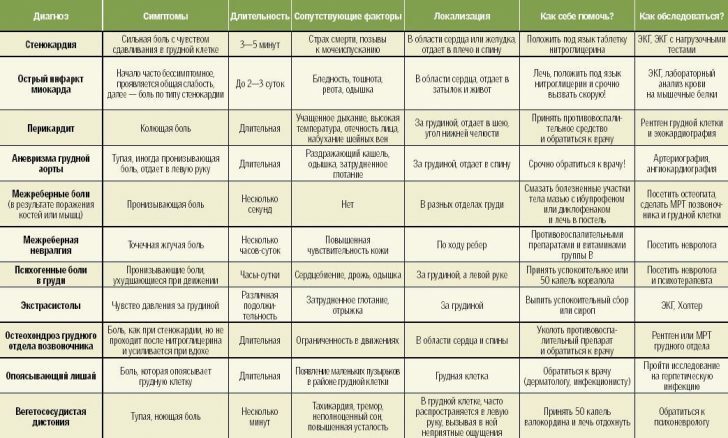
Encephalopathy of the brain: what is it, treatment and consequences
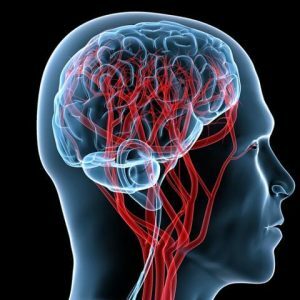 Encephalopathy is a pathological condition of non-inflammatory nature, for which dystrophic changes in the brain tissues are characteristic.Encephalopathy is a collective concept, behind which lies many diseases, both congenital and acquired.
Encephalopathy is a pathological condition of non-inflammatory nature, for which dystrophic changes in the brain tissues are characteristic.Encephalopathy is a collective concept, behind which lies many diseases, both congenital and acquired.
Types of encephalopathies
Most often, encephalopathy progresses gradually against the background of the existing disease.Although it is possible and rapid development of encephalopathy, for example, with acute renal failure( ARF) or hypertensive crisis.
Depending on the original cause, these forms of encephalopathy are distinguished:
- Post-traumatic - develops after brain injuries.
- Discirculatory - develops against the background of disorders of blood supply to the brain.There are atherosclerotic, hypertensive, venous forms.
- Dismetabolic - occurs when metabolic disorders occur.This includes hepatic, uremic, hyperosmolar, hypoklikemic and other encephalopathies.
- Toxic - occurs against a background of constant intoxication by toxic substances.In this group, alcoholic encephalopathy is separately isolated.
- Radiation - develops when exposed to ionizing radiation.
- Perinatal - occurs in children from the 28th week of intrauterine development and until the first seven days of life when exposed to various adverse factors.
Symptoms of acquired encephalopathy
The clinical picture of encephalopathy is due to impaired brain function due to dystrophic changes.Symptoms of the disease can have varying degrees of intensity in individual patients. In general, encephalopathy is characterized by the following symptoms:
-
 Memory impairment - difficulty in trying to recall current events;
Memory impairment - difficulty in trying to recall current events; - Attention concentration disorders - absent-mindedness, difficulties in memorizing new information;
- Narrowing the circle of interests;
- Emotional disorders - characterized by emotional lability( rapid mood swings, tearfulness), possible depression;
- Headache of uncertain localization;
- Dizziness;
- Rapid fatigue in the performance of physical and mental work;
- Sleep disturbance - daytime sleepiness, sleeplessness at night.
These are common symptoms of encephalopathy.With each form of encephalopathy, characteristic signs due to the pathological condition will also be observed.
Circulatory encephalopathy
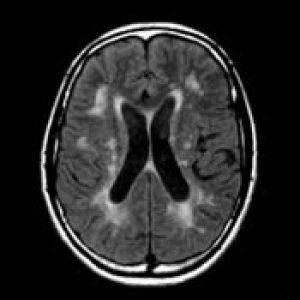 Circulatory encephalopathy is formed against a background of impaired blood flow to the brain. Distinguish atherosclerotic, hypertonic and venous forms.
Circulatory encephalopathy is formed against a background of impaired blood flow to the brain. Distinguish atherosclerotic, hypertonic and venous forms.
With atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels, the lumen of the vessel overlaps the cholesterol plaque, which creates an obstacle to normal blood flow.Long-term infringement of blood supply inevitably leads to the development of dystrophic changes in brain tissue.
With arterial hypertension, spasm of cerebral vessels occurs, which leads to cerebral ischemia.
Venous encephalopathy occurs when there is a venous outflow from the brain.There is a venous congestion, which is followed by swelling of the brain tissue.
Severity of symptoms of the disease depends on the stage of development of the pathological process. There are three stages of dyscirculatory encephalopathy:
- Stage 1 - the patient is concerned with headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, fatigue, impaired concentration, sleep, memory, emotional lability, tearfulness, episodic increase in pressure.At this stage, the above symptoms occur at the end of the working day, after a heavy load and decrease after rest.
- 2nd stage - characterized by the strengthening of the above characteristics.Symptoms become more persistent, they can be observed even after rest.
- 3rd stage - fainting, convulsive seizures, memory deterioration, coordination, shaky walk, cognitive activity and intellect decrease, vascular dementia develops - dementia.
Toxic encephalopathy
 Toxic encephalopathy can cause various toxic agents: alcohol, drugs, some medications.In addition, toxic effects on the brain are made by mercury, lead, manganese, toluene, arsenic, gasoline, which are encountered in their work by specialists in certain professions.
Toxic encephalopathy can cause various toxic agents: alcohol, drugs, some medications.In addition, toxic effects on the brain are made by mercury, lead, manganese, toluene, arsenic, gasoline, which are encountered in their work by specialists in certain professions.
The most common is alcoholic encephalopathy .This is a condition that develops against a background of chronic alcohol abuse.The reasons for the development of encephalopathy lie in the fact that the alcohol itself has a directly neurotoxic effect, and also reduces the flow to the neurons of important amino acids, minerals, vitamins.In addition, alcoholics, as a rule, inadequately eat, they have a deterioration in the absorption of vitamins.Because of this, a deficiency of B vitamins develops, which contributes to the development of encephalopathy.
Symptoms of alcoholic encephalopathy are:
- Loss of appetite;
- Insomnia;
- Memory impairment, including amnesia;
- Physical fatigue;
- Mood swings, often irritability;
- Tremor;
- Signs of personality degradation( the person is "flattened", the person is not interested in anything, the intellect is reduced, the humor becomes flat);
- In acute encephalopathy, delusions and hallucinations occur.
Dismetabolic encephalopathy
Dismetabolic encephalopathy develops against the background of metabolic disorders .It occurs with diseases of the liver, kidneys, as well as the pancreas.
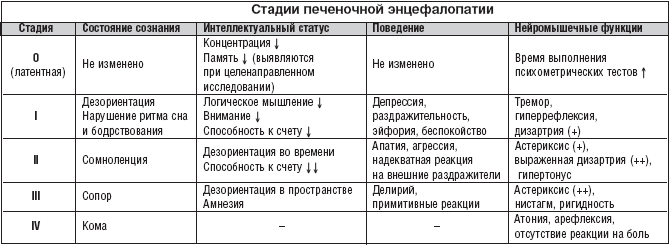
So, with liver diseases accompanied by death of hepatocytes, toxic substances are not neutralized and have a detrimental effect on the brain. Hepatic encephalopathy proceeds in four stages:
- 1st stage - absentmindedness, sleep disturbance, decreased attention and concentration, tremor;
- 2nd stage - daytime drowsiness and sleeplessness at night, fatigue, apathy, inadequate behavior, disorientation in time, monotonous speech;
- 3rd stage - pronounced disorientation, stopper, incoherent speech, delirium, convulsions;
- Stage 4( hepatic coma) - manifested by a lack of consciousness in the patient, the appearance of pathological reflexes.In addition to neurologic symptoms, signs of hepatic insufficiency( jaundice, hemorrhagic phenomena, etc.) are also observed.
In renal diseases, renal( uremic) encephalopathy develops.The first manifestations of uremic encephalopathy are drowsiness, as well as violations of concentration of attention.In the future, such symptoms as apathy or vice versa, agitation, headache, dizziness, short-term memory disorders, coordination disorders, convulsions are added.There may be mental disorders.
The most common pancreatic disease that causes CNS damage is diabetes mellitus .This is not surprising, because the brain cells are very sensitive to changes in the level of glucose in the blood, which is observed in diabetes mellitus. Diabetic encephalopathy is characterized by the following symptoms:
-
 Weakness, fatigue;
Weakness, fatigue; - Headache;
- Dizziness, precancerous condition;
- Meltshenie "flies" before the eyes;
- Shakiness;
- Impaired memory, attention;
- Apathy, depression;
- Sometimes confusion, convulsions may develop.
Post-traumatic encephalopathy
 Post-traumatic encephalopathy is characterized by the appearance of persistent impairment of brain function after the CCT .And signs of encephalopathy can occur both in the immediate after the trauma time, and in the long term, for example, after years. Post-traumatic encephalopathy is particularly susceptible to boxers, because for their professional careers receive many strokes on the head and as a result of micro-concussions of the brain.
Post-traumatic encephalopathy is characterized by the appearance of persistent impairment of brain function after the CCT .And signs of encephalopathy can occur both in the immediate after the trauma time, and in the long term, for example, after years. Post-traumatic encephalopathy is particularly susceptible to boxers, because for their professional careers receive many strokes on the head and as a result of micro-concussions of the brain.
Traumatic encephalopathy is manifested by weakness, fast fatigue.Many people with post-traumatic encephalopathy complain about problems with attention and concentration.The person has difficulties with memorizing new information.From this everything deteriorates working capacity.
In addition to memory impairment and concentration of attention, thinking disorders can also be noted.Thus, in a person with post-traumatic encephalopathy, mental processes can be slowed down, analytical activity may be violated.Apathy develops, the patient has little interest, he can not get out of bed for days.
There are also disturbances in the emotional sphere.There is emotional lability, manifested by a rapid change of mood, vulnerability, tearfulness.There may be short flashes of irritability, for which the patient then repents.
After an injury, epileptic seizures may occur, dullness of consciousness( twilight consciousness). For twilight consciousness is characterized by a violation of consciousness, in which a person performs as if purposeful, deliberate actions, but the person himself does not give an account of what was done and after the attack he can not remember anything.At this time, there may also be delusions, hallucinations. Such conditions can be dangerous for others, because a person does not control himself .
Symptoms of congenital encephalopathy
Congenital encephalopathy( also called perinatal encephalopathy) can form in the uterus in utero and the cause of this condition are all kinds of genetic defects, brain development abnormalities, infectious diseases, umbilical cord entanglement, fetal hypoxia, endocrine effects, intoxications, autoimmuneconflict.Also, encephalopathy can develop when an injury occurs during childbirth.
Symptoms of perinatal encephalopathy:
-
 General restlessness of the newborn, excessive motor activity;
General restlessness of the newborn, excessive motor activity; - Violation of muscle tone;
- Convulsions;
- Infringement of sucking, swallowing;
- Eyelids( ptosis), different pupil diameters( anisocoria), strabismus;
- Sleep disorder;
- A shrill scream;
- Bulging of a large fontanel, etc.
Diagnosis
If a patient is suspected of having encephalopathy, the doctor will ask the patient to undergo a diagnostic test. First of all, patients need to undergo clinical studies of ( such as general blood and urine tests, biochemical blood test, determination of blood glucose level).These studies will allow to determine changes in the body, in particular, which are caused by disturbances in metabolic processes.
In addition, in the diagnosis of encephalopathy resort to the use of instrumental research methods:
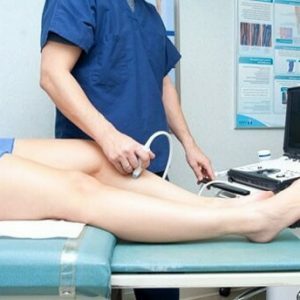
- US of extracranial arteries - allows assessing the patency of the neck located on the neck, blood supplying the brain;
- Transcranial dopplerography( TCDG) - allows an assessment of blood flow through arteries located directly in the cranial cavity;
- Computer and magnetic resonance imaging - allows detailed study of the structure of brain tissue and identify possible changes, blood clots, areas of softening of brain tissue, etc.
Treatment of brain encephalopathies
Dystrophic disorders in the brain tissues that formed with encephalopathy are by and large irreversible .However, to improve the patient's condition and prevent further progress of the pathological process is quite possible with the help of medications.In the fight against encephalopathy, first of all, one must take into account the cause of the development of the disease.
In general, for the treatment of encephalopathy apply such medicines:
-
 Antihypertensive drugs - in the presence of arterial hypertension in the patient;
Antihypertensive drugs - in the presence of arterial hypertension in the patient; - Hypolipidemic agents( Fenofibrate, Clofibrate) - in the presence of atherosclerosis;
- Group B vitamins - improve trophism of nervous tissue, as well as brain function;
- Detoxication means - excrete toxic substances from the body( alcohol, drugs, ammonia, etc.);
- Preparations that improve the blood supply to the brain( Caviton, Cynarizine);
- Nootropics( Noobut, Nootropil, Cerebrolysin);
- Antioxidant preparations( Tiotriazolin);
- Sedatives( Novopasit, Glyssid);
- Anticonvulsants( Diazepam).
From non-drug therapies, you should pay attention to the massage of the neck and collar zone, medical gymnastics, as well as physiotherapy( electrophoresis, magnetotherapy, UHF therapy), acupuncture .These methods will complement the existing basic treatment and improve the patient's condition.
Encephalopathy in each person proceeds in different ways.Here the role of the form of encephalopathy, and the duration of its existence, severity, the presence of complications play a role.Some people live peacefully with encephalopathy all their lives, others have expressed health problems.Therefore, the issue of disability is decided individually. If the ailment restricts a person's ability to work, or the patient loses the ability to move, to self-service - it is necessary to contact the Ministry of Healthcare for disability registration.
Grigorova Valeria, medical reviewer