Gastroesophageal reflux symptoms and treatment
Gastroesophageal reflux - a cast of gastric( GI) contents in the lumen of the esophagus.Reflux is called physiological if it appears immediately after a meal and does not give a person obvious discomfort.If the reflux occurs often enough at night, accompanied by unpleasant sensations - this is a pathological condition.Pathological reflux is considered within the framework of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Contents: Refluxes physiological and pathological classification of reflux Causes GERD Symptoms of GERD complications of GERD Gastroesophageal reflux in children Diagnosis Treatment PreventionRefluxes physiological and pathological
Hydrochloric acid has an irritating effect on the esophageal mucosa and provoke its inflammation. Preventing damage esophageal mucosa is performed by the following mechanisms:
- presence of gastroesophageal sphincter, the reduction of which leads to a narrowing of the esophagus lumen and prevents the passage of food in the opposite direction;
- Stability of the esophageal mucosa to gastric acid;
- The ability of the esophagus to self-clean from abandoned food.
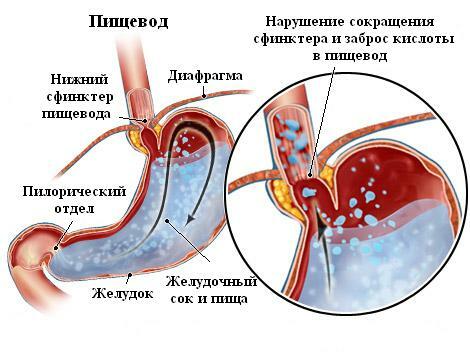
When any of these mechanisms is violated, there is an increase in frequency, as well as the duration of reflux.This leads to irritation of the mucous membrane with hydrochloric acid followed by the development of inflammation.In this case, one should speak of pathological gastroesophageal reflux.
How to distinguish physiological gastroesophageal reflux from pathological?
For physiological gastroesophageal reflux disease is characterized by such symptoms:
- emergence postprandial;
- No concomitant clinical symptoms;
- Low reflux rate per day;
- Rare episodes of reflux at night.
for pathologic gastroesophageal reflux disease is characterized by the following features:
- Occurrence of reflux and without meals;
- Frequent and prolonged reflux;
- Appearance of reflux at night;
- Accompanied by clinical symptoms;
- Inflammation develops in the esophagus mucosa.
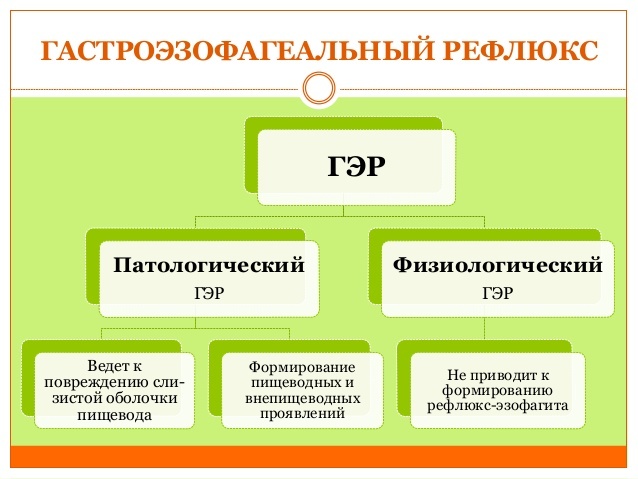
Classification refluxes
Normally esophageal acidity is 6.0-7.0.When gastric contents including hydrochloric acid are thrown into the esophagus, the acidity of the esophagus drops to less than 4.0.Such refluxes are called acidic.
With acidity of the esophagus from 4.0 to 7.0, they speak of weakly acid reflux.And finally, there is such a thing as superreflux.This is acid reflux, which occurs against a background of already reduced acidity level of less than 4.0 in the esophagus.
If gastrointestinal contents are included in the esophagus, including bile pigments and lysolecithin, the acidity of the esophagus rises above 7.0.Such refluxes are called alkaline.
Causes of GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease( GERD) is a chronic disease caused by spontaneous and systematically repeated throwing into the esophagus of gastric( gastrointestinal) contents, leading to damage to the mucosa of the esophagus.
GERD develops due to the following reasons:
-
 Decreased functional capacity of the lower esophageal sphincter( eg, due to the destruction of the esophagus in the hernia of the esophageal diaphragm);
Decreased functional capacity of the lower esophageal sphincter( eg, due to the destruction of the esophagus in the hernia of the esophageal diaphragm); - Decreased clearance of the esophagus( for example, due to a decrease in the neutralizing effect of saliva, as well as bicarbonates of esophageal mucus);
- Damaging properties of gastrointestinal contents( due to the content of hydrochloric acid, as well as pepsin, bile acids);
- Disorders of gastric emptying;
- Increased intra-abdominal pressure;
- Pregnancy;
- Smoking;
- Overweight;
- Admission of medications that reduce smooth muscle tone( calcium channel blockers, beta-adrenomimetics, antispasmodics, nitrates, M-cholinolytics, zhelchesoderzhaschie enzyme preparations).
The development of the disease is influenced by eating habits and eating patterns.Rapid absorption of a large amount of food with ingestion of air leads to an increase in pressure in the stomach, relaxation of the lower sphincter of the esophagus and casting of food.Excessive consumption of fatty meat, fat, flour products, sharp and fried foods leads to a delay in the food lump in the stomach and even increased intra-abdominal pressure.
Symptoms of GERD
Symptoms that occur with GERD can be divided into two subgroups: esophageal and extra-esophageal symptoms.
To esophageal symptoms, gastroenterologists include:
- Heartburn;
- Belching;
- Regurgitation;
- Acidic taste in the mouth;
- Swallowing disorder;
- Pain in esophagus and epigastrium;
- Hiccough;
- Vomiting;
- Sensation of the lump behind the sternum.
Out-of-oesophageal lesions occur due to the entry of refluxant in the respiratory tract, the irritant effect of the refluxant, the activation of esophagobrochial, esophagocardial reflexes.
Outside oesophageal symptoms include:
- Pulmonary syndrome( cough, dyspnea predominantly occurring in the horizontal position of the body);
- Otorhinolaryngopharyngeal syndrome( development of laryngitis, pharyngitis, otitis, rhinitis, reflex apnea);
- Dental syndrome( caries, periodontal disease, rarely aphthous stomatitis);
- Anemia syndrome - as the disease progresses on the mucosa of the esophagus, erosions are formed, accompanied by a chronic loss of blood in a small amount.
- Cardiac syndrome( pain in the heart, arrhythmias).
Complications of GERD
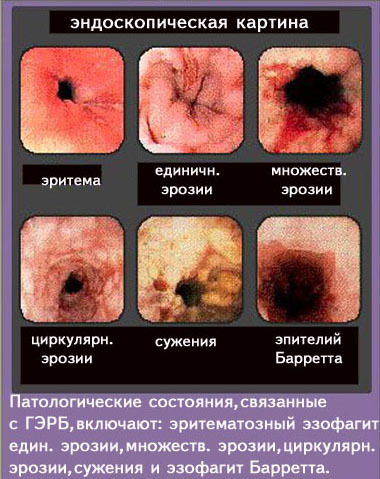
Among the most common complications is the formation of esophageal stricture, ulcerative-erosive lesions of the esophagus, bleeding from ulcers and erosions, formation of the esophagus of Barrett.
The most formidable complication is the formation of Barrett's esophagus.For the disease is characterized by the replacement of normal squamous epithelium by the cylindrical gastric epithelium.
The danger is that such metaplasia significantly increases the risk of esophageal cancer.
Gastroesophageal reflux in children
In the first few months of life, gastroesophageal reflux is normal.Infants have certain anatomical and physiological characteristics predisposing to the formation of reflux.This and the underdevelopment of the esophagus, and low acidity of gastric juice, and a small amount of stomach.The main manifestation of reflux is regurgitation after feeding.In most cases this symptom is eliminated by the end of the first year of life.
 When hydrochloric acid in reflux damages the mucosa of the esophagus, GERD develops.In infants this illness manifests itself in the form of anxiety, tearfulness, excessive regurgitation, passing into profuse vomiting, there may be bloody vomiting, coughing.The child refuses food, poorly gaining weight.
When hydrochloric acid in reflux damages the mucosa of the esophagus, GERD develops.In infants this illness manifests itself in the form of anxiety, tearfulness, excessive regurgitation, passing into profuse vomiting, there may be bloody vomiting, coughing.The child refuses food, poorly gaining weight.
GERD in older children is manifested by heartburn, pain in the upper chest, discomfort when swallowing, a feeling of food stuck, an acid sour taste in the mouth.
Diagnostics
Various methods are used to diagnose gastroesophageal reflux disease.First of all, if you suspect a GERD, you need an endoscopic examination of the esophagus.This method allows to identify inflammatory changes, as well as erosive and ulcerative lesions on the mucosa of the esophagus, strictures, areas of metaplasia.
Patients also undergo esophagomanometry.The results of the study will give an idea of the motor activity of the esophagus, a change in the tone of the sphincters.
In addition, patients should undergo a 24-hour monitoring of the ph esophagus.With the help of this method, it is possible to determine the number and duration of episodes with abnormal indicators of acidity of the esophagus, their relationship with the appearance of symptoms of the disease, food intake, change in body position, and medication.
Treatment
In the treatment of GERD, medical, surgical methods are used, and lifestyle adjustments are also made.
Medical treatment
Drug therapy is aimed at normalizing acidity, as well as improving motor function.
- Prokinetics( domperidone, metoclopramide) - to strengthen the tone and reduce the lower esophageal sphincter, improve the transport of food from the stomach into the intestine, reduce the number of reflux.
- Antisecretory agents( proton pump inhibitors, H2-histamine receptor blockers) - reduce the damaging effect of hydrochloric acid on the esophageal mucosa.
- Antacids( phosphalugel, almagel, maalox) - inactivate hydrochloric acid, pepsin, adsorb bile acids, lysolecithin, contribute to the improvement of esophageal cleansing.
- Repellents( sea buckthorn oil, dalargin, misoprostol) - accelerate the regeneration of erosive and ulcerative lesions.
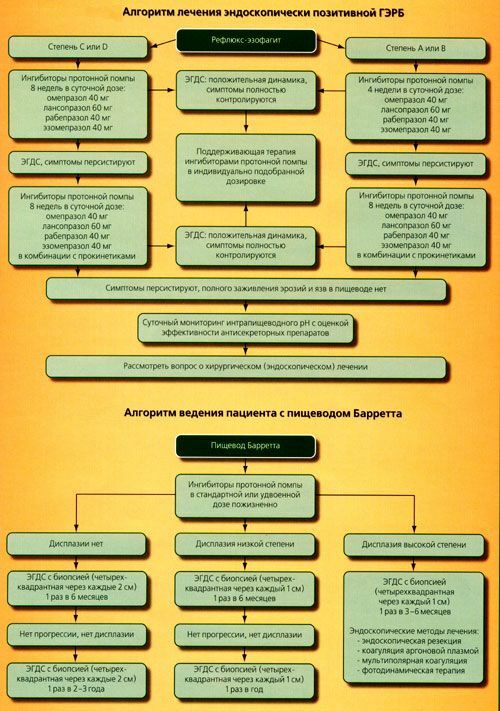
Surgical treatment
To surgical intervention resorted to the development of complications of the disease( stricture, esophagus Barrett, reflux esophagitis III-IV degree, ulcers of the mucosa).
An alternative in the form of surgical treatment is also considered if it is not possible to reduce the symptoms of GERD amid a correction of lifestyle and drug treatment.
There are various methods of surgical treatment of the disease, but in general they are reduced to restoring a natural barrier between the esophagus and stomach.
Prevention
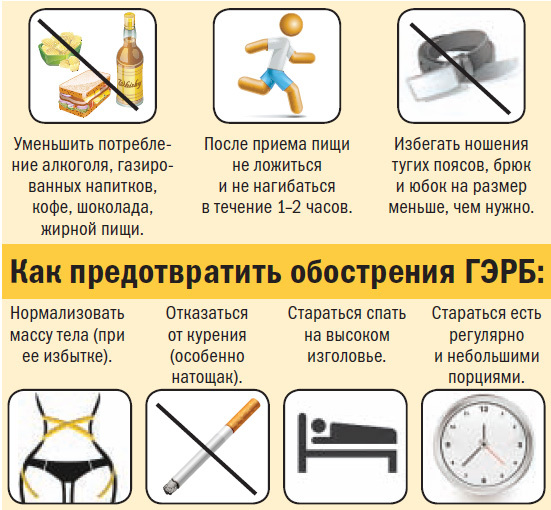
To fix the positive result of treatment, and also to prevent the occurrence of recurrences of the disease, the following recommendations should be adhered to:
- Fighting excess weight;
- Refusal from smoking, alcohol, caffeinated drinks;
- Restricting the use of products that increase intra-abdominal pressure( carbonated beverages, beer, beans);
- Restriction of the use of products with acid-stimulating action: flour products, chocolate, citrus fruits, spices, fatty and fried dishes, radish, radish;
- Should be eaten in small portions, slowly chewing, do not talk while eating;
- Restriction of lifting of weights( no more than 8-10 kg);
- Raising the head of the bed for ten to fifteen centimeters;
- Restriction of taking medications that relax the esophageal sphincter;
- Avoiding horizontal position after eating for two to three hours.
Grigorova Valeria, medical reviewer