Children's stomatitis
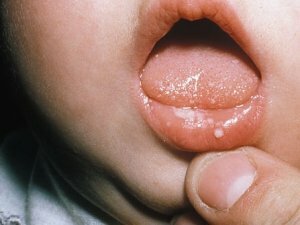 A familiar picture for parents - a small child refuses to eat, is capricious, perhaps he has a high fever. Immediately there is a suspicion of the virus. But just in case, check the baby's mouth. If pink sores or whitish spots are noticeable, then most likely the baby has a stomatitis disease. It was he who caused the indisposition. But do not rush to the pharmacy, first consult a doctor. How to treat stomatitis in young children, it is better for parents and pharmacists to know professional pediatricians.
A familiar picture for parents - a small child refuses to eat, is capricious, perhaps he has a high fever. Immediately there is a suspicion of the virus. But just in case, check the baby's mouth. If pink sores or whitish spots are noticeable, then most likely the baby has a stomatitis disease. It was he who caused the indisposition. But do not rush to the pharmacy, first consult a doctor. How to treat stomatitis in young children, it is better for parents and pharmacists to know professional pediatricians.
Types of stomatitis
Mucous in small children is very tender and delicate. Therefore it is easily injured. Even a too stiff spoon or an incorrectly selected nipple can cause damage to the palate. Traumatic sores occur often after biting cheeks, lips, tongue, due to burns with tea or milk, damage to toys and other objects. These wounds can become a gateway to both non-infectious stomatitis( traumatic, allergic), and infectious( bacterial, viral, fungal).
Allergic stomatitis
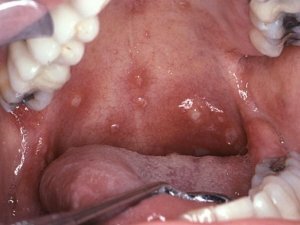 Do not arise independently, but accompany a general allergic disease. Most often it is pollinosis, bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis. When allergic stomatitis appears on the tongue, white spots or redness, and the language resembles a "geographical map".
Do not arise independently, but accompany a general allergic disease. Most often it is pollinosis, bronchial asthma, atopic dermatitis. When allergic stomatitis appears on the tongue, white spots or redness, and the language resembles a "geographical map".
Herpetic stomatitis
Begins with the appearance on the mucosa of the palate, cheeks, lips, tongue of small vesicles. They quickly burst, forming painful sores. The temperature of the body simultaneously increases to 38-39 degrees. The most sensitive to the herpes virus are children aged six months to three years. Herpes virus is very easily transmitted through toys, dishes, airborne droplets.
Viral stomatitis
Often are a concomitant disease of primary viral infections. It's measles, flu, chicken pox, scarlet fever. For example, when the first symptoms of measles on the oral mucosa appear whitish rashes similar to semolina, which are surrounded by reddish specks.
Fungal stomatitis( candidiasis)
Often found in infants, but may occur in older children. Especially after infectious diseases, accompanied by antibiotic treatment. Fungal stomatitis in children is characterized by whitish coating, reminiscent of curds or curdled milk.
Bacterial stomatitis
It occurs in young children, often with infectious and colds. More often than others, such diseases as OR3, tonsillitis, otitis, bronchitis provoke stomatitis. Bacterial stomatitis begins at a high temperature in children. The mucous membrane of the mouth shows a grayish-yellow coating and bubbles filled with bloody fluid or pus. A putrid unpleasant smell comes from the mouth. On the lips are formed layers of yellowish dry crusts that prevent opening the mouth.
Treatment of stomatitis in children
 After seeing the rashes in small children on the oral mucosa, first consult a doctor and then begin treatment. The more promptly to begin treatment, the less unpleasant consequences.
After seeing the rashes in small children on the oral mucosa, first consult a doctor and then begin treatment. The more promptly to begin treatment, the less unpleasant consequences.
- In the first three to four days of the disease, you should rinse your mouth as often as possible( every three hours).To do this, you can use a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, furatsilinom, rivanolom, solution of potassium permanganate. These preparations disinfect the mucous membrane well, soften and remove crusts. If scales and crusts are located on the lips, you can apply to them a cotton wool moistened with a light solution of potassium permanganate.
- To small children, the mouth cavity is conveniently irrigated from a small rubber pear. During the procedure, the baby's head bends over the basin. Children up to a year are safer to tilt their head to one side.
- You can fight with stomatitis rinsing raw chicken protein, because it contains an effective bactericidal component - lysozyme. Before rinsing, the protein of one egg is bred in half a liter of boiled water. Pharmacies also sell ready-made dosage forms with lysozyme. For example, hexaspase, hexalysis. Attention! Due to the ethanol content, these solutions for topical administration can not be swallowed! Therefore, children are appointed at the age when the babies already control the swallowing process.
- After rinsing it is necessary to lubricate the oral mucosa with special antimicrobial or antiviral ointments. In case of traumatic stomatitis, the mouth is smeared with a solution with linseed oil, with vitamin A, with rosehip oil, peach, sea-buckthorn.
- In the treatment of fungal stomatitis is simply indispensable soda. After each feeding it is useful to wipe the baby's mouth with a cotton swab dipped in a solution of baking soda. Proportion: for a glass of boiling water a teaspoon of soda. Soda can be replaced with a 10-15% solution of borax in glycerin.
- As soon as the herpetic stomatitis has poured out, it is necessary to use antiviral ointments. It is acyclovir, 50% interferon ointment, bonaflone, 0.5% oxolin ointment.
- For the anesthesia of the wound, it is possible to use the means that facilitate teething. This is Mundizal gel, Baby-dent, Calgel, Kamistad.
- Recipes for rinsing solutions with analgesic effect: 2 ml of O, 5% solution of novocaine + half a glass of warm water + egg of one egg;Water + peach oil + anestezin in proportions 1: 1: 1.
- If the treatment of stomatitis in young children leads only to temporary relief, and they are regularly repeated in the child, it is necessary to examine it from an immunologist and an allergist.
Nutrition for stomatitis
Food for stomatitis should be neutral taste, comfortable temperature, ground and semi-liquid. Sweets should be avoided, because in a sweet environment, fungi and bacteria multiply particularly rapidly. Particularly prohibited are hard candies. Naturally, salty and spicy dishes will irritate the mucous and inflamed gums.



