Sporadic goiter: symptoms and treatment, differential diagnosis
 Sporadic( non-toxic) goiter is a disease characterized by an increase in the thyroid gland and is diagnosed in patients living outside regions endemic for iodine deficiency.
Sporadic( non-toxic) goiter is a disease characterized by an increase in the thyroid gland and is diagnosed in patients living outside regions endemic for iodine deficiency.
The disease is progressive, i.e., as it develops, the organ increasingly increases in size.
Table of contents: Causes of sporadic goiter Classification Symptoms of sporadic goiter Diagnosis Treatment of sporadic goiterCauses of sporadic goiter
The development of sporadic goiter is caused by a violation of iodine intake to the thyroid gland.
Important: Sporadic goiter must be distinguished from endemic goiter, diffuse toxic goiter, autoimmune thyroiditis, thyroid cancer, neck cysts.
Among the possible causes of the delay in the admission of this element to the endocrine organ are:
- some exogenous factors;
- application of a number of pharmacological agents( in particular - lithium carbonate);
- pathology of the digestive tract, accompanied by a decrease in iodine absorption;
- high level in running water of humic compounds.
Sporadic goiter is often caused by genetic pathologies, in which the production of thyroid hormones is impaired.The cause of the disease can be a congenital absence of specific thyroid receptors or a decrease in their susceptibility to the thyroxine produced by the body.
The organ overgrowth most often begins to progress when the human body experiences the greatest need for the hormones TTG, T3 and T4.In this regard, sporadic goiter is more often diagnosed during puberty, as well as during childbearing.
Note: sporadic goiter may be triggered by taking oral contraceptives, as the percentage of free thyroxin under their influence decreases.
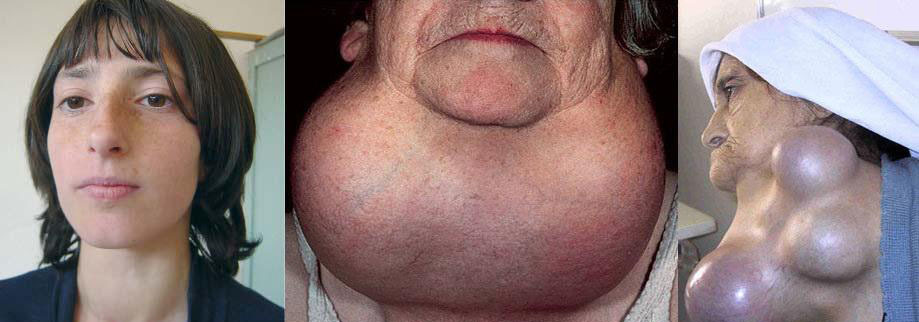
The growth of the gland in a number of cases is determined by the appearance of neoplasms in this organ.Sporadic goiter may be a consequence of thyroiditis and thyroid adenoma.
Regardless of the causes, the biosynthesis of thyrotropin increases.As a result, gland shows hypertrophy at the cellular level and growth - on the tissue level.
Important: Sporadic goiter is diagnosed in women 8 times more often than in men.
It can not be ruled out that in some patients the main etiologic factor of the onset of the disease is still a low level of iodine intake.The laboratory criterion is the isolation of this element with urine in an amount less than 60 μg per day.
Classification
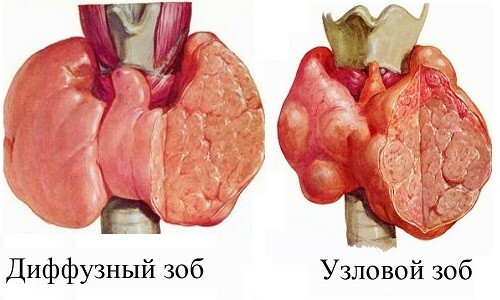
According to the accepted classification, this pathology is divided into:
- diffuse;
- nodal;
- mixed goiter.
The following varieties of sporadic goiter are histologically identified:
- follicular;
- is tubular;
- is colloidal;
- is parenchymatous;
- with macrofollicles;
- with microflicls.
Symptoms of sporadic goiter
Sporadic goiter differs from endemic small growth rates.
The main symptoms include:
- pressure on the organs of the neck and mediastinum;
- persistent bradycardia( with constant pressure on the neurovascular bundle of the cervical region).
Diagnosis
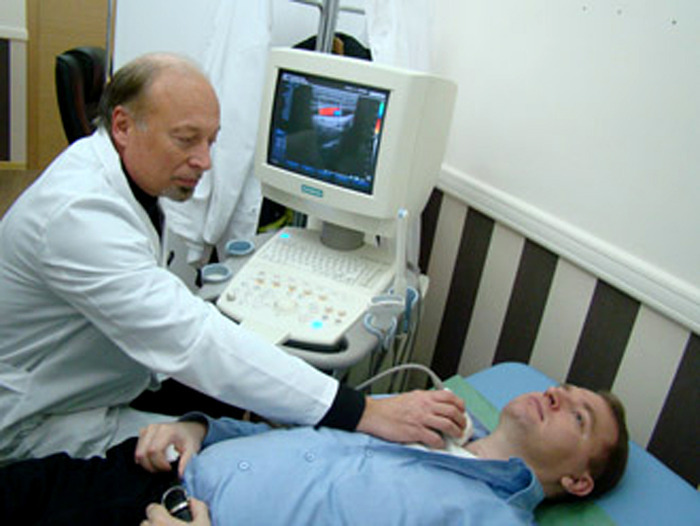 The endocrinologist makes a diagnosis based on external examination data, instrumental and laboratory tests.
The endocrinologist makes a diagnosis based on external examination data, instrumental and laboratory tests.
Thyroid gland is enlarged to some extent.To the touch, the growth can be soft and even, but as the pathology progresses, single or multiple nodes begin to be determined in it.
The basic method of instrumental diagnosis is ultrasound.In the course of this study, multiple strands of connective tissue are found that divide the tissue of the gland into distinctive "lobules".
To study the pathologically altered organ, the most informative is scanning with the use of radiopharmacological preparations of iodine.
A biopsy is performed for the histological examination of the nodules.
The hormonal level often remains normal, so the study of blood for hormones is informative only for long-term observation in dynamics.
Treatment of sporadic goiter
 The main drug that is used in the treatment of this pathology is potassium iodide.During the therapy, it is necessary to monitor the patient, since it is possible to separate the individual nodes with the subsequent manifestation of thyroiditis.
The main drug that is used in the treatment of this pathology is potassium iodide.During the therapy, it is necessary to monitor the patient, since it is possible to separate the individual nodes with the subsequent manifestation of thyroiditis.
Suppressive therapy with L-thyroxine is currently considered unjustified and impractical.
Vladimir Plisov, medical reviewer