Anthrax Treatment
 Anthrax is a common virus among livestock and wild animals. This article describes the causes and symptoms of the disease, as well as the treatment of ulcers.
Anthrax is a common virus among livestock and wild animals. This article describes the causes and symptoms of the disease, as well as the treatment of ulcers.
What is anthrax?
Anthrax is an acute infection caused by spore-forming bacteria Bacillus. Anthrax is most common among wild animals, domestic cows, sheep, goats, camels, antelopes and other herbivores. However, people can get sick by contact with infected animals or through their wool.
How common is anthrax?
Anthrax is more common in agricultural areas. Human contact with anthrax can occur in workplaces where people handle dead animals and animal products from other countries.
How does anthrax spread?
Anthrax spores of Bacillus can live in the soil for many years. Anthrax bacteria can penetrate the skin( dermal form of anthrax), poorly cooked meat of the animal, thereby the bacteria enter the gastrointestinal tract( intestinal anthrax), or through the nose and mouth( pulmonary form of anthrax):
- Skin form of the SiberianUlcers:
most anthrax infections( 95 percent) occur when bacteria get through a cut on the skin. Infection often occurs when working with contaminated wool, skins, skin or products of animal origin.
- Intestinal form of anthrax:
The use of undercooked meat from infected animals can cause acute inflammation of the intestinal tract.
- Pulmonary Anthrax:
Anthrax infection can occur when a person inhales spores from contaminated animal products.
Anthrax is not contagious when it comes to people's contact, at least the risk of infection is very small.
What are the symptoms of anthrax?
The following are the most common symptoms of anthrax. However, each person can experience symptoms in different ways. Symptoms may include:
When the cutaneous form of anthrax is :
- Infection begins as an increase in itching and redness of the skin.
- For one or two days, blisters develop on redness( small blisters), followed by a painless ulcer, which is from 1 to 3 centimeters in diameter. The ulcer has a characteristic black color.
- Lymph nodes in this area are expanding.
Intestinal form of anthrax :
- Usually the disease begins with nausea, and then there is loss of appetite, vomiting and fever. Pain in the abdomen is often accompanied by vomiting of blood and severe diarrhea.
Pulmonary form of anthrax :
- Symptoms can begin as with a cold, and after a few days leads to serious problems of breathing and shock.
Symptoms of anthrax may resemble other diseases or problems. Always consult your doctor for diagnosis.
Diagnosis of anthrax
Anthrax diagnosis will include the detection of bacteria from the blood, skin or respiratory tract. Disease can also be diagnosed with special blood tests used to measure specific antibodies in the blood in individuals with suspected exposure.
Anthrax treatment
When treating anthrax, a doctor will be guided based on your age, general health and medical history.
Treatment of anthrax with antibiotics is the most effective way when the disease only progresses. If individuals suffer from anthrax, antibiotics will be prescribed to prevent further spread of the infection. Listed below are antibiotics for the treatment of anthrax:
- ciprofloxacin
- penicillin
- doxycycline
In the absence of treatment, anthrax of all three forms leads to death.
Prevention of anthrax
To prevent infection, people should avoid contact with livestock and animal products, and there is only carefully cooked meat.
Anthrax vaccine
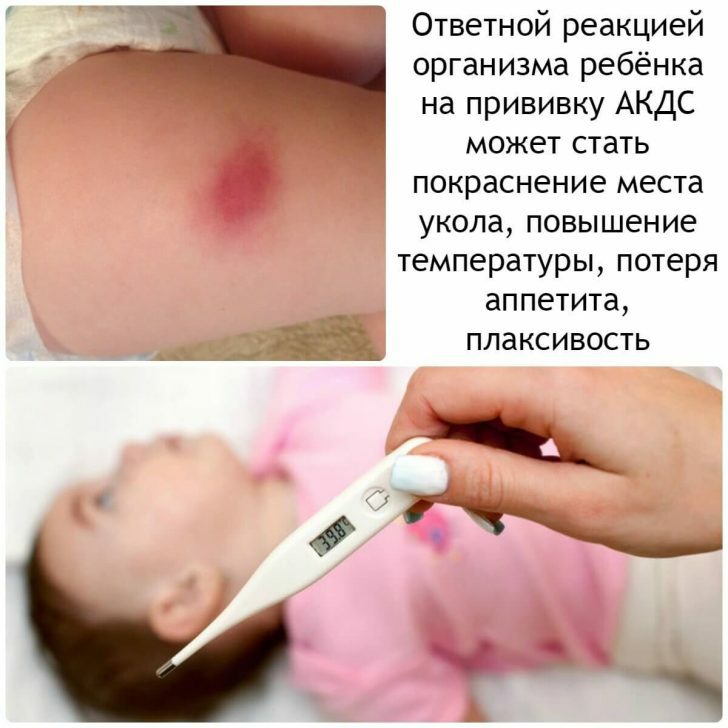
An anthrax vaccine exists and is reportedly effective at 93 percent. A cell-free filtrate vaccine, which means that it does not contain dead or live bacteria. Injection is carried out for 18 months with six doses of the vaccine. After that, annual revaccinations are recommended. Almost one-third of those vaccinated can experience mild local reactions to infection. Severe reactions are rare. The injection is carried out for the following groups:
- People who work in laboratories directly with anthrax
- People who work with imported animals or fur
- People working with potentially infected animal products, such as veterinarians
- Servicemen who serve in the field, Where there is a high risk of infection with
Pregnant women should be vaccinated only in case of emergency.