First aid for bleeding
 Bleeding - this is the flow of blood due to damage to the walls of blood vessels.
Bleeding - this is the flow of blood due to damage to the walls of blood vessels.
There are 4 types of bleeding:
- capillary,
- arterial,
- venous,
- internal.
Capillary bleeding
This bleeding occurs as a result of damage to the smallest vessels( capillaries), here also include nosebleeds.
Causes of capillary bleeding
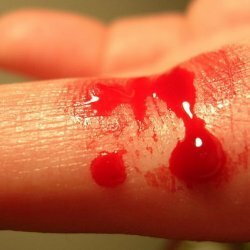 Occurs as a result of cuts, abrasions, usually in everyday life.
Occurs as a result of cuts, abrasions, usually in everyday life.
Symptoms of capillary bleeding
Blood oozes over the surface of the skin from a wound or abrasion, there is no blood vessels as such, bleeding force is small, in most cases it stops on its own.
First aid for capillary bleeding
Arterial bleeding
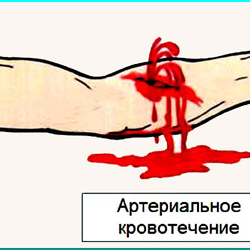 This is the expiration of blood from a damaged artery, this bleeding is the most dangerous becauseBlood flows very quickly, powerful pulsating tremors, blood loss, life-threatening, comes in 20 minutes.
This is the expiration of blood from a damaged artery, this bleeding is the most dangerous becauseBlood flows very quickly, powerful pulsating tremors, blood loss, life-threatening, comes in 20 minutes.
Symptoms of arterial bleeding
- blood of bright scarlet;
- comes out of the wound with a fountain;
- pulses.
First aid for arterial hemorrhage
The help in arterial bleeding consists in immediate application of twist, tourniquet, pinching of the artery above the injured site, and then urgent dispatch of the victim to the hospital.
- The temporal artery is pressed against the temporal bone with the thumb.
- The mandibular artery is pressed against the lower jaw.
- The carotid artery is squashed in the neck region and the pressure bandage is fixed with a roller of bandage or dense tissue.
- The subclavian artery is fixed to the rib in the supraclavicular fossa.
- Arterial bleeding in the shoulder area stops pressing the brachial artery to the humerus.
- When bleeding from the radial artery, it is necessary to squeeze it in the area of the wrist, closer to the thumb.
- The femoral artery is pinned to the pubic bone in the groin area.
- Arterial bleeding in the calf region is stopped by pinching the popliteal artery in the popliteal fossa region as follows: the thumbs are on the knee cap, the rest - fix the damaged artery to the bone.
- Arterial bleeding of the foot is stopped by applying a pressure bandage and fixing the damaged artery to the underlying bones.
 After the artery is pressed to the bone, it is necessary to apply a tourniquet or a cuff as quickly as possible.
After the artery is pressed to the bone, it is necessary to apply a tourniquet or a cuff as quickly as possible. How to apply a tourniquet?
- treat the wound with a sterile wipe;
- apply a tourniquet above the damaged area, if there is no special harness, you can use the improvised means: twist, rope, belt, etc. P;
- is better to apply a tourniquet on a bandage, cloth or clothes, so as not to injure the skin;
- the tourniquet should be applied strongly enough to cause bleeding to stop, if the damaged artery is retracted weakly, the bleeding may increase due to the transmission of veins. Excessive pinching of soft tissues can damage the nerve endings. With proper application of the tourniquet, there is no pulse below the bandage.
- The tow can not be applied for more than 1.5-2 hours, the time of application must be indicated in the note.
- The tourniquet should be reapplied if the limb is blue and swollen;
- the damaged limb after laying the harness is stacked higher and the heat is covered, but it is by no means possible to use the hot water bottle!
- If two hours have passed since the initial application of the tourniquet, the tourniquet should be loosened for 10-15 minutes, at which time the damaged artery is pressed down with fingers, then the tourniquet is reapplied, but slightly higher than the first time.
If it is not possible to apply a tourniquet, the injured limb should be bent and locked in this position.
Venous bleeding
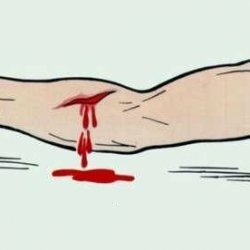 This is a bleeding due to a violation of the integrity of the veins.
This is a bleeding due to a violation of the integrity of the veins.
Symptoms of venous bleeding
- blood of a dark cherry color;
- blood flows continuously, quite intensively,
- pulsation is absent.
First aid for venous bleeding
- The wound is treated with an antiseptic;
- It is necessary to apply a pressure bandage: the damaged area, including the area before and after injury, is sufficiently tightly bandaged, if necessary, a roller impregnated with peroxide of hydrogen can be placed in the wound itself from bandage or gauze.
- The injured person should be sent to a medical facility for suturing the edges of the wound and damaged vessels if bleeding is abundant and the pressure bandage is not enough to stop it.
Internal bleeding
 This is the flow of blood into the internal cavity of the body, for example, the lungs, stomach, bladder, and the like.
This is the flow of blood into the internal cavity of the body, for example, the lungs, stomach, bladder, and the like.
Signs of internal bleeding
- dizziness;
- weakness;
- loss of consciousness.
Internal bleeding is difficult to diagnose and pose a great threat to the life of the patient.
The causes of internal bleeding are trauma, or some chronic diseases.
First aid for internal bleeding
- If suspected of internal bleeding, the patient must be immediately taken to hospital!
- The victim should be laid on a flat surface, to ensure peace.
- In the case of intrapleural or pulmonary hemorrhage, the patient is left in a semi-sitting position.
- A bleb with ice is applied to the bleeding area.
- In no case can warm up the damaged area, take a laxative and drugs that enhance cardiac activity.
Nasal bleeding in children
 Nasal bleeding occurs as a result of damage to the capillaries of the nasal mucosa. In most cases, nosebleeds occur in the Kisselbach zone - the front of the nasal septum, such bleeding is not dangerous, it is quite easy to stop them.
Nasal bleeding occurs as a result of damage to the capillaries of the nasal mucosa. In most cases, nosebleeds occur in the Kisselbach zone - the front of the nasal septum, such bleeding is not dangerous, it is quite easy to stop them.
In rare cases, the cause of nasal bleeding is damage to large vessels of the nasal cavity, stopping such bleeding causes difficulties and requires the help of a specialist.
Causes of nosebleeds in children
- injury to the nose;
- inflammation in the nasal mucosa due to chronic respiratory diseases;
- tumors, polyps;
- high blood pressure;
- poor blood clotting;
- thermal, sunny impact;
- hormonal adjustment;
- deficiency of vitamins and microelements.
First aid for bleeding from the nose
- The child should take the position of reclining, or sitting, with the head tilted forward. The head should be located above the trunk. In lying position, or with the head tilted backwards, there is a risk of getting blood into the respiratory tract and esophagus.
- Apply cold to the region of the bridge of the nose.
- Inject the vasoconstrictor and press the nostrils to the septum.
- If the bleeding is abundant enough, you need to insert a tampon of gauze moistened in hydrogen peroxide into the nasal cavity.
- If within 20 minutes the bleeding does not stop, you need to call an ambulance.
Immediately call an ambulance if:
- has a child's nose injury;
- bleeding is very abundant, there is a risk of rapid loss of blood;
- bleeding is combined with the discharge of a clear liquid from the nose after a head injury;
- is combined with vomiting, the blood from the nose is strongly foamed;
- the child suffers a diabetes, hemophilia, infringements of arterial pressure;
- the child lost consciousness.
Prevention and treatment of nasal bleeding
- supervision by a specialist doctor( ENT);
- moxibustion of the Kisselbach zone;
- reception of vitamins, ascorbic acid;
- instillation of an oil solution of vitamin A in the nose.
- diagnosis to determine the cause of bleeding, treatment of concomitant diseases.



