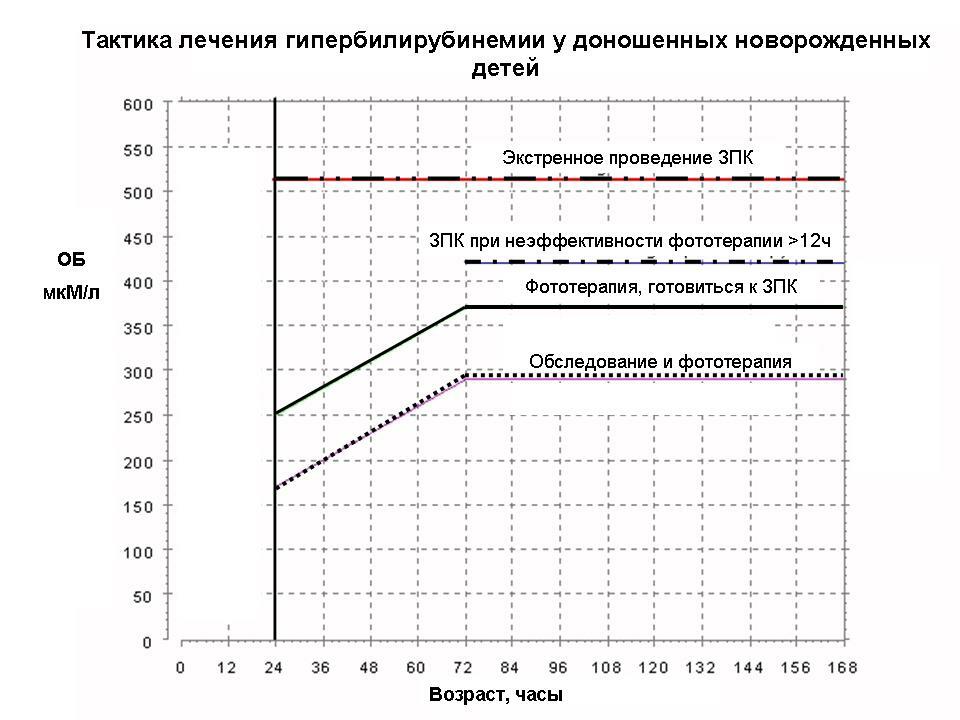
Recommended to read:Jaundice appears gradually: first sclera and solid palate( its mucosa) are stained, then the skin turns yellow, beginning with the head and ending with the terminal phalanges of the fingers on the legs and hands.It is believed that in full-term newborns, jaundice of the skin can be noticed if the level of bilirubin in the blood is 85 μmol / l or more, and in premature infants - 120 μmol / l and more, since the subcutaneous fat layer is less pronounced in them.The table shows the bilirubin in newborns, including premature infants.
CLASSIFICATION OF NEONATAL JAWS
- All jaundices of the newborn period are divided into two groups:
- physiological jaundice of newborns.It is approximately 9/10 of the total number of jaundice diagnosed in infants.
Physiological jaundice is a temporary condition due to the immaturity and functional imperfection of the enzyme systems of the liver of the newborn.In the fetus, part of the bilirubin formed, penetrating the mother's bloodstream through the placenta, is excreted by the mother's liver.A newborn has no such possibility.And his liver can not immediately cope with the increased load, so bilirubin begins to accumulate in the blood.
Physiological jaundice appears from 3 to 5 days of life and persists no longer than 10 days in full-term babies and no longer than two weeks in premature babies.The general condition of the child is not violated.The amount of indirect bilirubin in case of physiological jaundice does not exceed 200-222 μmol / l.
- pathological icterus.They constitute 1/10 of the total number of neonatal jaundice.Pathological jaundice, regardless of the mechanism of its occurrence, is always a symptom of the disease.

- Based on the results of laboratory tests:
- jaundice with hyperbilirubinemia due to direct bilirubin;
- jaundice with hyperbilirubinemia due to indirect bilirubin.
- By origin:
- congenital;
- purchased.
- By the mechanism of increasing the content of bilirubin in the blood. This classification will be considered in detail, since pathological jaundices, although they constitute only a small part of all jaundice in newborns, are mostly a sign of a serious hereditary or acquired disease.
CAUSES OF PATHOLOGICAL JAWS
Recommended to read:Recall that hyperbilirubinemia is an increase in the blood content of the bile pigment bilirubin.His metabolism in the human body is a complex process, consisting of several stages( production of bilirubin, a number of biochemical transformations of it and excretion from the body).Any even the slightest failure in the work of this biological mechanism leads to an increase in the concentration of bilirubin in the serum and the appearance of jaundice.Further, we will analyze various variants of such "malfunctions" in bilirubin metabolism and consider some of the diseases that arise from them.
Increased production of bilirubin.Jaundice of this type can be congenital and acquired:
- congenital:
- pathology of the erythrocyte membrane( shell) .
The disease begins gradually, progresses slowly.Jaundice appears sometimes already in the period of newborns, the liver and spleen increase, later anemia develops;
- deficiency of erythrocyte enzymes .
In newborns, the disease manifests more often on the second day of life: jaundice appears, darkens urine;
- defects in the structure and synthesis of hemoglobin and heme .
During the newborn period, the disease is extremely rare, making itself felt usually closer to the second half of life.
- Acquired:
-
 Hemolytic disease of the newborn( GBN ) is the result of the immunological conflict between fetal blood and mother's blood.Incompatibility develops according to Rhesus antigens, AB0 antigens( by blood group) or other group factors;
Hemolytic disease of the newborn( GBN ) is the result of the immunological conflict between fetal blood and mother's blood.Incompatibility develops according to Rhesus antigens, AB0 antigens( by blood group) or other group factors; - hemorrhages ( cephalohematoma or internal organ hemorrhage), in the resolution of which the products of the decomposition of hemoglobin enter the blood, and the jaundice of the newborn appears;
- Other causes of jaundice in the newborn, , among which polycythemia( increased red blood cell count), swallowed blood syndrome( develops when the baby enters the digestive tract of the baby), drug hemolysis, immunopathological diseases in the mother, and others.
Defects in the capture, conjugation and excretion of bilirubin.Jaundice of this type can also be congenital and acquired:
- congenital:
- Gilbert syndrome , which girls suffer 2-4 times less often than boys.Due to a defect in the cell membrane of hepatocytes, the processes of transport and binding of bilirubin are disrupted.Often in the maternity hospital appeared such jaundice, which does not cause anxiety, is regarded as a physiological jaundice of newborns.And only in school or even in adolescence is the disease diagnosed;
- Kriegler-Nayyar syndromes ( type I and type II).In the first case, when the liver completely lacks the enzyme glucuronyltransferase, the child turns yellow in the first hours after birth, the level of bilirubin( up to 700 μmol / l or more) is steadily increasing in the blood.The effect of treatment is absent.As a result of the fact that indirect bilirubin is deposited in the nuclei and the nervous nodes of the brain, nuclear jaundice of newborns develops, the consequences of which are the death of the child in the first year of life.In the second case, the activity of this enzyme is sharply reduced( less than 10% of the norm), therefore jaundice is not so difficult.In the first days of life, urine and feces are bright, but later they acquire a normal color.The level of bilirubin in newborns usually does not exceed 380 micromol / l, and nuclear jaundice develops less often.Against the backdrop of ongoing treatment, there has been a positive trend;
- Lucei-Driscoll syndrome , in which the mother's blood contains a substance that reduces the activity of the enzyme glucuronyltransferase.The kid turns yellow in the first days after birth, the concentration of bilirubin can be high, which threatens the development of nuclear jaundice of newborns, the consequences of which are tragic.But with proper treatment, the prognosis is very favorable;
- Dabina-Jones syndrome is a hereditary disease due to a defect in removing bilirubin from liver cells.Jaundice is usually expressed moderately, the liver is slightly enlarged.But in the maternity home the diagnosis of this disease is rarely put;
- symptomatic jaundice with congenital hypothyroidism, congenital insufficiency of enzymes involved in the metabolism of galactose( galactosemia) or fructose( fructose).With galactosemia, persistent jaundice appears in the first day, the liver and spleen increase.These symptoms are combined with diarrhea, vomiting, refusal to eat.By the end of the neonatal period, hepatic failure develops.Fructosemia proceeds more benignly.
- purchased:
- jaundice from an excess of hormones in the mother's milk occurs in 0.5-2% of newborns.It develops due to the peculiarities of the composition of breast milk: high concentrations of pregnanediol and free fatty acids, the presence of the enzyme beta-glucuronidase, high activity of lipoprotein lipase.All this leads to a disruption of conjugation and a greater degree of excretion of bilirubin.The jaundice that appears on the third day reaches a maximum by 6-14 days and resembles the physiological jaundice of newborns, but lasts much longer, sometimes up to two months.The concentration of bilirubin in the blood usually does not exceed 200-240 μmol / l.If the baby is weaned and transferred to the mixture for 2-3 days, the level of bilirubin decreases markedly.As a rule, the resumption of breastfeeding on days 4-6 does not cause increased jaundice;
- jaundice with a deficiency of hormones in the blood. It appears in ¾ of babies suffering from hypothyroidism.Due to the inadequacy of hormones produced by the thyroid gland, the maturation of the enzyme glucuronyl transferase is disturbed, which affects the metabolism of bilirubin.Jaundice is prolonged, appears on 2-3 day of life and lasts sometimes up to 16-20 weeks.It is combined with lethargy, dryness and "marbling" of the skin, rough voice, lack of mobility, swelling.With the appointment of hormone therapy, the level of bile pigment in the blood with a maximum of 200-220 μmol / l decreases to the norm of bilirubin in newborns;
- Neonatal hepatitis: is infectious( with toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus infection, listeriosis, etc.) and toxic( with sepsis) hepatitis.Frequently flow subacute, less often manifest sharply.The baby turns yellow or immediately at birth, or within the first 2-3 weeks.Jaundice remains from 2-3 weeks to 2.5-3 months.The urine becomes dark, the stool loses color, the liver is enlarged and compacted.There is bloating, vomiting, and neurologic symptoms.There may be a hemorrhage.
Mechanical or obstructive jaundice:
- Congenital causes:
- biliary tract malformation with complete obstruction or narrowing of the lumen.The outflow of bile is broken, bilirubin penetrates into the blood, inflammation begins in the bile ducts.Jaundice is determined from the first days of life, the skin gradually acquires a greenish shade, the feces become discolored, the urine darkens.The liver is dense, enlarged in size, veins visible on the abdomen.With atresia of extrahepatic bile ducts to prevent the development of liver cirrhosis the child is shown surgical treatment in 1.5-2 months;
- cystic fibrosis and other hereditary diseases, such as hemochromatosis, Niemann-Pick disease, Celebger syndrome, Caroli disease, etc. In cystic fibrosis, for example, blockage of bile ducts is accompanied by thick mucus.
- Acquired causes:
- Hypoplasia or atresia of the bile duct due to perinatal hepatitis;
- bile thickening syndrome, when ducts are clogged with slimy plugs.It often develops as a complication of jaundice with increased production of bilirubin;
- Other causes: of the cyst of the common bile duct, tumor compression, stones in ducts, etc.
YELLOW OF NEWBORNS: CONSEQUENCES OF
The danger of jaundice is primarily a high toxicity of indirect bilirubin.This substance penetrates the brain at a certain concentration of bilirubin in the blood( 400 μmol / l - in full-term, from 150 to 170 μmol / L - in preterm), and, accumulating in some of its nodes and nuclei, destroys nerve cells.This is a nuclear jaundice, which often acts as a complication of HDN.
The first signs of a nuclear jaundice in a newborn are:
- weak sucking, regurgitation and even vomiting;
- decreased muscle tone and frequent yawning;
- weak reflexes and lethargy.
Gradually the clinic grows: there are stops of breathing, immobility, lack of reflexes is replaced by spasm of muscles, neurological symptoms are expressed.After some improvement in the condition of the baby( at 3-4 weeks of age), severe bilirubin encephalopathy is formed at the age of 3-5 months: paralysis, paresis, hearing impairment, delayed psychomotor development, etc. The consequences of nuclear jaundice can cause disability of the child.According to statistics from a hundred newborns with a diagnosis of nuclear jaundice, two children die.
The main task facing neonatologists is to prevent a child with hyperbilirubinemia from developing nuclear jaundice.Without a constant control of the level of bilirubin in the blood it is very difficult.Therefore, the mother of the "yellow" baby should not be surprised and even more outraged, when laboratory workers come to the ward not once a day and take blood from the child for research.The concentration of bilirubin in the blood is also the most important criterion for choosing the method for treating jaundice.
Can neonatal jaundice be treated?It is possible only if the bilirubin level is raised very slightly, and the overall well-being of the baby does not suffer, which in most cases is characteristic of physiological jaundice.
But even in this situation the child is constantly observed by the doctor of the maternity hospital and the district pediatrician after discharge from the hospital.And the mother must feed the baby with the breast, drink it more with water and "catch" sunny days for walking.
METHODS OF TREATMENT OF YELLOWS IN NEWBORN
In case of jaundice of newborns, the physician selects the treatment individually for each child.Tactics depends primarily on the severity of hyperbilirubinemia, on the severity of the condition of the baby and on the diagnosis diagnosed( HDN, hereditary disease, etc.).
Phototherapy
The first thing that jaundice is treated with is phototherapy.Phototherapy of newborns is an effective method of treatment based on the fact that in the skin under the influence of light with a wavelength of 440-460 nm the toxic form of indirect bilirubin turns into nontoxic water-soluble forms.
The smaller the body weight of the newborn, the less the bilirubin content in the blood, the irradiation begins.So, to children weighing 2.5 kg or more, light treatment begins at a bilirubin level of 255-295 μmol / l, and children with body weight less than 1.5 kg - already at 85-140 μmol / l.
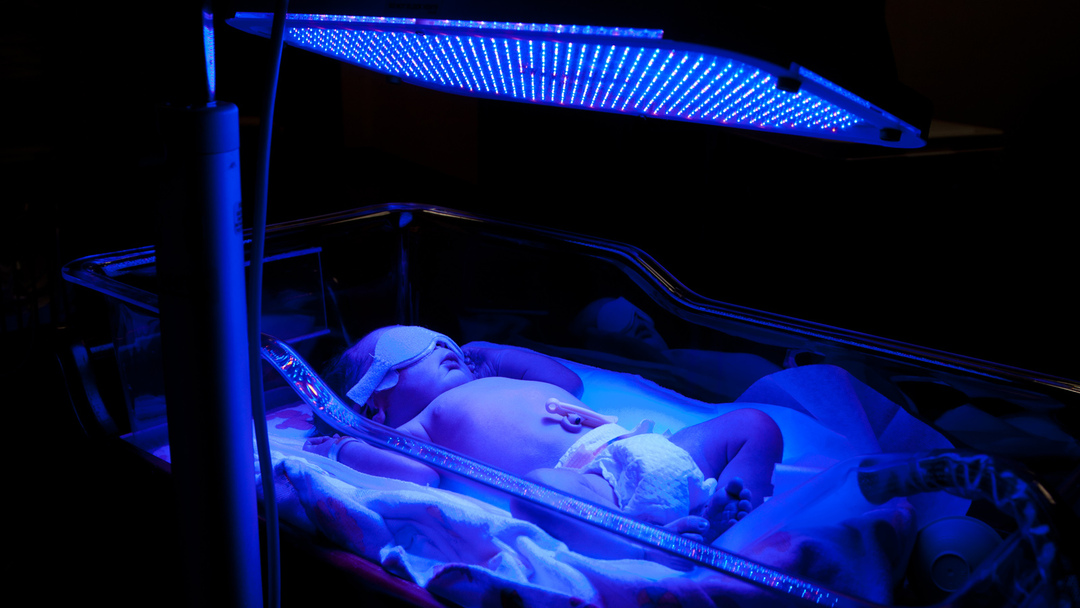
Special lamps are used for phototherapy of newborns.The lamp for the treatment of jaundice can be blue, green or blue.The toddler is put nude in a kuvez, where he is under a lamp to treat jaundice at least 12 hours a day.In this case, the area of the gonads and eyes protect from exposure to the rays.
The duration of the phototherapy course is determined not by hours or days, but by the results of a biochemical blood test.As soon as the concentration of bilirubin in the child's blood returns to the physiological norm for his age, irradiation is canceled.
Phototherapy does not cause any harm to the health of the newborn.But provided that it is conducted in a medical institution, where the doctor determines the regime of the child's stay under the lamp, constantly monitors the weight of the child's body, tracks the dynamics of hyperbilirubinemia and other laboratory indicators.
When after the discharge from the maternity home the parents of the baby are engaged in amateur activity and, having obtained a lamp for phototherapy, begin to "treat" jaundice themselves, the risk of the child's overheating and dehydration increases at times!Will you take risks?Or stop being lazy and start walking with the baby to the procedures in the clinic?
 There are strict criteria for the planned and emergency OZPK:
There are strict criteria for the planned and emergency OZPK:
- laboratory is the level of bilirubin in cord blood at birth and its hourly gain with phototherapy or without it, the concentrationHemoglobin and others;
- clinical - proven sensitization in a woman and signs of severe HDN in her baby, the appearance of symptoms of intoxication with bilirubin.
 Blood components for transfusion physicians are selected strictly for the individual newborn and the type of incompatibility of the mother's blood and blood of the child.
Blood components for transfusion physicians are selected strictly for the individual newborn and the type of incompatibility of the mother's blood and blood of the child.
The OZPK is performed after carrying out the compatibility tests through a catheter mounted in the umbilical vein.Even with perfectly matched material for surgery and sterility observed during surgery, complications such as cardiac dysfunction, air embolism, thrombosis, infection, anaphylactic shock and some others are not excluded.Therefore, within three hours after OZPK, the medical staff does not take their eyes off the child.
Infusion therapy
Infusion therapy with solutions of glucose and sodium chloride is carried out to relieve intoxication, accelerate the binding and excretion of bilirubin from the child's body.If the blood content of the child is reduced protein content, apply a solution of albumin.
Medical treatment
The drug treatment is aimed at activating the binding of bilirubin in the liver and on its adsorption in the intestine.
Popular about 15 years ago, phenobarbital, activating the binding system of the liver, is not currently used in the period of newborn.It begins to act only after 4-5 days from the beginning of admission, so it is used for prolonged jaundice.Instead, it is prescribed zixorin.
Carboline, agar-agar and cholestyramine are used, adsorbents that release intestinal bilirubin.Sometimes they are supplemented by cleansing enemas.To stabilize the liver cell membranes, ATP and vitamins are prescribed, to maintain the vital activity of hepatocytes - riboxin and essential( hepatoprotectors).To prevent the development of hemorrhagic syndrome use etamzilate, dicinone or adroxone.
Cholagogue drugs are prescribed inside( magnesium, allochol), and in the form of electrophoresis( magnesia) on the right hypochondrium.
Mothers of newborns are often "afraid" of drug therapy prescribed for their "yellow" children.Even if the drugs have some side effect on the body, the harm from it is negligible compared to the impact that the baby can inflict on bilirubin intoxication.And in this regard, you should not worry.
Zaluzhanskaya Elena Aleksandrovna, pediatrician, medical reviewer