Bronchoectasis
Description
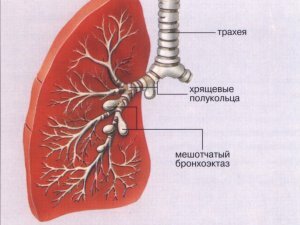
Bronchiectasis is an irreversible disease of the bronchus that develops with a purulent inflammation of the bronchial wall. Sacks and cylindrical bronchiectasis differ.
There are in one segment of the lung( limited) and can capture all of the lungs or even both( common).Bronchoectasis is observed more often in the lower lobe of the lung.
It is accompanied by attacks of very strong cough with allocation of considerable volume of a sputum having an unpleasant smell. There is a loss of tonus of the walls of the bronchi, the affected areas expand and become flabby. Increased production of mucus leads to a rapid increase in pathogenic microbes.
May be self-evident or a manifestation of some pathology. It is more often fixed in men.
Children have local lung damage with chronic suppuration.
Types of bronchiectasis:
- Spindle-shaped.
- Varicose.
- Cylindrical.
- Sirloin.
Lesion of the lungs with bronchiectasis is a serious problem. May lead to pulmonary hemorrhage, as well as lung abscess.
Causes of
 The causes of the development of the disease are those previously transferred: cystic fibrosis, tuberculosis, bronchitis, measles, whooping cough. Especially detrimental are the infections that were experienced in childhood, when the respiratory system is formed. Bronchiectasis can develop in the prenatal period.
The causes of the development of the disease are those previously transferred: cystic fibrosis, tuberculosis, bronchitis, measles, whooping cough. Especially detrimental are the infections that were experienced in childhood, when the respiratory system is formed. Bronchiectasis can develop in the prenatal period.
Congenital causes include:
- congenital infections;
- Marfan syndrome;
- cystic fibrosis;
- immunodeficiency;
- syndrome of Jung.
The reasons for the acquired nature include :
- tuberculosis;
- speed;
- pneumonia;
- whooping cough;
- ulcerative colitis;
- allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis;
- bronchial tumors;
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- pulmonary aspiration;
- Crohn's disease;
- hernia of the esophagus;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
 The causes of bronchiectasis can be poisoning with toxic substances, alcoholism, the use of narcotic drugs.
The causes of bronchiectasis can be poisoning with toxic substances, alcoholism, the use of narcotic drugs.
Symptoms of
Symptoms of the pathology include:
- frequent sputum green or yellow;
- hemoptysis;
- bad breath;
- bronchial infections;
- shortness of breath;
- wheezing when breathing.
Exacerbation caused by infection can cause:
- increased sputum production;
- increased sputum viscosity;
- sputum smell;
- subfebrile( long-term) temperature;
- increased fatigue and malaise;
- shortness of breath, shortness of breath;
- pain in the lungs.
The first symptom is the presence of a strong cough after waking, accompanied by a profuse purulent sputum with a specific odor.
Diagnosis of
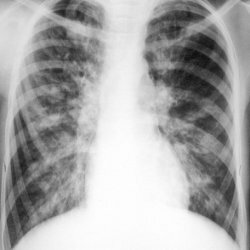
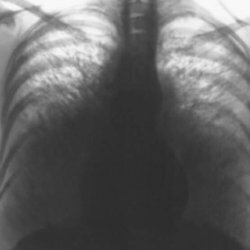
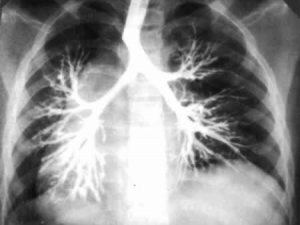
Bronchoectasis of the lung is diagnosed on the basis of clinical analysis. To confirm the diagnosis, computer tomography is additionally performed.
Diagnosis of bronchiectasis is based on the following actions:
- General blood test.
- Sputum analysis.
- Tests for genetic disorders.
- Chest X-ray.
- Check the quantitative content of the level of immunoglobulin.
- Autoimmune screening tests.
Treatment of
 There are 2 types of treatment of the disease:
There are 2 types of treatment of the disease:
- Medicated.
- Surgical.
The purpose of drug treatment is to curtail the aggravation of the pathological process, to prevent the development of complications.
For this, the patient is prescribed:
- high-calorie diet;
- mucolytic drugs( dilute sputum);
- vitamins A and B;
- modulators of the immune system;
- biogenic stimulants;
- physiotherapy procedures.
Surgical intervention is indicated if medication failed to produce a positive result, and the patient's condition worsens.
In lung disease, when a process affects two of its lobes, a resection is performed. If the disease progresses, then lung transplantation is performed.
Contraindications to surgery are:
- bilateral bronchiectasis;
- exacerbation with accumulation of purulent discharge;
- amyloidosis of the kidney;
- signs of kidney failure;
- a deep disposition of bronchiectasis;The age of the patient is 14 years.
Rehabilitation
With bronchoectatic disease, rehabilitation is a permanent process that includes:
- respiratory gymnastics;
- physiotherapy;
- treatment and general physical education;
- kinesitherapy( simulators).
 It is important to completely stop smoking and prevent secondhand smoke.
It is important to completely stop smoking and prevent secondhand smoke.
Folk remedies
In combination with traditional treatment it is recommended to use folk remedies:
- A tablespoon of badger fat is thoroughly stirred in a cup of hot milk and immediately drunk.
- Badger fat is falling on the st. Spoon sugar, take and drink milk.
- Black radish juice takes 2 dessert spoons before breakfast and before dinner. You can add honey to the juice.
- Juice of plantain mixed with liquid honey in a ratio of 2 to 1 and a spoon to take before eating with a chronic cough.
- Infusion from the roots of comfrey. Grind the roots of comfrey, put in a thermos for 5 hours. Infusion beforehand. Drink warm for 3 mouthfuls before eating.
- Eliminates the unpleasant smell of phlegm tincture on vodka kidney poplar, birch, aspen( 5: 1).Insist for a week, use for inhalations.
Complications of
Bronchoectatic disease is a pathology that causes many complications.
The main complications are:
- chronic respiratory failure;
- pulmonary hemorrhage;
- pneumosclerosis;
- malignant neoplasms;
- pulmonary heart( extension of the right divisions);
- amyloidosis of the kidneys( formation of deposits);
- septicemia( intoxication of blood).
Prevention
To prevent exacerbations of the disease requires:
- to treat colds and respiratory infections in a timely manner;
- prevent the development of caries and other infections of the oral cavity;
- restrict contact with patients;
- to avoid hypothermia;
- visit the therapist and pulmonologist 4 times a year;
- to quit smoking;
- limit dust inhalation( change workplace);
- vaccinate children against measles and whooping cough.
These measures allow to achieve a long-term remission and significantly reduce the likelihood of complications of the disease.