Surgery to remove hemorrhoids: methods, their advantages and disadvantages
Operations with hemorrhoids are the most radical method of treatment, allowing to prevent the progression of the disease and the development of its complications. In modern clinical practice, large( traditional) surgical interventions and minimally invasive procedures are used. They differ in the volume of the removed tissues, the duration of the recovery period, the likelihood of postoperative consequences and the possibility of relapse.
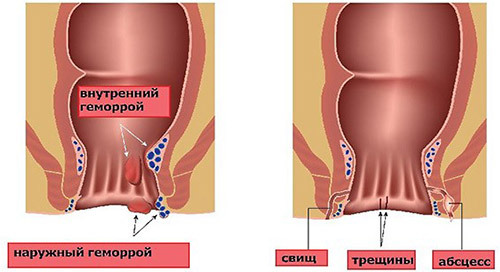
Operation with hemorrhoids is the most radical and effective method of therapy.
Content
- 1 Classical methods of surgical correction
- 1.1 operation to Milligan-Morgan
- 1.2 operation to Antonio Longo
- 2 Minimally invasive techniques
- 3 Features laser use
- 3.1 Indications and contraindications
- 3.2 Preparation for surgery
- 3.3 course of surgery and postoperative
- 3.4 Possible complications
Classical methods of operative correction
Operation on Milligan-Morgan
The most traditional method is theAlenia hemorrhoids( hemorrhoidectomy) by Milligan-Morgan. It is an extensive operation requiring high qualification of the surgeon. It is performed with external, internal, and combined hemorrhoids. The essence of the operation lies in the capture of the hemorrhoidal node, drawing it outward on the vascular pedicle and its intersection. Thus, the hemorrhoids are completely removed.

Allocate modifications to the Milligan-Morgan operation:
- with open access( a cut of the outer tissues), while the surgeon does not make external seams at the sites of the remote nodes, but only crosses the nodes;
- closed, with suturing of postoperative wounds, which contributes to their faster healing;
- submucosal( according to Parks), in which a mucosal dissection is performed over the hemorrhoids and local removal of them.
Variants of these surgical interventions vary not only in terms of volume and type of anesthesia. If a closed hemorrhoidectomy can be performed under local anesthesia, then other methods require general anesthesia and epidural( the introduction of an anesthetic into the zone of the spinal cord membranes).Thus, the choice of a specific operation is influenced not only by the features of the course and severity of hemorrhoids, but also by the age, general condition of the patient. Since the presence of severe concomitant diseases is a contraindication to the introduction into general anesthesia.
Operation of Antonio Longo
In the presence of internal hemorrhoids, circular( the entire circumference) prolapse of hemorrhoids, as well as parts of the rectum, the most modern is the procedure by the method of Antonio Longo.
Procedure:
- Removal of a portion of the rectal mucosa located above internal hemorrhoids.
- Pulling inside the fallen mucosa and restoring the normal location of the venous plexuses.
- Mucosal lining with titanium staples, which subsequently leads to the formation of a small scar.
As a result of the operation, due to the removal of a part of the blood vessels from the mucous membrane, the blood supply of the enlarged hemorrhoidal nodes is significantly reduced, their desolation and further complete replacement with a connective tissue. For the operation, local anesthesia or conductive anesthesia is sufficient with the introduction of an anesthetic into the area of a large nerve trunk.

Advantages of the method:
- a short duration of the operation( up to 20 minutes);
- there is no need for bandaging;
- not expressed postoperative pain syndrome, which is effectively removed by small doses of non-narcotic analgesics( paracetamol, analgin);
- a short recovery period( in a hospital it is necessary to stay no more than a day, the patient can start working after 7-10 days);
- is effective in relapses after other treatments.
Minimally invasive techniques for
Less so-called minimally invasive methods for treating hemorrhoids. They do not require hospitalization of the patient, are conducted under local anesthesia and do not provide for suturing the postoperative wound.

Basic techniques:
- sclerotherapy;
- ligation of nodes using latex rings;
- cryodestruction;
- coagulation( infrared, electric, laser).
Sclerotherapy is the introduction of drugs into the hemorrhoidal node, which results in a thrombus, overlaps the lumen of the vessel, and the node collapses. This type of treatment is a method of choice in the presence of contraindications to traditional surgical interventions, including with severe concomitant pathology, as well as bleeding.
The ligation of is most indicated in isolated, isolated hemorrhoidal nodes no more than 2 cm in diameter. Use latex rings that pinch the leg of the node and stop the blood flow in it. As a result, the vessel empties, and the ligature disappears.
Cryodestruction allows to freeze hemorrhoids when exposed to liquid nitrogen, as a result of which they lose vitality, wrinkle and fall off.
Coagulation is a process of irreversible changes( folding) of protein structures. If the corresponding device is directed to the leg of the altered node( which occurs during surgical interventions), then it sticks together, the lumen of the vessel overlaps and the node becomes empty. With infrared photocoagulation, a heat flux acts, which is created by an infrared beam, focused and transmitted through the lightguide. For electric use the properties of electric current. These methods can be used both independently at small sizes of hemorrhoids, and for increasing the effectiveness of other interventions and reducing the traumatic nature of the operation.
A feature of laser exposure is the ability to both cauterize tissues due to coagulation and cut them, which greatly expands the possibilities of effective use of this method of exposure.
Features of the laser
Laser coagulation is one of the most modern methods for treating hemorrhoids. With internal hemorrhoids, the effect is that the laser beam burns the hemorrhoidal nodes layer by layer. Small wounds remaining in place of the nodes, due to the coagulating properties of the laser, do not bleed and quickly heal. With an external process, the laser cuts the expanded node. Cauterization of tissues and blood vessels occurs, which prevents bleeding.
Indications and contraindications
Laser treatment is a highly effective treatment if used according to indications.
It is recommended to use laser coagulation with:
- internal, external and combined hemorrhoids 1-2 stages;
- attaching an inflammation of the rectal mucosa;
- development of anal fissure;
- bleeding internal hemorrhoids;
- thrombosis of nodes.
In the presence of contraindications to hemorrhoidectomy, laser treatment is also used in stages 3 or 4 of the disease. Since it is not always possible to completely excise large hemorrhoidal vessels, in a number of cases a combination of laser and other methods of surgical correction is used.
Contraindication to the use of this technique is the pronounced inflammatory process of the anal zone. In this case it is necessary to conduct conservative therapy( antibacterial, anti-inflammatory).After the abatement of the inflammatory process, the use of laser treatment is possible.
Preparation for operation
In the preoperative period, a male therapist is required to examine a man, determining the presence of concomitant diseases of internal organs. If necessary, also consults a cardiologist, a pulmonologist. Blood and urine tests, an electrocardiogram and other tests for the appointment of specialists are conducted. After the diagnosis is established and the general condition of the patient is determined, an anesthesiologist must be examined. This doctor determines the risks of surgery and selects the type of anesthesia.
One week before the procedure, it is necessary to begin to follow a specific diet of .Should:
- not use products that cause bloating( fizzy drinks, fresh buns, legumes, corn, cabbage, kvass);
- refrain from indigestible food and contributes to the development of constipation( canned goods, fat broths, rice, pasta, pears, dogwood);
- preference to give vegetable food( carrots, beets, zucchini) and sour-milk products( fresh yogurt, fermented baked milk, a small amount of cottage cheese).
Course of operation and postoperative period
Laser treatment is performed under local anesthesia. To do this, use an anesthetic( benzocaine, lidocaine), which is injected into the anal zone. A few minutes after the disappearance of sensitivity in this area begin to interfere.

With external hemorrhoids, the skin is cut with the laser and the underlying tissues, varicose veins are annealed layer by layer. At internal - with the help of an optical device( an anoscope) determine the location of the node and through the slots there is layered coagulation. Large hemorrhoids are completely removed, excising his body and base, and for small ones, cauterization of his foot is effective. As a result, the remaining base elements are replaced by a connective tissue.
After completion of manipulation, the patient remains in the horizontal position for another half an hour, and in the hospital is until the end of the analgesics( about 3 hours).For one procedure, it is recommended to delete no more than 3 knots.
The main recommendations:
- to eliminate pain when emptying the intestines in the early days to take painkillers( baralgin, analgin, paracetamol);
- to prevent strain, difficulty in defecation, use a sufficient amount of liquid( up to 1.5 liters per day), sour-milk products, fresh and processed( stewed) vegetables;
- carefully handle postoperative wounds with antiseptic means, after each emptying of the intestine wash away with warm water;
- refrain from physical activity and sexual activity.
After full recovery if necessary( a large number of changed nodes) repeat procedures are performed, on average, after 3 weeks.
Possible complications of
Adverse effects may be associated with technical errors in the operation or be a result of violations of prescriptions of a doctor in the postoperative period.
Complications:
-
 bleeding in the early period due to poor cauterization of tissues, during rehabilitation - when injuring the rectal tissues with dense feces;
bleeding in the early period due to poor cauterization of tissues, during rehabilitation - when injuring the rectal tissues with dense feces; - difficulty in bowel evacuation due to fear of pain or bleeding( psychological causes);
- urinary excretion delay( temporarily, after application of anesthetics);
- infection of postoperative wounds in violation of hygiene rules.
In case of a violation of normal bowel movement, a soft laxative( macrogol) may be used along with a special diet, with a delay in urine - putting the catheter on for a short time until the normal function of urination is restored.
If you see signs of bleeding( impurities of blood in the stool, traces on the laundry), you should consult a doctor. And if you join such symptoms as general weakness, cold sweat, lower blood pressure, you need to contact the doctor urgently.
Also, if signs of infectious complications appear( increased body temperature, increased pain, the appearance of excretions from the wound surfaces), the examination of the doctor should also be urgent.
Recommended for viewing: