Preparation and conduct of urethroplasty in men
Urethroplasty is a complex operation to restore the patency of the urethra. Due to the special structure of the urethra, this intervention is most often shown to men. What should I know about this difficult operation?
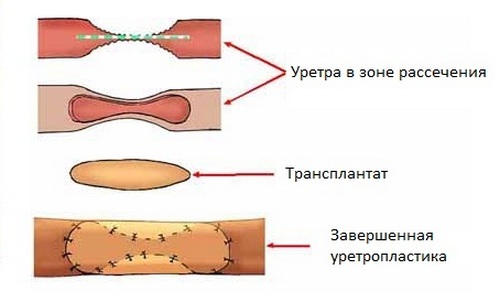
open reconstructive surgery for urethral stricture( urethroplasty)
Content
- 1 Brief information about the male urethra
- 2 Indications for surgery
- 3 Examinations
- 4 Preparation for surgery
- 5 methods of operation
- 6 postoperative
- 6.1 duration of postoperative
- 6.2 Complications urethroplasty
- 6.3 The late consequences of the operation
Summary of the male urethra
To better navigate the indications for operaradiotherapy and the course of surgical intervention, it is necessary to understand how the male urethra is arranged.
The urethra can be divided into several sections( beginning with the canal opening, and ending with the prostatic department):
- The urethral opening.
- Pit( also known as scaphoid fossa).
- The Penile Department.
- Buldose department.
- Membrane Department.
- Prostatic department.
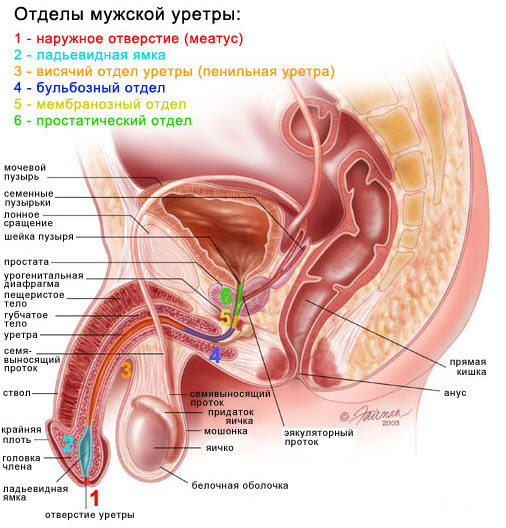
Anatomy of the genitourinary system of a male
Indications for operation
There is no exhaustive list of indications for the operation. Nevertheless, there is a stable practice in urology, based on which doctors offer surgical intervention to patients. The main indication, which, one way or another, appears, is the narrowing of the urethra of a different nature. Among the specific reasons for the appointment of the operation:
- Presence of stricture. Stricture is a partial narrowing of the urethra, with stenosis up to half the lumen of the urethra. With stricture, urine is still able to pass through the canal, but due to high pressure on the walls of the urethra, tissue rupture is possible. Especially dangerous are strictures of large size( more than 2 centimeters) in the bulbous section, penile, and prostatic sections. Why is that? The reason lies in the anatomical structure of the male urethra. The closer the anatomical curves of the urethra, the greater the risk of constriction.
- Obliteration of the urethra. The most dangerous condition requiring urgent surgical correction. If there is partial constriction of the urethra with stricture, then with full obliteration, occlusion or fusion of the walls of the organ occurs.
- Congenital malformations. First of all, hypospadias. This is a condition in which the opening of the urethra moves relative to its normal position.
- Epispadia. Complete or partial splitting of the urethral wall.
- Finally, urethroplasty is indicated in restorative reconstruction of the penis( phalloplasty).
In all other cases, surgeons prefer to limit themselves to less radical measures, since the operation requires jewelry precision and skill.
Diagnostic measures
During the preparatory period, a repeated examination of the patient by a urologist is performed to determine the structure and size of the stricture or the site of the obliteration. For obvious reasons, it is impossible to identify the nature of the process "by sight".The following objective studies are shown:
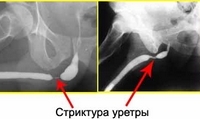
Type of urethral stricture on X-ray
- anamnesis, oral interview with the patient;
- urethroscopy( not always possible, as narrowing of the urethra occurs);
- bacterial seeding of biomaterial from the urethral mucosa;
- ultrasound of the organs of the scrotum and small pelvis;
- urethrography;
- analysis of PSA.
If the ability to self-urinate is lost, limited to ultrasound and visual inspection. Up to certain limits, the introduction of a urethroscope is possible.
These activities are required to verify the diagnosis and determine the prevalence of the process. In addition to these, other examinations are needed that will show the general condition of the patient's body and readiness for surgery. Shows:
- general blood test( for detection of inflammatory process);
- general urine analysis;
- electrocardiography;
- Fluorography;
- tests for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis;
- coagulogram.
At the end of the preparatory activities, doctors are identified with the possibility of prompt intervention and its tactics.
Preparing for operation
Preparatory activities include:
- Restriction of diet( forbidden to eat a day before the intervention).
- Taking laxatives for cleansing the colon.
- Shaving the groin area.
- Mouthwash with antiseptic solutions( it is necessary that pathogens do not settle in the lower respiratory tract during intubation of the trachea).
Methods of carrying out the operation
The operation starts with the patient entering the state of anesthesia. Since this is not an ordinary case, but a complex therapeutic manipulation, the duration of the intervention varies from 2 to 5 hours and requires a lot of experience on the part of the doctor. Usually, two surgeon teams take part in the operation at once.
There are at least two main ways of performing surgical treatment:
- Anastomotic urethroplasty. Assumes excision and removal of the affected area of the urethra. The remaining ends of the urethra are sewn together. This technique is considered obsolete, because it is "famous" for complications: it may shorten the penis, its curvature.
- Buccal urethroplasty. The most modern technique, involving the transplantation of the tissues of the cheek, tongue, lips or scrotum instead of stenotic urethral epithelium.
The course of this operation involves several steps:
- Excision of the cheek tissues for the removal of the mucosal flap. This stage, along with the fifth step, requires jewelry accuracy from the surgeon.
- Cheek closure.
- Perineal incision( the length of the incision varies from 2 to 7 cm).
- Removal of stenotic urethral tissue.
- Sewing of the mucosa from the cheek.
Postoperative period
The duration of the postoperative period
is about two weeks. The patient remains in the urological hospital for the first 5-10 days. All this time the patient should take antibacterial drugs. Treatment of a postoperative wound, dressings is carried out.
Complications of urethroplasty
Severe complications:
- infection with postoperative wounds;
- development of bruising( bruising) of the perineum.
Late consequences of
- operation. Curvature of penis.
- Narrowing( stenosis) of the anastomosis.
- Relapses of obliteration and stenosis of the urethra are possible.
Read: Stink and pain when urinating in men - causes and treatment
Recommended for viewing: