How is the operation to lower the testicle( orchipexy)?
Operation of testicular ossification( orchipexy) is a method of surgical correction to move a testicle into the scrotum, if it does not fall down in time. During surgery, it is necessary not only to eliminate the factors preventing the erection of the testicle, but also to preserve the integrity of its tissues.
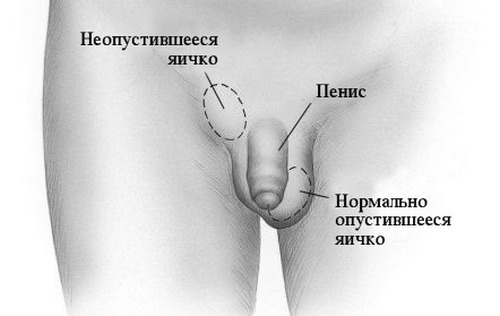
Cryptorchidism - the testicle is not in the scrotum: the testicles are located outside the scrotum, or the
is not correctly lowered. Normally, the testicles descend during the first two months of the boy's life, much less often - during the year. Already at the age of 8 months at non-admission testicles( cryptorchidism) in it structural disorders of tissues begin to develop. Their maximum, that is, partial or complete loss of viability, these changes reach to 5-7 years. Therefore, is the child's best age for surgery - 2-3 years .If an undescended testis is found, only during adolescence or in an adult is also performed a surgical procedure. Indications and contraindications
- 2.1 Analyzes and consultations of specialists
- 2.2 Preparation for operation
- 4.1 Features in children
- 5.1 Postoperative complications
- 5.2 WhenShould I see a doctor?
Indications and contraindications
The operations are performed not only when the testicle is not in the scrotum, but also in cases of complications.
Main indications:
- true cryptorchidism( in which it is impossible to move the testicle into the scrotum, unlike the false one, when at low temperatures or stress the testicle is temporarily pulled into the abdominal cavity);
- twisting of the elements of the spermatic cord, their pinching;
- combination of cryptorchidism and inguinal hernia;
- changes in the shape, size and structure of the testicle, associated with eating disorders and metabolic processes in it;
- inefficiency of conservative treatment.
In both boys and men, this surgical intervention is contraindicated in the presence of severe somatic diseases( severe abnormalities of the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular system) and a significant decrease in the activity of the blood coagulation system.
Features of preparation for operation
Before the operation the pediatrician examines the child, reveals acute inflammatory processes, allergic reactions, concomitant diseases.
During the preparation of an adult male, a physician-physician should be examined to prevent exacerbation of chronic diseases of the ENT organs and the respiratory system( sinusitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis).
If, for the treatment of concomitant illnesses, the patient takes medications that slow blood clotting, then, according to the doctor's prescription, their administration is canceled within a week before the operation. The entire list of used medications is important to inform the doctor, as the drugs interact with each other and can change the response to painkillers and other medications.
Analyzes and consultations of specialists
The following studies are required:
- general and biochemical blood test( for the detection of signs of inflammatory processes, evaluation of the functional state of the liver, kidneys);
- urine analysis( for assessment of the filtration capacity of the kidneys and exclusion of chronic pathology);
- electrocardiogram and measurement of blood pressure( for determining the state of the cardiovascular system);
- repeated ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis, MRI( to detect the exact location of the testicle for the purpose of choosing the method and access to surgical intervention).
After receiving the research data and consulting a general practitioner, the patient is examined by an anesthesiologist, who identifies possible risks in the operation and individually determines the type of anesthesia.
If the operation is carried out by the child, parents or other adults - the legal representatives of
- consent to the intervention. Before surgery, the surgeon tells the adult patient the features of the operation, the options for other treatment, possible complications and consequences. The patient asks the doctor all the questions of interest to him and, at the end of the discussion, signs an informed consent to the operation.
If surgical correction is performed under general anesthesia( in both the adult and the child), the possibility of removing the testicle is discussed in advance, if its atrophy( irreversible changes) is revealed. In the case of an operation under local anesthesia, when the man is conscious, this issue can be discussed during the operation. However, in advance it is stipulated, in what case there can be a question on removal of a testicle.
Preparing for operation
Direct preparation for surgery:
- You can take food to the patient no later than 10 hours before surgery. The presence of food in the stomach is extremely dangerous by throwing it into the respiratory tract during anesthesia.
- The night before, it is necessary to clean the intestines( setting the enema), before the operation - empty the bladder.
- Men need to shave their hair in the groin.
Operations and their features
Perform a surgical operation with both open access and laparoscopy. When open, cuts of the skin and underlying tissues are made, with small lacaroscopic incisions, through which tubes are inserted, surgical instruments and endoscopic systems are placed to control the operation. The advantage of the laparoscopic method is a shortened rehabilitation period of approximately 2 times, as well as a significantly smaller size of postoperative scars.
In addition, operations to reduce the testicle in the scrotum are divided into single-stage and two-stage .
Basic stages of single-step operation :
- Isolation of spermatic cord and testicle from surrounding tissues.
- The formation of the location of the testicle in the scrotum, it is necessary to carefully stretch the half of the scrotum, in which the testicle did not descend in time.
- Fixation( fixation) of the testicle in the scrotum and its elastic stretching with a special thread( ligature).

A wide selection of endoprostheses( implants of the testicle) allows selecting the appropriate option for each patient
Such operations are carried out only with the complete absence of tension in the tissues of the spermatic cord. In all other cases, requires two-step interventions. At the first stage, the testicle is cut through the incision in the scrotum, attached to the wide fascia of the thigh, forming an anastomosis( joint) of the skin of the scrotum and thigh. And after 3 months dissect this anastomosis, move the testicle into the scrotum and fix it with ligature, conducting the final, second stage of correction.
During the operation, the testicular biopsy is always examined. When identifying signs of malignant neoplasms, atrophic and necrotic changes indicating a loss of viability, the testis is removed. Also, it is removed during ectopia, when it is located outside the normal path by which the testicle descends from the abdominal cavity. A prosthesis( implant) is placed on the site of the removed testicle and the natural appearance of the scrotum is restored( for more details on prosthetic testis read here).
Recovery period
Given the large amount of intervention, it is recommended that bed rest is maintained in a hospital for 2-3 days for both the child and the adult. The medical staff observes the state of the seams and the process of tissue healing.
The main activities in the first week after the operation:
- the appointment of antibacterial agents( a group of fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins) to prevent the development of infection;
- for the removal of pain and acceleration of healing used anti-inflammatory and analgesic( paracetamol, ketorol);
- , once a day, the medical staff carries out a dressing: examination of the postoperative wound, treatment of the edges of the skin with antiseptics, replacement of a sterile bandage.
It is important to keep the bandage clean and dry, do not wet it. Independently, you can only treat the skin around the gauze, it is better to use a soapy warm solution, then - clean water and wipe the skin with a tissue or towel.
A week after surgery, the surgeon removes the seams, removes the ligature, which fixes the testicle and stops the stretching. With a positive dynamics of recovery the patient is discharged from the hospital for 8-10 days after the operation.
Features in children
Children are also in the hospital for about a week, and after removing the stitches can be discharged home. It is necessary to refrain from moving games, running for 2-3 weeks after the operation until the tissues are completely healed.
A month after the operation, the doctor prescribes a follow-up examination, where it determines the localization, the condition of the testicle and the scrotum as a whole. It is also recommended to visit the doctor again, in another six months.
Complications of
Local edema, tenderness in the area of a postoperative wound in the first days after the operation are not complications, but a normal manifestation of the recovery period. These phenomena pass independently under the influence of therapy, which are carried out at the stage of rehabilitation.
Postoperative complications
Postoperative complications include:
- bleeding from the vessels of the scrotum;
- violation of the integrity of the vas deferens;
- damage to the testicles caused by dissection of blood vessels and malnutrition;
- infection in a postoperative wound;
- abnormal position of the testicle in the scrotum;
- marked swelling of the entire scrotum;
- is an inflammatory process in the testis and its epididymis( orcoepididymitis).
In laparoscopic operations, in rare cases it is possible to accumulate air in the preperitoneal adipose tissue, puncturing the internal organs( bladder) with a needle.
For timely treatment of complications, it is important to seek medical help as soon as possible.
When to see a doctor?
Urgent doctor consultation is necessary for:
- elevated body temperature( more than 37.5 ° C);
- abundant, unceasing bleeding from the area of a postoperative wound;
- secretions of yellow, greenish color with an unpleasant odor;
- divergence seams.
Forecast
Postoperative prognosis with timely correction is favorable. In most cases, surgery performed at the age of 3 years provides a normal reproductive( ability to have children) function and does not cause psychological trauma to the boy. If the operation is performed by an adult male( and also during adolescence), then, considering the high risk of developing a tumor and a low probability of maintaining the normal functional ability of an unremitted testicle, in most cases it is removed and replaced with a prosthesis.
Recommended for viewing: