Periodontitis of the tooth: its types, symptoms, diagnosis and complications
 Almost everyone knows about the need to visit the dentist at least once every 6-12 months for the purpose of prevention.However, few people adhere to this rule: permanent employment, lack of time, etc. And the dentist's office itself is not a pleasant place. ..
Almost everyone knows about the need to visit the dentist at least once every 6-12 months for the purpose of prevention.However, few people adhere to this rule: permanent employment, lack of time, etc. And the dentist's office itself is not a pleasant place. ..
So it turns out that we are applying for help not at the last stages of development of any dentalA disease, one of which is periodontitis.
What is periodontitis: Species
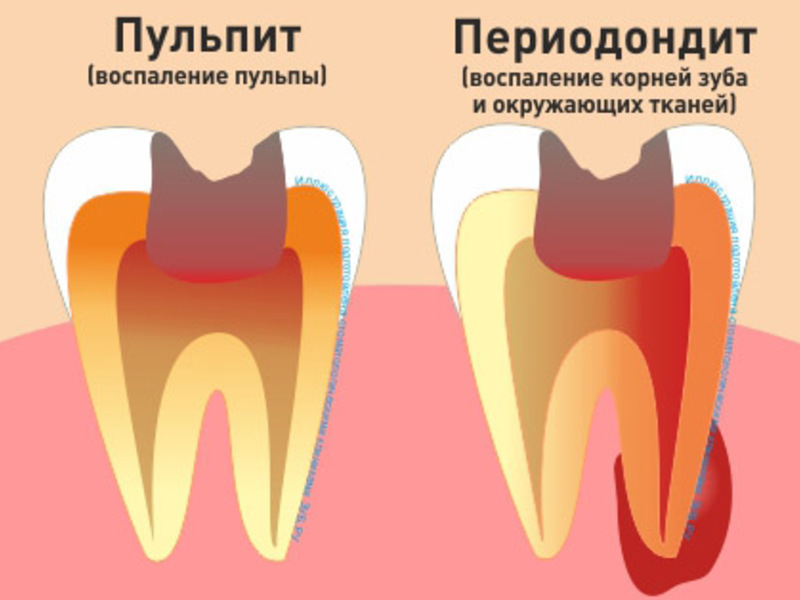
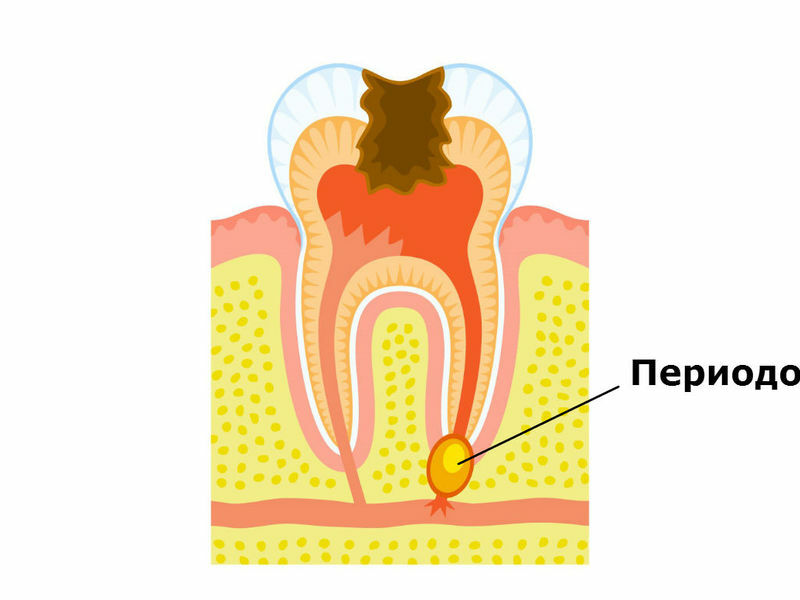
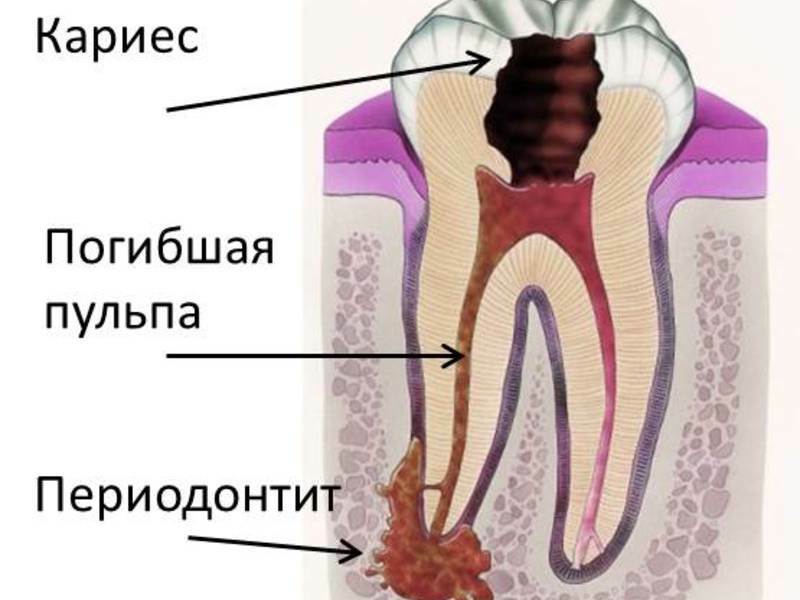
Periodontitis is the inflammatory process of that occurs in the peri-toothed tissue that connects the tooth bone with the retaining element of its root.At the very beginning of development, periodontitis may not manifest itself at all or be erased by a symptomatology that does not allow to detect the disease in time and to consult a doctor.
Classification of periodontitis
By type of origin, the following types of disease are distinguished:
- Medicated;
- is traumatic;
- is infectious.
According to the course of the disease, periodontitis is determined by the following forms:
Acute - is rare.
Chronic - requires rather lengthy therapy.The chronic form develops with disregard for the treatment of acute periodontitis.There are two periods of a chronic illness:
- The remission of the inflammatory process for a while;
- exacerbation of the disease with spread to the entire oral cavity.
 Exacerbated chronic .According to the form of the liquid formed in the periodontal tissues, the disease can be purulent or serous.In the chronic course of inflammatory processes in the tissues surrounding the tooth, at the top of the root, a focus of inflammation can be formed over time, filled with granulation or coarse-fiber tissue with a large number of different pathogenic cells.
Exacerbated chronic .According to the form of the liquid formed in the periodontal tissues, the disease can be purulent or serous.In the chronic course of inflammatory processes in the tissues surrounding the tooth, at the top of the root, a focus of inflammation can be formed over time, filled with granulation or coarse-fiber tissue with a large number of different pathogenic cells.
The following types of disease are distinguished according to the nature of changes in the apical near-root tissues:
- Chronic granulating periodontitis;
- chronic fibrous periodontitis;
- chronic granulomatous periodontitis.
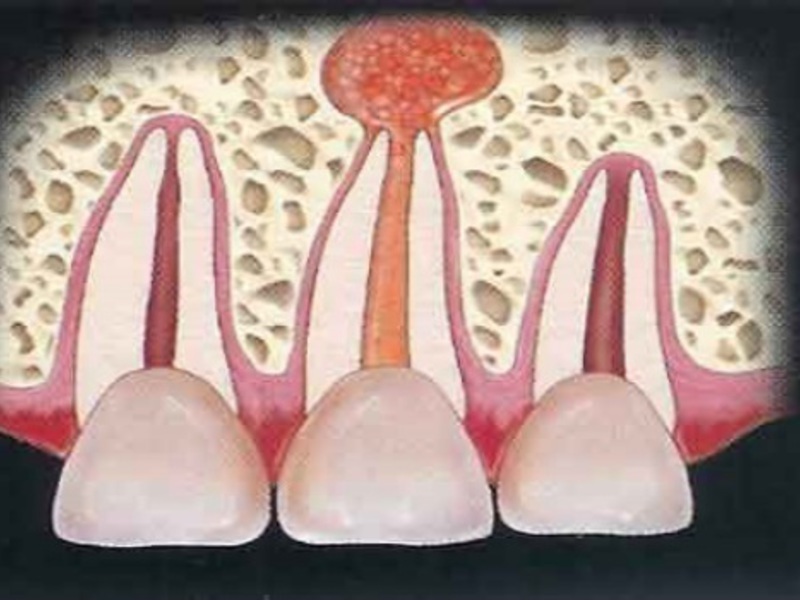
This form of the disease has a foci of inflammation that is limited by a capsule from the connective tissue.The granuloma develops slowly and is always clearly visible to the X-ray.According to the form of the structure, the granuloma is divided into simple, cystic and epithelial.
Causes of the disease
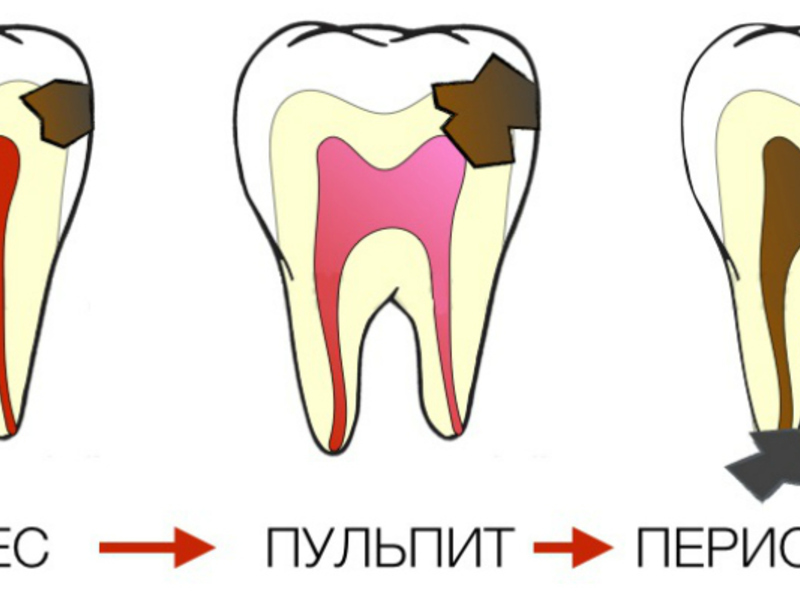
Periodontitis has a different development mechanism, but as a rule, this disease is a consequence of the complicated pulpitis .Simply put, periodontitis is a kind of reaction of the body, reporting a serious health problem, for example - about the source of the infection.
Infectious periodontitis develops as a result of the penetration of harmful microorganisms into the peri-toothed tissues.The most common types of microbes are fusobacteria, spirochetes, fungi, non-hemolytic and hemolytic streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus.The toxic substances released by them, together with the products of the decomposition of the pulp, several times increase the degree of inflammation.
If we talk about periodontitis as a result of other diseases, it can appear due to infection in the periodontium:
-
 traumatic way;
traumatic way; - through the bloodstream in pathologies such as scarlet fever, typhoid;
- by a contact way at a genyantritis and an osteomyelitis;
- if you get strong preparations in the dental tissues that are used in dentistry for dentistry: formalin, acids, arsenic.
Traumatic periodontitis is manifested as an acute process due to a sharp biting of a solid object, bruising, impact on the tooth, etc. In some cases, the pathology arises from unprofessional actions of the dentist: infecting the infected contents from the internal dental cavity at the root apex,Root, removing a small amount of filling material in the periodontal tissue.
A microtrauma of the tooth can also appear as a result of improper filling of the or prosthetics, in which the filling or crown is in an over-position.This creates additional stress and pressure on the tooth during chewing food.
Medicated periodontitis develops when strong chemicals enter the apical tissues of the tooth.It can be substances such as eugenol, chloksidin, iodine, resocin-formalin or arsenic paste, formalin, phenol, etc. Clinical signs of the disease in these cases are clearly associated with the time of dental treatment.Often secondary inflammation of the periodontium is a consequence of such pathologies as periodontitis and gingivitis.In children, the disease in most cases occurs against the background of caries.In addition, periodontal inflammation can be caused by factors such as micronutrient deficiency, vitamin deficiency, non-compliance with the rules of oral hygiene.
There is also a number of somatic diseases of provoking the development of periodontitis:
- Chronic diseases of bronchopulmonary system;
- diabetes mellitus;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- pathology of the digestive tract;
- chronic disorders of the endocrine system.
Symptoms
 Symptoms of acute and chronic forms of the disease vary widely.The main manifestation of the acute form of periodontitis is severe pain .Moreover, it has a permanent character and is strengthened when the jaws are closed, biting on the tooth and the slightest touch to it.As a rule, patients complain of a feeling of pressure inside the bone and internal raspiraniya, the feeling of a seemingly grown tooth.Over time, exudate accumulates in the affected tissues, and pus appears.
Symptoms of acute and chronic forms of the disease vary widely.The main manifestation of the acute form of periodontitis is severe pain .Moreover, it has a permanent character and is strengthened when the jaws are closed, biting on the tooth and the slightest touch to it.As a rule, patients complain of a feeling of pressure inside the bone and internal raspiraniya, the feeling of a seemingly grown tooth.Over time, exudate accumulates in the affected tissues, and pus appears.
Pain syndrome captures surrounding areas: infraorbital region, temple, ear .There is a throbbing pain and redness and swelling of the peri-toothed tissues is observed.Under the artificial crown or a seal, a carious cavity may appear.
If the purulent discharge does not find an outlet through the tooth and accumulates inside, the patient experiences a worsening of the condition: the body temperature rises, the edema of the tissues increases.
If the time is not taken to treat acute periodontitis, complications may occur in the form of sepsis, phlegmon, osteomyelitis, the development of which can lead to death.
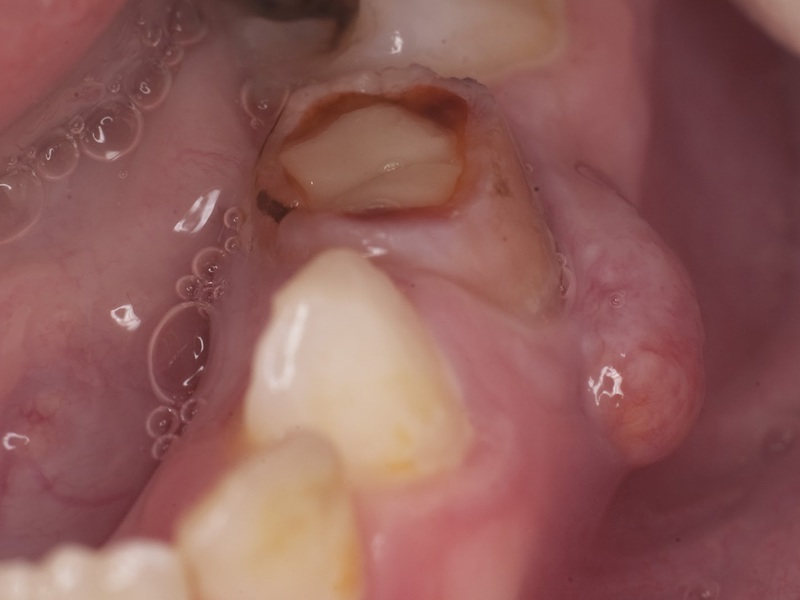
The chronic form of is characterized by the absence of obvious clinical signs.The affected tooth may be under the seal or have a carious cavity, but in almost all cases it can easily be distinguished from the rest by a modified grayish hue.A person may notice that the tooth periodically aches a bit, but calms down after taking medications, sometimes a fistula( a small capsule with white and gray contents) is formed on the gum next to the aching tooth.
In some cases, an unpleasant odor of decay from the oral cavity.When the tooth is tapped on the crown of the tooth, a peculiar deaf sound of is heard.
An accurate diagnosis is established by conducting an additional examination.For the exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, the same manifestations are characteristic as in the acute form, with the exception of some differences: the periodicity and duration of the onset of the pain syndrome, the color of the tooth( the longer the process, the darker the crown), the x-ray picture( when there is a change in the pattern of bone tissue), The presence of a fistula.In addition, with exacerbation of the chronic form there is a slight mobility of the tooth.
Exacerbations of the chronic form of periodontitis may occur for the following reasons:
- decreased immunity;
- trauma to the shell inflammatory focus;
- opening of the fistula and aging of the abscess;
- violation of outflow of purulent contents.
Periodontitis in children
Children's periodontitis is fixed in 50% of cases when they go to dental clinics.The most common cause of periodontitis in children is caries.Inflammation of periodontal in children is conditionally divided into two categories:
- Periodontitis of infant teeth;
- periodontitis of permanent teeth.
In the rest, children's periodontitis is systematized according to the same principle as in adults.
Complications
 Periodontitis is a fairly strong source of infection and can provoke the development of various pathologies of systems and organs.(Eg, septic endocarditis - heart disease).The greatest danger of periodontitis is for pregnant women.
Periodontitis is a fairly strong source of infection and can provoke the development of various pathologies of systems and organs.(Eg, septic endocarditis - heart disease).The greatest danger of periodontitis is for pregnant women.
Complications after the inflammatory process of periapical tissues can be divided into general and local.
Complications of a general nature
- Temperature rise, sometimes as much as 39-40 degrees.
- Persistent headache.
- General poisoning of the body( mainly in the acute form of periodontitis purulent nature).
- Chronic periodontitis provokes the emergence of many autoimmune pathologies, among which endocarditis and rheumatism are particularly prominent, and kidney diseases are sometimes encountered.
Complications of a local nature
- osteomyelitis;
- fistulas, cysts;
- odontogenic genyantritis when the contents are released into the maxillary sinus;
- development of purulent inflammation can provoke phlegmon of the neck;
- formation( with purulent contents) in the form of abscesses.
The most dangerous consequences occur with purulent inflammation, when the pus spreads throughout the jaw and goes under the periosteum.Melting and necrosis of the tissues cause an extensive phlegmon of the cervical region.Frequent complications with purulent periodontitis are odontogenic sinusitis and submucosal abscess.
Since the movement of microorganisms occurs rather quickly and they, localizing in the jawbones, spread along neighboring sites, the outcome of complications of periodontitis is very difficult to predict. The process speed of depends on the protective properties and condition of the body, as well as the shape and type of periodontitis.
Timely diagnosis and on-time treatment help minimize the risk of complications, however, this applies more to the patient than to the doctor: the earlier the patient turns to a specialized clinic, the better for him.
Diagnosis of periodontitis
 Diagnosis is of great importance and is one of the main criteria on which the result of the treatment of periodontitis depends.Diagnosis of the disease involves examination of the oral cavity, collection of anamnesis, additional methods and methods of examination to assess the condition of the periapical zones and apex .
Diagnosis is of great importance and is one of the main criteria on which the result of the treatment of periodontitis depends.Diagnosis of the disease involves examination of the oral cavity, collection of anamnesis, additional methods and methods of examination to assess the condition of the periapical zones and apex .
In addition, diagnostic activities are conducted to identify the root cause of the inflammatory process, however, due to untimely treatment of citizens in the dental clinic, to find the factors that provoked the appearance of periodontitis is quite difficult.Disease in the acute form is diagnosed more easily than a chronic triggered process.
In addition to the above actions, the diagnosis includes the following important points:
- Presence of acute or chronic pathologies of internal systems and organs;
- general condition of the patient and the presence of concomitant pathological changes;
- intolerance to dental material or medicinal products;
- states that present a threat: a violation of the blood circulation of the brain, a heart attack;
- assessment of the red border of the lips inflammation of the oral mucosa in acute form.
The main role in the diagnosis of periodontitis is given to an X-ray study that helps to accurately determine the diagnosis of the disease.
Periodontitis is a serious enough and dangerous disease of the mouth, which affects not only the periodontium and surrounding tissues, but penetrates the bones of the jaw area of the , causing complications.At the slightest suspicion on the development of the inflammatory process, you need to urgently go to the dental clinic, where you will be provided with qualified assistance.