Tularemia: symptoms in humans, treatment
Tularemia refers to an acute natural focal infection that affects mainly the lymphatic system and the skin.In some cases, respiratory organs, mucous membranes of throat and eyes suffer.The course of the disease is accompanied by a long fever, general intoxication of the body, lymphadenitis, the appearance of rash, hepatosplenomegaly( simultaneous increase in the spleen and liver) and other signs.
Tularemia is an acute infection of bacterial etiology, which is manifested by severe fever, lymphadenitis, and cutaneous manifestations at infection sites.
Table of contents: Forms of tularemia Symptoms of tularemia in humans Diagnostic measures Treatment of tularemia ProphylaxisForms of tularemia
Tularemia is diagnosed during skin-allergic test, polymerase chain reaction, various serological reactions.The treatment is divided into a conservative one, which includes a set of measures to combat intoxication and carrying out antibacterial therapy, and surgical, which consists in opening the bubonic nodes and installing drains.
The types of this disease are classified as follows:
- By the method of infection, subdivide into pulmonary, ulcerative-bubonic, generalized, anginal-bubonic, bubonic, abdominal, globose-buffered forms.
- Degrees of severity of the disease: severe, moderate, mild.
- According to the duration of the course: prolonged, acute, recurrent.
Natural foci of tularemia are located mainly in the northern hemisphere, in the territory of the Russian Federation the bulk of the outbreaks is in Western Siberia and the European part of Russia.Epidemiologists tularemia is included in the list of especially dangerous infections.
Please note! Tularemia is caused by Francisella tularensis - aerobic gram-negative rod bacterium.This pathogen differs enviable tenacity.The death of tularemia bacillus occurs when exposed to disinfectants and high temperature.
 Wild animals and birds are a natural source of infection.Most often, rodents( muskrats, voles, chipmunks, etc.) are infected, but larger animals( sheep, dogs, foxes, hares, etc.) can become infected.A pathogen is not transmitted from a sick person.With the transmissive mechanism of transmission of the pathogen, the animals become infected with bites of ticks and other bloodsuckers.
Wild animals and birds are a natural source of infection.Most often, rodents( muskrats, voles, chipmunks, etc.) are infected, but larger animals( sheep, dogs, foxes, hares, etc.) can become infected.A pathogen is not transmitted from a sick person.With the transmissive mechanism of transmission of the pathogen, the animals become infected with bites of ticks and other bloodsuckers.
Infection of people occurs with direct contact with sick animals, for example, during skinning or carcass cutting, or when eating food and water contaminated with tularemia bacillus.
Infection can enter the human body and respiratory tract - in simple terms, in various agricultural industries a person can inhale dust contaminated with bacteria.When the causative agent of tularemia enters the human body, the development of the disease is inevitable.
Symptoms of tularemia in humans
Tularemia has a fairly vague incubation period that lasts from one day to one month, but, as a rule, the symptomatology manifests itself during the first week.Initially, a sharp increase in body temperature, up to forty degrees.Against the background of increased temperature, the symptoms of intoxication of the body increase in the form of severe head and muscle pain, general weakness.The fever can keep as constantly, and proceed in the form of two, three waves.The patient usually has a fever of up to three weeks, but in some cases this condition can last up to three months.
During the initial examination of the patient, reddening of the face, eye sclera, mucous membranes of the nasopharynx and oral cavity is observed.There may be a slight swelling of the skin and an injection of the sclera, in which the eyes turn red.Arterial pressure is lowered, the heartbeat is slow.A few days after the onset of fever, the liver and spleen are simultaneously enlarged, and rashes of various types may appear on the skin.
Depending on the method of infection, the clinical picture of the disease also differs:
-
 When the infection penetrates through the skin, a bubonic form develops, which is nothing more than regional lymphadenitis.Any lymph nodes can be affected: they grow up to the size of a chicken egg, with palpation there is soreness, which gradually fades to nothing.For several months, buboes dissolve or become inflamed, turning into an abscess, which later breaks through, forming a fistula.
When the infection penetrates through the skin, a bubonic form develops, which is nothing more than regional lymphadenitis.Any lymph nodes can be affected: they grow up to the size of a chicken egg, with palpation there is soreness, which gradually fades to nothing.For several months, buboes dissolve or become inflamed, turning into an abscess, which later breaks through, forming a fistula. - In case of vector-borne infection, the ulcerative-bubonic form develops.At the site of penetration of pathogenic bacteria appears an ulcer with a dark bottom, swollen edges, in shape similar to a cockade.The healing process takes a very long time.Against this background, there is regional lymphadenitis.
-
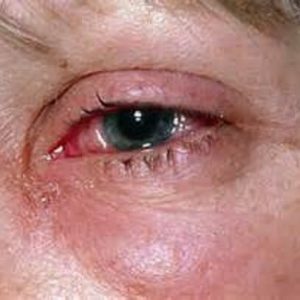 If the tularemia rod penetrates the mucous membrane of the eye, an eyeball-shaped form appears in the form of ulcerative purulent conjunctivitis.First, there are symptoms of inflammation( swelling, redness, a feeling of sand in the eye, pain), then erosion and small ulcers with purulent discharge.Corneal lesions, as a rule, are not observed.Treatment of this type of tularemia is very difficult and takes a very long time.
If the tularemia rod penetrates the mucous membrane of the eye, an eyeball-shaped form appears in the form of ulcerative purulent conjunctivitis.First, there are symptoms of inflammation( swelling, redness, a feeling of sand in the eye, pain), then erosion and small ulcers with purulent discharge.Corneal lesions, as a rule, are not observed.Treatment of this type of tularemia is very difficult and takes a very long time. - When the infection enters the body through the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx, an anginous-bubonic form of tularemia arises.In such a case, a person becomes infected through infected food and water.Initial symptoms strongly resemble angina: there is difficulty swallowing( dysphagia), pain in the pharynx, tonsils swelling and blush, covered with a gray, hard to remove plaque.In later stages of the disease, tonsil tissues begin to die, forming ulcers, after the healing of which remain rather coarse keloid scars.From the side of the aching amygdala there is lymphadenitis of cervical, submandibular and parotid lymph nodes.
- Abdominal form occurs when the causative agent is affected by the lymphatic vessels of the mesentery of the intestine.The main symptoms are nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, intestinal distress in the form of diarrhea.With a prolonged course of the disease, weight loss is observed.When palpating the abdominal cavity pain sensations are localized in the umbilical region, palpated liver and spleen are probed.
- As a result of inhalation of the infected dust, a pulmonary form develops, which takes place in the pneumonic or bronchogenic variant.In the bronchial variant, bronchial, paratracheal mediastinal lymph nodes suffer.Symptom is manifested in the form of moderate pain behind the sternum, dry cough, signs of intoxication.This form of tularemia is the easiest, in which the patient usually recovers after about two weeks.
- Pneumonic appearance is much heavier, resembling focal pneumonia, often complicated by pleurisy and bronchiectasis.In especially neglected cases, abscesses, caverns, possibly even the onset of pulmonary gangrene.
The most severe form of tularemia is the generalized form.Its course is very similar to septicemia, or typhoid and paratyphoid infections.There is pronounced intoxication, prolonged, improperly remitting, fever, severe muscle and headaches, dizziness, confusion, hallucinations, delusions.
Complications occur, as a rule, in the generalized form of tularemia.The most common complication is secondary pneumonia.Perhaps the emergence of arthritis, meningitis, meningoencephalitis, pericarditis and even infectious-toxic shock.
Diagnostic measures
It is possible to diagnose tularemia only with the help of laboratory tests.
Nonspecific laboratory methods are general tests of urine and blood.These studies will directly indicate the presence of inflammation and intoxication in the body.At the initial stage of the disease, a general blood test will show neutrophilic leukocytosis, with time the number of leukocytes decreases, and the concentration of monocytes and lymphocytes increases.
 Specific serological diagnosis is performed using the indirect hemagglutination reaction and the direct agglutination reaction. In the process of development of the pathological process, the growth of the titer of specific antibodies is fixed.After a week after the manifestation of the disease, it is necessary to carry out immuno-fluorescent analysis, which is the most sensitive serological test for tularemia. For early diagnosis, a polymerase chain reaction is used, which allows to reveal pathology literally in the first days.Skin and allergic test with tularemic toxin shows the disease in the first week.
Specific serological diagnosis is performed using the indirect hemagglutination reaction and the direct agglutination reaction. In the process of development of the pathological process, the growth of the titer of specific antibodies is fixed.After a week after the manifestation of the disease, it is necessary to carry out immuno-fluorescent analysis, which is the most sensitive serological test for tularemia. For early diagnosis, a polymerase chain reaction is used, which allows to reveal pathology literally in the first days.Skin and allergic test with tularemic toxin shows the disease in the first week.
Important! Bacteriological seeding for the detection of the causative agent of tularemia is practically not used, as it is rather difficult to isolate bacteria from biomaterials and blood.
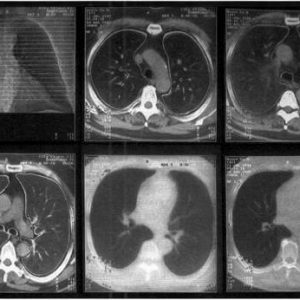
To confirm the pulmonary form of the disease, a computerized tomography of the lungs is used, in the absence of a tomograph, it is possible to perform an X-ray examination of the lungs.
Treatment of tularemia
 Due to the fact that tularemia belongs to the category of especially dangerous diseases, its treatment is performed in conditions of the infectious hospital .To destroy the pathogen in the body, antibiotics of a wide spectrum of action( gentomycin, kanamycin, doxycycline) are prescribed.In case of ineffectiveness of the prescribed treatment, second-line antibiotics( rifampicin, levomycetin, third generation cephalosporins) are prescribed.
Due to the fact that tularemia belongs to the category of especially dangerous diseases, its treatment is performed in conditions of the infectious hospital .To destroy the pathogen in the body, antibiotics of a wide spectrum of action( gentomycin, kanamycin, doxycycline) are prescribed.In case of ineffectiveness of the prescribed treatment, second-line antibiotics( rifampicin, levomycetin, third generation cephalosporins) are prescribed.
With severe intoxication, infusion detoxification therapy is performed.Appoint antipyretic, antihistamine, anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins.Open sores on the skin are closed with bandages.Bubbons subjected to suppuration are opened by surgical methods followed by drainage.
Prevention
 Important! The main method of prevention is vaccination of people with tularemia vaccine in epidemic disadvantaged areas.Persistent immunity persists for up to seven years, so re-vaccination is given after five years.If there is a threat of an epidemic, emergency prevention is possible by injecting antibiotics intravenously.
Important! The main method of prevention is vaccination of people with tularemia vaccine in epidemic disadvantaged areas.Persistent immunity persists for up to seven years, so re-vaccination is given after five years.If there is a threat of an epidemic, emergency prevention is possible by injecting antibiotics intravenously.
Anti-epidemic measures include suppression of possible ways of transmission of the pathogen of tularemia and disinfection of sources of infection.In epidemic disadvantaged areas, in agricultural enterprises and catering facilities, a full range of measures to combat the spread of infection( disinfection, disinsection, deratization) is carried out.
Special attention should be given to individual protection from the causative agent of tularemia for people engaged in hunting for wild animals, especially in the process of skinning and carcass splitting and persons taking part in deratization activities in the collection of rodent bodies.Hands are necessarily protected by rubber gloves, after removal of which, it is absolutely necessary to conduct disinfection of the skin.Water should only be used from reliable, trusted sources.
If the patient becomes diagnosed with tularemia, then all the things that could have been contaminated must be disinfected.
Tularemia is a dangerous disease that requires compulsory treatment.Only constant monitoring of the patient by the doctors and correctly conducted therapy ensure complete recovery without complications.
Konev Alexander.Therapist