Diabetes. How to care for the skin
 Diabetes mellitus is a very insidious disease. It does not show itself for a long time, a sick person can not even guess that he is sick. With already started illness, complications appear. Very unpleasant when it comes to the skin of the body. It is she who needs protection in diabetes mellitus. Neglect the protection of the skin can not, otherwise it will itself be a source that spreads the infection. Endocrinologists advise patients to prevent such complications.
Diabetes mellitus is a very insidious disease. It does not show itself for a long time, a sick person can not even guess that he is sick. With already started illness, complications appear. Very unpleasant when it comes to the skin of the body. It is she who needs protection in diabetes mellitus. Neglect the protection of the skin can not, otherwise it will itself be a source that spreads the infection. Endocrinologists advise patients to prevent such complications. Skin
Human skin healthy is a protective barrier against all kinds of bacteria. People with a disease can not afford this. She herself is exposed to microbes. The reasons for this should be found in the disease itself. Diabetes mellitus does not spare, in the first place, the vessels. This is especially true for small vessels that supply blood to the skin of the human body. Vessels, plugging, disrupt the nourishment of the skin.
This disease is characterized by nerve damage, which prevents the normal operation of the sebaceous glands and sweat. The skin becomes dehydrated and inelastic. The sensitivity of the skin is reduced. High blood glucose and improper metabolism are very attracting microorganisms.
Antioxidants begin to be produced in a reduced volume. The skin remains without protection from the effects of microbes, becomes very vulnerable. It easily forms cracks, ulcers and wounds. Since nerves are affected, the person does not experience pain. Any skin lesion can go into purulent inflammation.
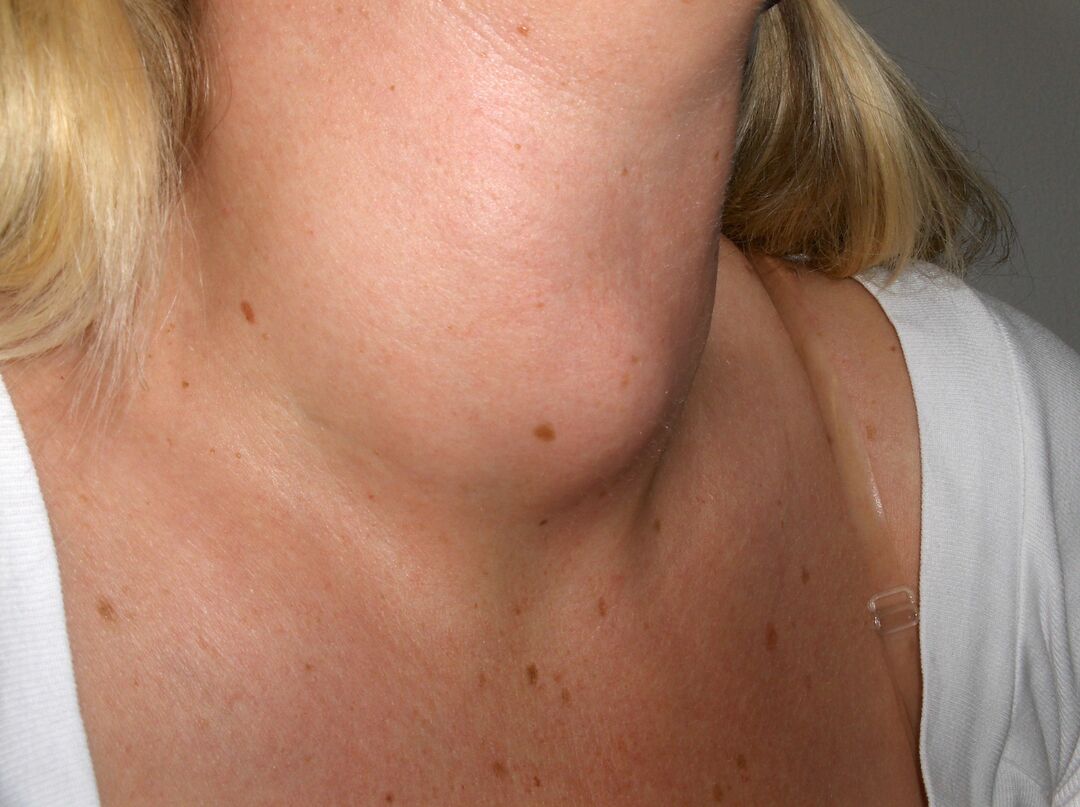
Insidious abscesses on the skin
Furuncles, which often appear, give reason to think about the disease with diabetes mellitus. At a simple furuncle only one hair bag inflames. In diabetics, several hair roots simultaneously become inflamed. This disease is called carbuncle. The sweat glands are filled with germs that cause hydradenitis. This disease is typical for patients with diabetes mellitus.
In diabetics, often there is pyoderma - pustular rash, panaritium - inflammation of the finger, face and purulent ulcers. These diseases lead to phlegmon - diffuse or partial inflammation of the skin, as well as fatty tissue. Measures should be taken immediately, otherwise sepsis may begin( blood infection).
Skin Care
You can avoid skin diseases with diabetes. The skin must be kept clean. But simple hygiene rules are not enough for diabetes. It requires close attention.
Daily( or every other day) you have to take a shower. The hot water bath will further dry the skin. Rinse the skin with a hard towel can not. Doctors recommend simply to soak it with a soft towel. After showering, you must apply a moisturizer to your body.
The usual toilet soap, too, should not be used. It can further reduce the acidity of the skin, and this will reduce the resistance of microbes. Acquire pH-neutral, and preferably sour soap. Clean the face with cosmetic milk or water lotion.
Skin of feet and hands requires special attention. These places often become inflamed due to frequent micro-traumas. Wash hands and feet after washing thoroughly, especially between the fingers. Moisturizing cream can not be applied to these areas. Constant friction with poor evaporation can cause inflammation. It is recommended to apply antioxidant cream, which can be purchased in the OTC department of the pharmacy.
It is advisable to inspect the skin daily. Nails should be cut in time to prevent ingrowth into the skin. It is forbidden to pair your legs or walk barefoot. Shoes should always be dry, wide enough. This will help prevent abrasions. Socks are recommended either woolen or cotton. They absorb moisture perfectly.
In frosty weather, it is necessary to inspect the legs very carefully. Slowed blood supply and sensitivity of the skin can imperceptibly lead the legs to frostbite.
In residential areas in winter, air is always dry. It must be moistened by any means. You can buy a special device to humidify the air, hang wet towels on radiators or put a bottle of water.
If at all precautions the skin all the same has inflamed, the doctor will help to solve a problem. But the best option is to maintain an acceptable level of glucose in the blood of the diabetic patient himself.