Omphalit
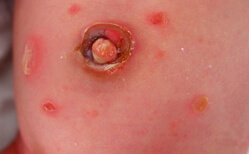 Omphalit is a multifactorial pathological process of the navel area that affects the skin, the underlying subcutaneous layer, while the blood, lymphatic vessels can be affected. More often umbilical omphalitis affects infants in the first days of life. In modern realities, severe forms of the disease with complications occur sporadically. This is due to the active methods of preventing hospital infections, the transition to a "dry" treatment of the umbilical stump. In adults, inflammation of the periapical region is rare. The course of the process is easy, and adequate, timely treatment brings effect in a short time. Bacterial omphalitis refers to surgical diseases, with the development of severe forms of omphalitis, surgery is sometimes required. It will help to avoid this knowledge of the causes, characteristic symptoms, methods of treating the inflammation of the navel area.
Omphalit is a multifactorial pathological process of the navel area that affects the skin, the underlying subcutaneous layer, while the blood, lymphatic vessels can be affected. More often umbilical omphalitis affects infants in the first days of life. In modern realities, severe forms of the disease with complications occur sporadically. This is due to the active methods of preventing hospital infections, the transition to a "dry" treatment of the umbilical stump. In adults, inflammation of the periapical region is rare. The course of the process is easy, and adequate, timely treatment brings effect in a short time. Bacterial omphalitis refers to surgical diseases, with the development of severe forms of omphalitis, surgery is sometimes required. It will help to avoid this knowledge of the causes, characteristic symptoms, methods of treating the inflammation of the navel area.
Omphalitis: causes of
The main cause of omphalitis is the attachment of a pathogenic bacterial infection. For the occurrence of this, factors predisposing to inflammation must be present. In newborns, it can be:
- decreased immunity, thin and vulnerable skin, due to prematurity, immaturity, smallness;
- superfluous loose subcutaneous fat layer in large-sized;
- catheterization of umbilical cord vessels exceeding 3 days if it is performed without observing asepsis rules( for resuscitation, blood transfusion, infusion therapy, other medical procedures);
- infectious skin diseases( pemphigus, vesiculopustulosis, erysipelas, phlegmon);
- purulent processes of internal organs( osteomyelitis, meningoencephalitis, pneumonia);
- non-observance of the principles of the heat chain( the child did not lay out on the mother's abdomen), the absence of a joint stay of the mother with the child after childbirth;
- a large number of caring staff, non-compliance with health standards by medical personnel;
- treatment of the umbilical cord with alcoholic antiseptics without indications;
- poor social and living conditions at home, poor care of an infant;
- bacterial infections during pregnancy and during labor in the mother;
- prolonged abaissement of the umbilical stump with congenital hypothyroidism;
- full and incomplete navel fistulas.
To the emergence of omphalitis in adults predispose:
- inflammatory, pustular skin diseases;
- injuries to the navel area of traumatic origin( scratches, brushing, cuts, nyxes);
- irritation of the umbilical region with close clothing, buttons, belt buckle;
- inadequate hygiene in the anatomy of the navel( deep, knobby umbilicus);
- piercing, scarring, tattooing;
- inflammation of postoperative sutures or punctures;
- fistulas in the peri-oophoric region;
- obesity, metabolic syndrome;
- diabetes mellitus.
In the presence of predisposing factors cause omphalitis:
- gram-negative bacteria( proteus, Klebsiella, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli);
- Gram-positive bacteria( strepto- and / or staphylococci);
- fungal infection caused by candida;
is an anaerobic flora.
The causative agent of omphalitis, getting into the place of damage or in the umbilical cord penetrates into the skin and subcutaneous layer, causing a pathological response there. In this case, if there is no or ineffective treatment, consistently there is a productive, purulent and necrotic inflammation. Fixing on the walls of blood vessels, microbes affect them, phlebitis and arteritis occur. Penetrating the umbilical vein into the interior, the infection can cause abscesses along the intrahepatic veins. The purulent process persists even after the cure of the omphalitis itself.
Omphalitis: Symptoms and Signs
Omphalitis can occur as a primary process if the infection immediately enters the navel and as a secondary one, if there is another purulent focus and the pathogen with the blood stream enters the umbilical region.
There is no established classification of omphalitis in clinical practice. Conventionally, several types of pathological process are distinguished, they are also consecutive stages of inflammation development.
Catarrhal omphalitis, it is also a "wetting" navel. It is characterized by:
- slight reddening( hyperemia) of umbilical cord skin;
- light mucous ungulate detachable;
- body temperature is not increased;
- does not suffer;
- periodically formed a light crust, under which are located granulation( fresh connective tissue);
- there are no changes in the blood test.
This stage of development of omphalitis is well amenable to local therapy. If treatment does not start on time, purulent omphalitis will develop. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- increased redness of the umbilical ring;
- the discharge becomes cloudy, yellow-green, an admixture of blood may appear;
- the crust becomes dark and dense;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- the condition does not deteriorate, but the child may have anxiety;
- body temperature can rise to 37.5 ° C;
- in blood tests there may be a slight leukocytosis( an increase in the level of white blood cells).
If, with a purulent process, treatment is not initiated or proved to be ineffective, omphalitis passes into a phlegmonous stage. Phlegmonous omphalitis is manifested:
- the exit of hyperemia beyond the umbilical ring;
- the tissues around the navel are edematous, raised, feel hot;
- when inflammation of the lymphatic vessels on their skin, red bands are detected on the skin;
- the venous pattern on the abdomen becomes more pronounced;
- palpation of the navel region is painful;
- at the bottom of the umbilical wound in newborns are identified sores with dented edges;
- detachable copious purulent, creamy, dark brown, fetid;
- body temperature becomes higher than 38 ° C;
- symptoms of intoxication are expressed( weakness, weakness, headaches, loss of appetite);
- babies become capricious, restless or lethargic, sleep badly, give up breast, lose weight, regurgitation and loose stools appear;
- the skin becomes pale with an earthy tinge;
- in blood tests expressed leukocytosis, neutrophilia( high level of neutrophils), shift of blood formula to the left to young forms - indicators of bacterial inflammation, increased ESR;
- with ultrasound is determined by edema of tissues, inflamed vessels.
The next stage is necrotizing omphalitis. In adults it is extremely rare. It occurs in premature infants and severely weakened babies. It appears that:
- inflammation goes deep into tissues;
- the skin in the vast focus of inflammation becomes crimson-cyanotic, sharply edematous and begins to exfoliate layers;
- the underlying tissues( muscles, fascia, peritoneum) begin to tear away, deep wounds are formed, into which the intestine can exit;
- the condition is severely disrupted, right up to the coma;
- body temperature above 39 ° C;
- in the analyzes a pronounced inflammatory reaction.
If omphalitis is not treated in a timely manner, complications such as:
- dermal fistula;
- peritonitis( inflammation of the peritoneum);
- abscesses( pus accumulation) of different localization;
- pneumonia( inflammatory process in the lungs);
- meningoencephalitis( inflammation of soft membranes and brain substances);
- osteomyelitis( inflammation in the bone marrow of the bone marrow);
- enterocolitis( inflammation of the intestine);
- sepsis, when the infection enters the bloodstream.
Differential diagnosis in omphalitis is carried out with erysipelas and phlegmon. Phlegmon of the newborn is caused by staphylococcus, inflammation localized on the lateral, posterior surface of the thorax, less often on the buttocks. The disease begins with the appearance of a stain around the affected sweat gland, which in a short time increases in size. The course of the process is similar to phlegmonous omphalitis. The difference is that with phlegmon the tissues of the umbilical cord are not involved in the process, and if the lesion affects the navel region, it is only secondary.
Newborns have an erythematous form of erysipelas that is caused by streptococci. With it, the skin of the lower abdomen, the groin area is involved in the process. In a place of typical localization, a bright-burgundy foci of inflammation appears. The edges of the affected area are uneven, resembling flames. The skin is edematous, displaced in relation to the underlying tissues, the surface is shiny. During the resolution of the process, the skin is returned to its former color, and the peeling remains on the site of inflammation, which eventually disappears. The umbilical region, unlike omphalitis, is usually not involved in the process.
Omphalitis in newborns
In the concept of omphalitis in a newborn, in addition to the forms described, the following conditions are included: fungus of navel, phlebitis and arteritis of umbilical cord, gangrene of umbilical cord.
Fungus navel - a bright red mushroom formation located on the bottom of the umbilical wound. It is formed as a result of proliferation of connective tissue( granulation), which occurs with a "wet" navel. The child does not affect the general condition and well-being.
Inflammation of the umbilical cord often occurs when they are catheterized. Inflammation of the vein( phlebitis) is defined as a tight cord from above over the umbilical ring, when pus pressure is applied, pus is released at the bottom of the umbilical wound. When the arteries are inflamed, the dense strands stretch radially below the navel. The skin over the inflamed vessels is hyperemic, edematous. Defined symptom Krasnobaev( muscles of the abdominal wall tense at palpation).The condition, in most cases, is not violated, but sometimes the child is listless.
The gangrene of the umbilical cord is not encountered during childbirth in a medical institution. When anaerobic flora joins, the umbilical cord becomes wet, dirty-brown, sticky and fetid. With this form of omphalitis, sepsis inevitably develops.
An important point in the diagnosis of inflammation of the umbilical wound in catarrhal omphalitis is the exclusion of the fistula of the navel. If the yolk duct is not flushed out of the navel in a timely manner, intestinal contents may be released. When urinary duct( urachus) is not enlarged, urine expires. There is a constant irritation of the tissues and inflammation occurs. For diagnosis, sounding is used. In the course of the probe, it is determined where the fistulous opening leads.
An important fact remains the traumatization of the perepuscular region. Treating the stump of the umbilical cord with alcohol-containing antiseptics, if they get on the baby's skin, you can cause a chemical burn that will provoke omphalitis. A thermal burn in the area of the umbilical ring may occur when it is washed away when the water temperature is not adjusted. Also, the cause of a burn can be the application of a hot diaper or a warmer in infantile colic. These factors increase the susceptibility of the skin to the attachment of pathogenic flora.
Newborns are more susceptible to developing omphalitis, because among other things, the gateway for infection is the unhealed umbilical wound. For this reason, much attention is paid to the cultivation of the umbilical cord stump. Earlier, the remainder of the umbilical cord and umbilical wound were routinely treated with antiseptic solutions daily. But according to the new guidelines for the administration of the umbilical cord, based on the methods of evidence-based medicine, the "dry" method is increasingly used in the departments of newborns.
The method of "dry" cultivation of the umbilical cord is based on the fact that its mummification( drying) occurs naturally, through exposure to air. It is important to ensure the cleanness of the stump( if soiled, it is wiped off with a gauze swab dipped in water and dried) and free air access( tucking in the diaper, free swaddling, air baths).This method helped to reduce the incidence of omphalitis in newborns at times.
Omphalitis in adults
Inflammation of the umbilical region in adults is rare. The cause of omphalitis development is often navel piercing. When an inflammation occurs in omphalitis, it is taken for a normal reaction after a puncture and therefore treatment begins already with a purulent process.
Omphalitis in adults may occur against the background of entero-or colostrums that have been removed to the anterior abdominal wall( with severe intestinal diseases).Often, the cause of the purulent process are postoperative sutures, especially with regard to hernia operations.
The course of omphalitis in adults is much easier than in children. But with phlegmonous omphalitis, there may be an intoxication syndrome, the state of health worsens, there is a sharp pain in the place of inflammation, interfering with daily activities. In the absence of treatment, adults may also develop purulent-septic complications. With necrotic form on the lesion, after healing, remains a rough scar tissue.
Especially dangerous is omphalitis for:
- elderly weakened people;
- having clinical manifestations of AIDS;
- pregnant;
- oncological patients undergoing treatment with cytostatics;
- people receiving glucocorticosteroids in high doses.
Omphalitis: treatment of
Timeliness of omphalitis therapy provides a favorable further prognosis. Treatment of the disease should be comprehensive and continue until full recovery. An important aspect of omphalitis therapy is the determination of the pathogen and the spectrum of its sensitivity to the available antibacterial drugs. To do this, it is necessary to sow the separated navel. The basis of therapeutic measures is local and systemic effects on the pathogen.
With catarrhal and purulent omphalitis treatment can be carried out at home, provided the patient feels well. In other forms, admission to a pediatric or surgical department is mandatory. In the treatment of omphalitis use:
- for newborns daily hygienic bathing in a bath with the addition of a solution of potassium permanganate( 1: 10000), chamomile, marigold, turn or celandine infusion;
- local therapy of omphalitis is carried out with antiseptic solutions three times a day first with 3% hydrogen peroxide, then with 5% iodine solution or 2% with brilliant green. This mixture proved to be very successful: dilute 1 ml of brilliant greens and methylene blue to 10 ml with 70% ethyl alcohol;
- application of ointments with Bacitrocin or Mupirotsin( Bactroban), Levomecoli, Vishnevsky;
- antibacterial therapy with a wide spectrum of action. In newborns, Oksacillin is used together with Gentamycin, clavulan-protected aminopenicillins, cephalosporins;
- with phlebitis and arteritis in omphalitis, the areas above the inflammation are treated with heparin or troxerutin ointment alternating every 2 hours with Bactroban;
- immunotherapy for staphylococcal infection with anti-staphylococcal immunoglobulin;
- infusion-transfusion therapy if necessary, in terms of severity parenteral condition( bypassing the digestive tract, intravenously) nutrition;
- vitamins, in particular vitamins A, C and group B;
- surgical treatment in adults in the case of purulent and phlegmonous omphalitis, is performed as follows: an abscess is opened, pus is excreted by a special probe and further treatment is performed at home. In newborns in the case of gangrene of umbilical cord, it is immediately cut off. In the presence of fistulous moves, their excision is performed. With necrotic omphalitis, the wound is cleared from anesthetized tissues;
- physiotherapy( UHF, UHF, UFO, electrophoresis with antibacterial drugs).
An important aspect in the fight against omphalitis is the prevention of its occurrence. For this purpose, you can use:
- careful hygienic skin care, especially around the navel;
- for newborns, the umbilical cord should be treated in a "dry" manner, in the absence of indications for treatment with antiseptic agents;
- since birth, to establish skin-to-skin contact with the mother, to colonize the skin and the umbilical cord with the saprophytic flora of the mother's skin, the initiation of breastfeeding in the first minutes of life, the joint stay with the mother;
- adherence to anti-epidemic norms and regulations by medical personnel;
- providing proper skin care for the baby at home( bathing, washing, timely diaper changing, prevention of diaper rash, control of the skin around the navel, air baths, clean underwear);
- strengthening the body's defenses;
- adults are recommended to wear free natural clothes that do not injure the navel area, refusal of piercing, tattooing, scarring.
Omphalitis is a microbial infection that can cause severe purulent and septic complications, especially in infants. For its occurrence, a combination of predisposing factors and penetration of the infectious agent into the umbilical region is necessary. A bright characteristic symptomatology allows you to accurately diagnose and start treatment in time. The therapy of omphalitis is not complicated, with its timely beginning. Observance of preventive measures allows keeping the incidence of omphalitis at a low level.



