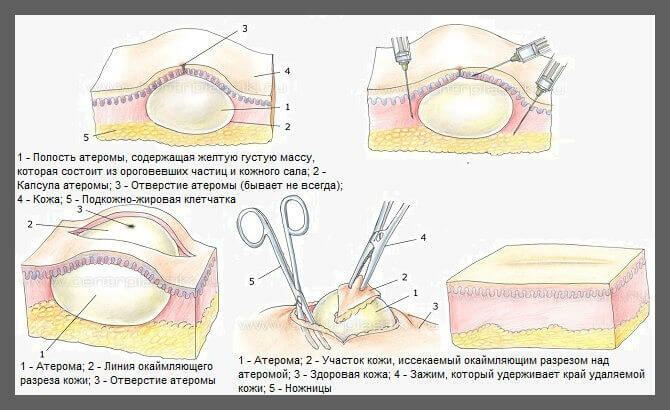
Microsporia of the scalp: symptoms, treatment
This article will detail the topic "Microsporia of the scalp: symptoms, treatment", which will describe in detail all the answers to your questions about this disease. Microsporia is a fungal skin disease caused by anthropophilic rusty fungi( Microsporum ferrugineum) and zoo anthropophilic canine fungi( Microsporum canis).
Clinic and symptomatology of
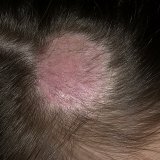
The symptoms of microsporia are different, depending on the form and stage of the disease. The appearance of this skin disease is characterized by the formation of pink-red spots, which have a rounded shape and clearly delineated boundaries, and a small amount of white scales is found on the surface of these spots. The favorite places for their placement of the microsporia are the crown, parietal and temporal areas of the head. It can be as several foci as large as five centimeters, round or oval, with clear boundaries and contours, and located near larger foci somewhat smaller with dimensions not exceeding 1.5 centimeters in diameter.
At its initial stage, the disease manifests itself as a site on which a certain peeling is formed. At this point, the pathogenic fungus is only at the very mouth of the hair follicle. If the infected area is subjected to a more precise examination, it will be possible to see how the whitish ring-shaped scaly surrounds the hair in the form of a cuff. Next, within seven days, the disease actively passes directly to the hair, which in turn becomes very fragile and brittle and often subject to skin breakdown by four to six millimeters, which from the side resembles a hair cut very short. And in the people this disease is called nothing else but "ringworm."Hair broken, look at times very dull and have a touch of grayish-white color. The skin in the affected area also suffers. It has a reddened, swollen appearance, and the affected areas are completely covered with a touch of grayish-white scales. Microsporia, acquiring a deep or suppurative form, is characterized by inflammation of the hair follicle itself and the development of deep cyanotic-red infiltrates. This form is very dangerous for the patient and requires mandatory treatment to a dermatologist.
Diagnosis of this disease
Microsporia of the head requires mandatory diagnosis, which should be performed by a dermatologist. To establish an accurate and correct diagnosis, three methods of research are commonly used: luminescent, microscopic and cultural.
Luminescent study characterizes the process of detecting a bright green glow, which indicates the damage caused by pathogenic fungi of the genus microsporium, thanks to a special Wood lamp. Until now, the cause of this phenomenon has not been clarified. This study should be conducted in a dark premise, after cleaning the hair and scalp from crusts, scales or ointments. Glow in the initial stages of the disease may be almost completely absent, in order to more clearly define the infection, it is necessary to remove the hair from the hair bulb and if it really is present, then the root part will certainly have a glow. A study of this kind serves to: determine the specific pathogen, determine the amount of affected hair, determine the actual results of the therapy, control the spread of the disease, determine the animal that spread the infection. The next diagnostic method is microscopic. This form of the study is designed to confirm fungal disease, in which flakes taken from foci are examined, and if necessary, hair fragments taken in the scalp are involved in the study. The conclusion of the microsporia diagnosis is a culture test. This type of study is carried out only in the case of a positive result of the previous two studies and serves to identify fungi-pathogens. Thanks to this method, it is possible to determine the type and genus of the pathogen, and accordingly to prescribe adequate medication and means for the prevention of the disease.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of microsporia is a long-term process. The main drug effective in treating this disease is griseofulvin. The drug is administered by a doctor, the treatment is carried out according to a special scheme and under control, both over the composition of urine and on the composition of blood once a week. The intake of this drug is 1 kg of human weight = 22 mg, i.e., only one teaspoon of the drug is needed, which is best taken with meals, preferably with vegetable oil or fatty foods. The drug is used daily until a negative analysis is obtained for this type of fungus, then, without changing the dose, take two weeks of taking the medicine in a day and the next two weeks only twice a week in the same amount. In total, treatment should last at least forty-forty-five days. Regardless of the drug, the foci affected by the disease are lubricated with a mixture of 5% iodine solution, 10% sulfuric ointment and 10% sulfur-tar paste.
Another option for treatment may be to superimpose a pre-cut infection site of a 4% epilin patch, which is fixed to the usual one. It is imposed first for the first ten days, then it changes to a new one and ten more days. The amount of epilene patch depends on the weight of the patient.
Also in the treatment of microsporia, the use of triderm cream will be beneficial. If the disease has a deep form, then it is necessary to connect the use of drugs containing dimexide. A mixture of 10% solution of quinazole, salicylic acid - 10, dimexide - 72 and distilled water - 8 was widely used. This mixture should be applied to the affected areas twice a day, until complete recovery.