Treatment of acute and chronic form of orhoepididymitis
Orhoepididymitis is an inflammatory process that encompasses the epididymis and directly the testicle itself. This is a fairly common problem that occurs in urological practice. The appendage is anatomically located on the posterior wall of the testicle: it is the connecting link of the testicle with the vas deferens.
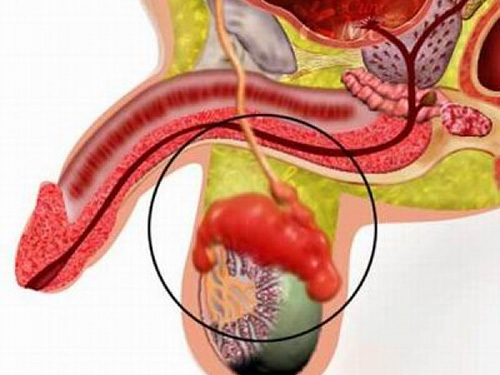
Orchoepididymitis is an inflammation of the testis and its epididymis.
The pathological process develops both independently and as a complication of the main infection that exists in the body - influenza, mumps, pneumonia. The disease has an infectious and non-infectious genesis, requires immediate treatment to the urologist. If you do not take appropriate therapeutic measures, you can not rule out the possibility of infertility.
Contents
- 1 Reasons
- 2 Symptoms
- 2.1 Acute form
- 2.2 Chronic form
- 3 Diagnosis
- 4 Treatment
- 5 Possible complications
- 6 Preventative measures
Reasons for
There are several causes of inflammation of such a vulnerable anatomical structure as the epididymis. They are classified into two groups - inflammation of an infectious origin and caused by factors of chemical and mechanical origin.
-
Sex infections cause orhoepididymitis in most cases.
Postponed damage. Sports injuries, the consequence of interference on the tissues of the genitals( inept use of the urethra, recent operation in the groin area).
- Bacterial microflora. In men of young age, the disease causes causative agents of sexually transmitted infections( trichomoniasis, gonorrhea, chlamydia).Patients over 40 years old suffer from orchid epididymitis, which arose in response to penetration of the testicles of E. coli, a pathogen that is in the digestive tract.
- Uncured diseases that encompass the organs of the urinary tract or the prostate gland.
A predisposing factor to the development of inflammation of the epididymis is the preference for anal sex, the use of certain medications, the periodic stagnation of urine( mainly when an adenoma is formed in the prostate tissue - a benign tumor).Fungal flora, mycobacteria, despite its pathogenic ability, rarely become a source of inflammation within the testicle.
Symptoms
Depending on the form of the disease, the manifestations of the pathological process become noticeable one day after the negative effect on the organ. The disease is acute and chronic. If the inflammation is not suppressed in the first phase, the process acquires a lingering course, causing not only permanent discomfort, but also certain complications. It is possible to establish in what form orchid epididymitis is present, by observing the nature and manifestations of symptoms.
Acute form
The disease begins suddenly, the first signs that attract attention are pronounced discomfort during motor activity and the inability to stay in a sitting position. Other pathological events are divided into the following categories:
-

Pain, swelling and redness of the scrotum are the main symptoms of orchoepidymitis.
Pain syndrome. The pain extends to the testicle( in some clinical cases, immediately to both - then the disease is called bilateral orchid epididymitis), scrotum, perineum. An intense unpleasant sensation makes it impossible to walk normally, rest, when you come in contact with clothing - it intensifies. Accompanying the entire period of the disease.
- Hyperthermic syndrome. The affected area of the intimate zone is hot touch, the overall body temperature rises to high figures, the patient has chills, malaise. When the fever gets worse, the man has a headache, muscle ache and bones are noted.
- Swelling and redness of the scrotum. The inflamed testicle increases in size, reaching a value 3-4 times higher than the physiological parameters of a healthy male organ.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes. The regional segments, which are part of the human immune system, become inflamed, indicating the presence of pathology in the area of their location.
- Problems with urination. Urinary discharge occurs more often, in its composition it is possible to visualize an admixture of blood( hematuria).
In certain cases, the seed ducts are involved in the process, which causes the formation of a specific dense strand in the inguinal region.
Chronic form of
Symptoms are observed over half a year. The size of the scrotum is often not increased: this leads the patient into delusions, encouraging that the disease receded without the need for medication. The fertilizing property of sperm is reduced, the condition is complicated by inflammation of the spermatic cord. Attempts to palpate the epididymal tissue cause considerable pain to the patient; at other times, discomfort occurs only with motor activity( unlike the acute form of the disease, when an uncomfortable sensation worries even when lying down).
Diagnosis
Examination is the logical actions of a patient who is concerned about the manifestations of the disease in question. The urologist will propose the diagnosis - this specialist needs to be addressed, noticing pain, swelling of the testicle, fever and chills.
Data collection. A doctor interrogates a man, collecting information about his main complaints about the condition of the reproductive organ, clarifies the nature and characteristics of his sexual life( to suggest the connection of orhoepididymitis with a venereal infection).The urologist needs to know whether the patient has recently undergone surgical interventions in the groin area, whether he has a urethral catheter. Important information - was there no recent damage to the scrotum( bumps, squeezing, falls), as a long time the man was sick with viral diseases.
Inspection. The next stage of diagnosis is inspection. The Urologist wears disposable gloves, asks the patient to lie down on the couch. Then he examines the affected area. If the orhoepididymitis is unilateral, the scrotum will be skewed in one direction, and asymmetric edema, in conjunction with the crimson color of the testicle and the general hyperthermia - leave no doubt in establishing the correct preliminary diagnosis.
Assays. Also a man has to undergo several types of tests:
- Clinical and biochemical examination of blood and urine. The analysis clearly reflects the presence of inflammation in the body - elevated levels of leukocytes, ESR.
- Bacteriological examination of a smear from the urethra. The procedure is aimed at identifying a pathogenic microorganism, which will simplify the appointment of an antibiotic, which is prescribed taking into account the characteristics of the primary pathogen.
- PCR and ELISA are tests that detect the presence of a venereal infection( this factor is the most common cause of orchid epididymitis).
Supporting methods. From auxiliary methods, scrotal ultrasound is used - sound oscillations help visualize the presence of a hernia, hydrocele( hydrocele), a tumor process. The specialist can resort to CT or MRI, but the need to implement them is rare.
Treatment of

The main treatment for orhoepididymitis is taking antibiotics.
First of all, the urologist appoints antibiotic therapy .To achieve a therapeutic effect, the drug should not be resistant to the causative agent of orchoepidymitis, since the treatment will be useless. Therefore, the specialist is guided by the data of bacteriological research. Effective antibiotics are Ceftriaxone, Amikacin, Ceftazidime. The optimal course of administration is 10 days( twice a day).
Further treatment is symptomatic. Hyperthermia is eliminated with antipyretics. Be sure to perform anesthesia patient.
Because the disease causes tissue scarring, constriction of the ureter and seminal duct lumen, the urologist prescribes administration of lidase and aloe , which hinder the development of these complications. The drugs are administered intramuscularly and subcutaneously.
To achieve a more rapid recovery, a specialist prescribes the performance of physiotherapy procedures( course - at least 10 sessions).
If the orchoepidymitis is caused by sexually transmitted diseases, the venereologist is connected to the main treatment - he will make the appointment of the appropriate antibiotics and immunomodulators, taking into account the sexual infection. Treatment will take at least a month. The peculiarity is that to pass it simultaneously you will need a male sexual partner.
Surgical treatment is used in extreme cases - when suppuration has a sufficiently large spectrum and the probability of sepsis is high. The wound is drained, the patient is in a urological hospital, under the supervision of doctors. Starting from the second day after the operation, the man performs dressings using an antiseptic solution. The prognosis is favorable.
Possible complications of
Negative consequences and complications of orcoepidymitis:
- Necrosis of testis. Inflamed tissue is destroyed and dies.
- Sepsis is a pathological phenomenon in which a bacterial flora moves into the bloodstream and a person dies. Untreated orcoepididymitis provokes loss of testicular functions.
Scrotal abscess is a vast purulent inflammation that causes a constant increase in body temperature, unbearable, paroxysmal pain and an extremely unfavorable general condition of the body. Treatment - only operative. If delayed with surgical intervention, sepsis will occur.
- Spread the inflammatory process to nearby organs and anatomical structures.
- Gangrene Fournier is an extremely pernicious consequence of orcoepididymitis. Purulent inflammation covers the scrotum and perineum. Sometimes the anal opening is involved in the pathological process. The tissue is destroyed, rotted, decomposed. The treatment is very complex, long, requires constant dressings and the introduction of large amounts of medication.
- Infertility. Complication of inflammation of the epididymis develops for several reasons - the testicle produces antibodies against its own germ cells, as a result of which spermatozoa are deprived of fertilizing ability. In addition, they can not move along the seminal canal, because its lumen is narrowed by the inflammation.
Preventative measures
Prevention of orchid epididymitis requires caution during exercise or physical activity. It is equally important to avoid hypothermia, to seek medical help in time for viral and infectious diseases. Perform hygienic procedures daily( see 5 rules of intimate hygiene of a man), regularly replace underwear, in order to avoid the development of bacterial infection. Cleanliness in intimate life will help to avoid the development of venereal infections - for this, a man needs to give up casual sexual relations and use contraceptives.
Orhoepididymitis refers to a disease that can never be encountered during life, the main thing is to review the attitude towards one's own health and objectively assess the level of possible complications in the event of the refusal of timely treatment.
Recommended for viewing: