Details about the brachytherapy of prostate cancer
Brachytherapy is one of the radiological methods for treating prostate cancer( PCa), which is based on the introduction of closed sources of ionizing radiation directly into the prostate gland. Suitable for the therapy of localized or locally advanced cancer. Distinguish: high-dose and low-dose brachytherapy( see below).
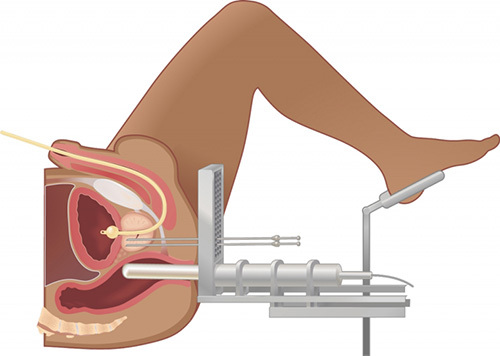
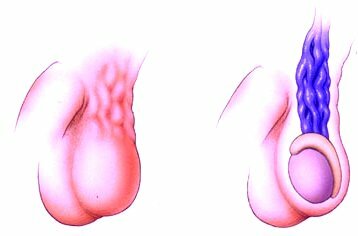
Fig.1 - Brachytherapy.
Contents of
- 1 Procedure features and benefits of
- 2 When is brachytherapy effective?
- 3 The possibility of brachytherapy
- 4 The types of brachytherapy and the procedure
- 4.1 Low-dose brachytherapy
- 4.2 High-dose brachytherapy
- 5 Complications of brachytherapy
- 6 Forecast and further actions
Procedure features and benefits
This type of prostate effect differs from the remote radiation therapy in the way the radiation sources are delivered. When carrying out brachytherapy, a microscale with a radioisotope is inserted into the tumor( see Figure 2), which allows local exposure and does not affect surrounding tissues. This is not available for remote radiation therapy.
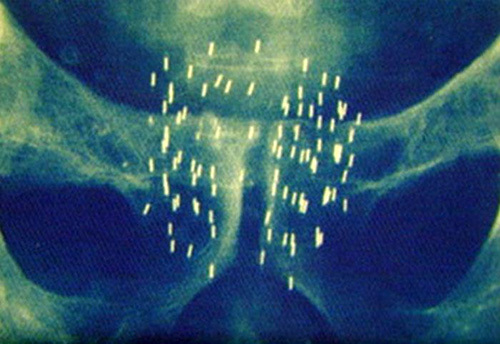
Fig.2 - Microline with a radioisotope after brachytherapy.
The advantages of the method include the fact that there is practically no external irradiation and the patient does not present a "radioactive" danger to others.
In oncourology literally until recently there was a standard approach to patients with PCa at the stage of T1-T2, which used:
- Operative treatment( prostatectomy);
- Medical therapy;
- DLT( Remote Radiation Therapy).
This approach to treatment was much more difficult for the patient to tolerate due to invasiveness and the development of undesirable side effects.
Brachytherapy is an alternative method that is suitable for patients with contraindications to the above complex treatment.
When is brachytherapy effective?
This type of treatment is effective in the following cases:
- The tumor is localized by the prostate and does not spread to neighboring organs. This is caused by the fact that the radiation exposure is able to cover the field no more than 1-2 mm from the capsule of the prostate gland.
- The size of the prostate gland with a tumor should not be more than 50 cm3 in volume. To correct the volume of the prostate, in some cases, prescribed hormonal therapy for 3 months. This leads to the desired reduction in size and enables brachytherapy.
The possibility of brachytherapy
Before deciding to conduct interstitial radiation therapy( second name of brachytherapy), the oncourologist evaluates the results of the patient's examination:
- The level of prostate specific antigen for effective brachytherapy outcome should not exceed 20 ng / ml.
- Brachytherapy for Gleason scores greater than 7 points is not advisable, since the probability of tumor release beyond the capsule of the prostate is high. In this case, treatment will not help.
- Contraindication to brachytherapy is postoperative surgical treatment in the form of transurethral resection, since in this case complication is the total incontinence of urine in the patient.
Types of brachytherapy and procedure
Treatment is carried out in a day hospital or for short-term hospitalization. Before conducting interstitial radioactive treatment, it is necessary to undergo a series of clinical examinations:
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance imaging( MRI);
- transrectal examination of the prostate( TRUS).
This complex was called "bulk prostate examination" and allows to assess the shape, size, degree of infiltration of the tumor. Based on these parameters, the tactics of reference are planned.
Low-dose brachytherapy
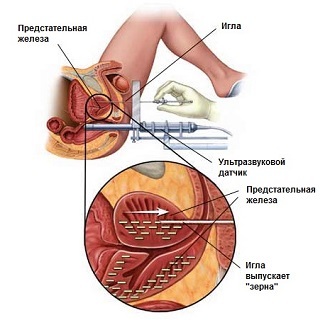
Fig.3 - Low-dose brachytherapy.
Before the procedure, a cleansing enema is performed. The procedure itself is performed under operating conditions under anesthesia. The patient is on a special urological chair.
The implantation of grains into the tumor( in the case of low-dose brachytherapy) is controlled by ultrasound images on the monitor screen with special needles, which are extracted after the procedure( see Figure 3).The dose of the radioactive component is calculated for each patient individually.
The procedure lasts 1.5 hours, and all this time the patient is under the supervision of doctors: an anesthesiologist, urologist, oncologist, radiologist.
High-dose brachytherapy
A combined effect of high-dose brachytherapy with external radiation therapy is often performed in the fight against malignant neoplasm of the prostate.
To carry out high-dose( temporary) interstitial therapy for a short time in the tumor tissue, the source of irradiation is introduced. A radioactive implant is extracted after exposure to tumor cells. Radioisotopes iridium-192 and cesium-137 are used as consumables.
In contrast to low-dose interstitial therapy, several irradiation procedures are performed to achieve a therapeutic effect. Usually limited to three manipulations for 5-15 minutes with a break of 48 hours.
After carrying out irradiation, anti-inflammatory antibacterial therapy must be prescribed for the prevention of prostatitis, cystitis, prostatocystitis, and rectitis.
Complications of brachytherapy
Because brachytherapy is considered a high-tech, gentle method for treating prostate cancer, adverse complications are rare. Some patients after the performed procedure observe:
- Urination disorders. Dysuric disorders, which are characterized by complaints of frequent urination with cuts, indicate an inflammatory process in the urinary tract( cystitis).
- Urethral stricture. As a complication of brachytherapy, the stricture( constriction) of the urethra may develop, which, if worse, will lead to an acute delay in urination.
- Urinary incontinence. Urinary incontinence is a rare undesirable effect of treatment, occurring in 1-2% of patients.
- Disturbance of erectile function. The degree of probability of the onset of erectile dysfunction directly depends on the age of the man. The higher the potency before the intervention, the greater the likelihood of maintaining sexual function after brachytherapy.
- Radiation inflammation of the rectum. A rather serious complication is the erosion on the inner surface of the rectum. Erosions can lead to the development of bleeding. The pathological process is accompanied by a sensation of itching, pain in the affected area.
The risk of migration of radioactive grains into the bladder is minimal, although such complications are described in the literature as casuistic. At the same time, the implants are not capable of causing any harm, since they have insignificant radioactivity and small size.
After performing low-dose brachytherapy, it is recommended to use a condom for several months.
Prognosis and further actions of
The survival rate for an unin- tected oncological process is high and does not depend on the methods of anti-cancer treatment performed. But oncology can be considered as a chronic process with periodic exacerbations. Therefore, after brachytherapy, it is necessary to regularly undergo a clinical urological examination:
- every 6 months( unless otherwise prescribed by an oncologist) to donate blood to the prostate-specific antigen;
- pass ultrasound of the prostate with a transrectal sensor;
- for suspected relapse of the tumor process - MRI.
Urological doctor Mishina V. V.
Recommended screen viewing: