Elevated blood platelets in the child's blood: what does it mean?
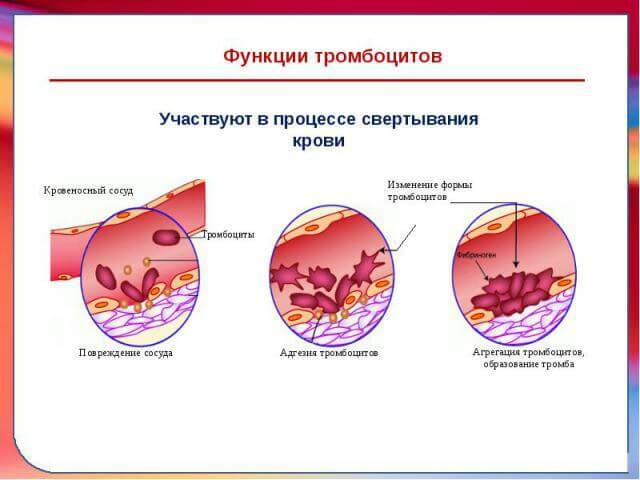
Platelets are the smallest blood cells that have the appearance of blood platelets and are responsible for the process of blood clotting.In fact, it is the platelets that provide the liquid state of the blood and participate in the formation of clots( thrombi).
Platelets are produced by special cells of the red bone marrow, are short-lived - their lifetime is only 10 days, and then the platelets are destroyed in the spleen and liver.Instead of the already destroyed blood platelets, new ones are formed, and this process is continuous.In some cases, platelet counts in the blood can be increased in childhood, and parents should know not only why this happens, but also how to solve the problem.
Table of contents: Rates of platelet count in children Causes of thrombocytosis in children Symptoms of thrombocytosis in children General principles of treatment Child nutrition for thrombocytosisRates of platelet count in children
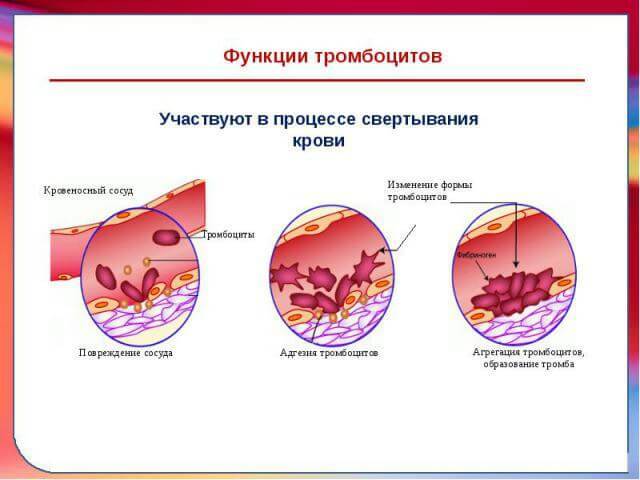
The number of platelets can be determined by a general clinical blood test - theyAre recalculated to 1 cubic milliliter.This indicator is considered one of the important, since it is he who characterizes the child's ability to cope with bleeding and assess the level of coagulation of the blood.
The norm of the number of platelets in the blood in children depends on their age:- in newborns, the norm is the platelet count of 100-420 thousand per 1 cubic milliliter of blood;
- in children aged 10 days to 12 months - 150-350 thousand;
- at the age of over 12 months - 180-320 thousand.
Note: in girls in adolescence, the first days of menstrual bleeding can be characterized by a decrease in the number of platelets, so the norm will be the figure of 75-220 thousand.
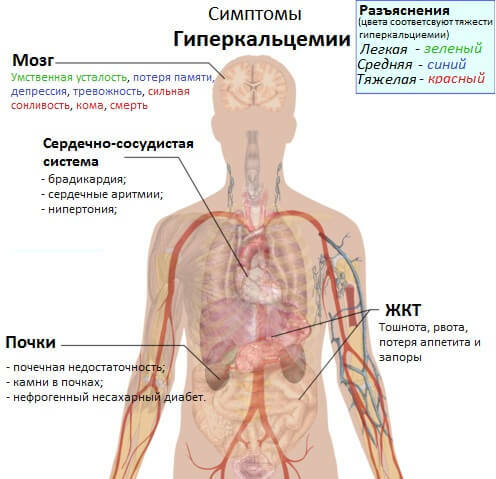
A high number of platelets in the peripheral blood is classified as thrombocytosis or thrombocythemia, while a decrease in their number is of thrombocytopenia .An increase in the norm may indicate the possibility of increased thrombus formation, but a reduced amount of platelets - about bleeding.
Blood for the determination of the number of platelets is taken from the finger or vein, in newborn children the fence is carried out from the finger on the foot or from the heel.The study requires any specific preparation - the patient must donate blood on an empty stomach, but the child can be given a drink.If it is a question of taking blood from a babe, then the manipulation is carried out 2 hours after the feeding.
Doctors warn that emotional or physical exertion is undesirable before the test is submitted, because even the usual hypothermia will show distorted results of the analysis.In addition, the results of the study may affect the use of certain drugs - antibacterial, corticosteroids.If a doctor has doubts about the correctness of the results, then it is possible to donate blood for the number of platelets 3-5 times.The results of the study will be ready on the day of blood donation.
Calculation of platelets in a blood test is done quite often in childhood.This can "push" frequent nasal bleeding, or parents noticed that the baby often has hematomas on the body, there is bleeding gums.The reason for giving blood tests for the number of platelets can be dizziness of the child, along with fatigue and periodic swelling of the upper / lower extremities.
Unconditional indication for the type of study under consideration is the presence of certain diseases in the history:
- iron deficiency anemia;
- viral infections;
- systemic lupus erythematosus and any autoimmune pathologies;
- enlargement of the spleen;
- Malignant blood diseases.
Causes of thrombocytosis in children
In medicine, it is considered that the causes of the development of thrombocytosis can be:
- erythremia - increased formation of blood platelets by the red bone marrow;
- too slow "utilization" of platelets - this usually occurs when the spleen is removed;
- disrupted distribution of platelets in the bloodstream - most often observed against mental or physical overwork.
If a high level of platelets is detected in blood tests, the doctor will have to establish the true cause of the development of this pathological condition, for which additional patient examinations will be assigned.In children, thrombocytosis can develop at any age, but parents should know that such a diagnosis is made by doctors even with a minimal increase in the number of platelets in the blood.
Thrombocytosis in medicine is divided into three main types:
- Clonal thrombocythemia.In this case, there is a defect of stem cells in the bone marrow, which may be due to the defeat of their tumor process.Stem cells do not react to ongoing endocrine processes, in connection with which the formation of the considered component of the blood becomes uncontrollable.
- Primary thrombocythemia.This condition is always associated with the proliferation of several sections of the red marrow, and the result is an incredible number of newly formed platelets.To lead to a similar pathology can some hereditary / congenital diseases, as well as erythremia or myeloleukemia.Primary thrombocythemia is characterized not only by an increase in the number of platelets, these blood components have huge dimensions and a modified shape.
- Secondary thrombocytosis.The mechanism of its development is quite variable:
- on the background of spleen removal, when the old platelets are not yet destroyed, and the new ones are already being actively formed;
- in the inflammatory process - the body intensively produces a hormone that promotes the maturation of blood platelets;
- for malignant neoplasms - they produce biologically active substances that exert a stimulating effect on the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow, which increases the number of newly formed platelets.
Secondary thrombocythemia can develop and in the presence of a number of pathologies in humans:
- any malignant neoplasm;
- tuberculosis;
- amyloidosis;
- anemia of iron deficiency or hemolytic type;
- cirrhosis;
- rheumatism, which proceeds in the active stage;
- fractures of tubular bones;
- ulcerative colitis;
- acute blood loss;
- osteomyelitis;
- removal of the spleen;
- acute and / or chronic infectious diseases;
- any extensive surgical intervention.
Secondary thrombocytosis will be characterized by a less pronounced increase in the number of platelets in the blood, while their morphology and functions are not completely disturbed.
If the examined pathology was diagnosed for the first time, the physician will necessarily refer the patient to the following tests:
- Determination of C-reactive protein;
- determination of serum ferritin and iron;
- ultrasound examination of abdominal and pelvic organs;
- blood coagulation analysis;
- bone marrow examination.
Symptoms of thrombocytosis in children
Primary thrombocytosis will be characterized by the following symptoms:
-
 enlargement of the spleen;
enlargement of the spleen; - formation of thrombi of different localization;
- possible bleeding in the digestive organs;
- pain in the fingertips;
- intolerable itching of the skin;
- , there are disorders from the central nervous system;
- disturbed by the process of urination, pains in the anatomical location of the kidneys may be noted.
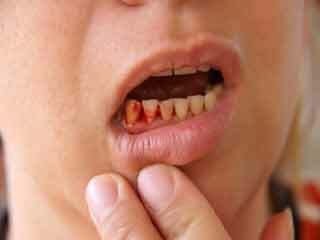
Specifically in childhood, this pathological condition can be accompanied by frequent nasal bleeding, gingival bleeding, bruising on the body even with a light touch.In addition, the child has cold extremities, recurring headaches, variability of blood pressure, increased heart rate.
General principles of treatment
 When diagnosing a primary type of thrombocytosis, doctors use cytostatics Mielobromol and Myelosan.Treatment will last for a long time, until the result is obtained, namely, the normalization of the number of platelets in the blood.
When diagnosing a primary type of thrombocytosis, doctors use cytostatics Mielobromol and Myelosan.Treatment will last for a long time, until the result is obtained, namely, the normalization of the number of platelets in the blood.
If the pathology in question is severe, then in addition to medicinal purposes, thrombocytopheresis is used as a treatment, when platelets are removed from the bloodstream using special equipment.
An integral part of therapy for thrombocytosis is the administration of medications that improve microcirculation and prevent the gluing of blood platelets - for example, Aspirin, Trental.But it is worthwhile to know that Aspirin is used only if there are no erosive changes in the digestive tract against the background of the pathology in question.
When diagnosing clonal thrombocytosis, patients are given Ticlopidine or Clobidogrel in an individual dosage - these are antiplatelet agents.
Often against the background of the pathology in question, thromboses and ischemic manifestations occur - with this development of events anticoagulants Heparin, Livarudin, and Argotoban are used.Such treatment should be carried out under strict laboratory control of the number of platelets.
Secondary thrombocytosis is an occasion for not only general therapy, but also preventive measures that prevent the development of thromboses.To worry in any case it is not necessary, because doctors even at a secondary thrombocytosis give quite favorable forecasts.
Nutrition for a child with thrombocytosis
The medical treatment of this pathology is important, but doctors say that to obtain the expected result, it is necessary to follow the diet of the patient. Breastfeeding, of course, the best option will be breastfeeding, but for older children it is extremely important to include the following products in the menu:
- seafood and nuts;
- milk and dairy products;
- red meat and by-products( liver, heart);
- fresh juices( pomegranate, lemon, orange, cowberry), diluted with pure water in a 1: 1 ratio.
Ginger, olive oil, beetroot, tomato juice, fish oil, cranberry, lemons, viburnum and sea buckthorn have an excellent liquefying effect on blood.It is important that the child uses the right amount of fluid per day - at least 30 ml per kilogram of weight, without fail it is necessary to give the child tea, compotes and vegetable broths.
During the treatment of thrombocytosis, it is strictly forbidden to consume walnuts, dog rose, bananas and mangoes - these products actively condense the blood, which can lead to the development of complications.
We recommend reading:The increased number of platelets in the blood of a child is a pathology that needs to be investigated.Make competent examinations, identify the true cause of the pathology and prescribe an effective treatment can only the doctor - independent decisions lead to deterioration of the child.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical reviewer, therapeutist of the highest qualification category