Causes of increased bilirubin in the blood
 Bilirubin refers to substances involved in the pigmentary metabolism of the body.It is formed from the products of the decay of erythrocytes.An increase in the norm of bilirubin in the blood is called by hyperbilirubinemia and occurs in certain types of diseases associated with liver dysfunction.Externally in the patient, the increase in the content of this pigment is manifested by jaundice.
Bilirubin refers to substances involved in the pigmentary metabolism of the body.It is formed from the products of the decay of erythrocytes.An increase in the norm of bilirubin in the blood is called by hyperbilirubinemia and occurs in certain types of diseases associated with liver dysfunction.Externally in the patient, the increase in the content of this pigment is manifested by jaundice.
Location blood appears bilirubin
Erythrocytes, red blood cells live on average about 4 months, after which they collapse in the organs of the reticuloendothelial system( most in the spleen, less in the liver and bone marrow).During the day approximately 1% of the red blood cells are disintegrated.During the decomposition, hemoglobin, a proteinaceous pigment of blood, is released, which further decomposes with the formation of verdoglobin.It is split off protein - globin and iron, resulting in biliverdin, recovered in bilirubin - an orange pigment, which enters the blood.Reactions of decomposition of erythrocytes release about 300 mg of bilirubin.Thus, about 85% of bilirubin appears in the blood, 15% is formed by the breakdown of other substances containing gems( organic compounds in iron) - myoglobins, cytochromes.
stages of bilirubin
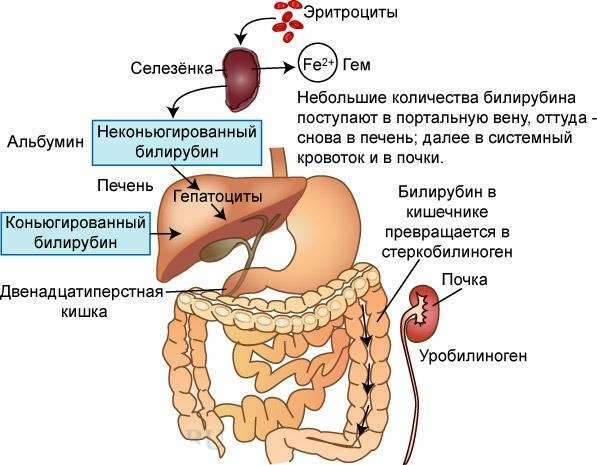
After disintegration erythrocyte bilirubin goes through the following steps changes:
- Initially it is in the free state ( unconjugated bilirubin) and practically insoluble in water( hence the name - insoluble ), Forms a complex with proteins and circulates in the blood.The second name is - "indirect bilirubin", because it is not able to give the so-called direct reaction of Van den Berg.This type of bilirubin has a pronounced toxicity to the body and can not be excreted by the kidneys.
- neutralizes indirect bilirubin in the liver cells by binding with glucuronic acid( conjugation) and forming a new form called bilirubinglyukuronid.This kind of bilirubin is already able to dissolve( soluble ), does not have toxic properties and is able to excrete with bile in the lumen of the intestine.It gives a direct reaction of van den Berg, therefore it is called "direct" bilirubin.
- With bile( excretion), bilirubin enters the lumen of the intestine, where it is restored to sterocilinogen.Part of it is transformed into sterkobeline and is excreted with feces( from 50 to 300 mg).It is this pigment that stains the feces in a dark color.The main part of the sterocilinogen is absorbed into the bloodstream and enters the kidneys, where it passes into urobilinogen, which changes into urobilin and is excreted in urine, staining it in a specific straw color.The amount of urobilin secreted by the kidney is about 4 mg per knock.
Indirect bilirubin is constantly transformed into a direct form.
The blood contains bilirubin and evaluated two types:
- indirect( free, unconjugated, insoluble) - toxic.Appears immediately after the breakdown of red blood cells.Normally its content does not exceed 17 μmol / l;
- direct( bound, conjugated, soluble).It forms in the baking after compounding with glucuronic acid.It is already non-toxic and harmless to the body.Normally contains up to 2.5 micromol / l;
There is also a common bilirubin.The blood content is about 20 μmol / l.
Different pathological conditions can cause an increase in the total content of bilirubin - hyperbilirubinemia, which is accompanied by jaundice.Depending on the cause of the painful process, the increase in bilirubin occurs due to its direct or indirect fractions.
Important: in severe cases bilirubin numbers several tens of times higher than normal, suggesting the need for immediate assistance to such patients.
On the problem of increase of bilirubin in infants tells the doctor:
What accounts for violation of pigment metabolism
Exchange pigments may fail for the following reasons:
- inability to receive free fraction of bilirubin from the blood into the liver cells;
- reduced transition( conjugation) of free bilirubin to bilirubinglucuronide;
- decreases the release of direct bilirubin from the hepatic cells into bile.
Any type of metabolic disorder leads to an increase in bilirubin in the blood.In patients with this problem, icteric staining of the skin and sclera of the eye appear.In the beginning, the face turns yellow, then the palms of the hands, the soles and the rest of the skin surface.The intensity of jaundice can depend on the appearance of the patients.At full it is less appreciable, and at people of a thin constitution appears more obviously.
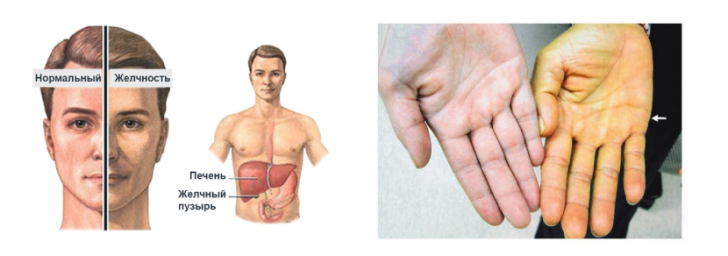
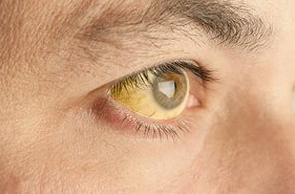 But do not call any change in the color of the skin jaundice, because the causes of skin discoloration are different, for example, when eating foods high in carotene( carrots).Also, skin color can change in diseases that are not related to the problems of pigment metabolism( pathology of the thyroid and pancreas).A distinctive feature in this case is the normal color of the sclera.
But do not call any change in the color of the skin jaundice, because the causes of skin discoloration are different, for example, when eating foods high in carotene( carrots).Also, skin color can change in diseases that are not related to the problems of pigment metabolism( pathology of the thyroid and pancreas).A distinctive feature in this case is the normal color of the sclera.
Note: bilirubin is able to accumulate in the nervous system, causing poisoning( intoxication).Also in this case, the balance of the ratio of direct and indirect bilirubin is disturbed.
What does "increased bilirubin" mean than what is called this state
What processes occur in the body, why does normal metabolism suddenly change?
High bilirubin occurs in the case of:
- Pathological processes leading to increased decay of erythrocytes( hemolysis).There is superhepatic jaundice , or hemolytic.This type of disorder can cause different types of anemia( anemia), infectious diseases, toxic lesions, a group of hereditary jaundice( Gilbert syndrome, Dabin-Jones, Kriegler-Nyar, Rotor), antibiotics, hormones, anti-inflammatory drugs.
The liver does not have time to "dispose" large amounts of indirect bilirubin and translate it in a straight line.Excess amount of indirect bilirubin accumulates in the blood.The content of urobilin in the urine, stercobilin in the stool increases.
- Infectious inflammation of the liver( hepatitis), cirrhotic processes that cause damage to liver cells( hepatocytes).In these cases, the hepatic-cell jaundice develops.In the damaged liver cells, indirect bilirubin does not go straight.Increased membrane permeability of hepatocytes promotes the release of indirect and direct bilirubin into the blood.The sterilization of the stool in the feces is reduced, so the color of the excrement becomes light.Also, as a result of the inadequacy of the enzyme, which turns indirect bilirubin into a direct one, an increase in total bilirubin in the blood due to the indirect fraction is observed.In the urine, the content of bilirubin and urobilin increases.
- Stagnant phenomena in the bile passages, with a disturbance in normal outflow due to obstruction of the duct with stones, swelling, because of swelling due to inflammation.The bile vessels swell, their permeability increases, and direct bilirubin goes directly into the blood, arises the mechanical jaundice .
- Insufficient intake of cyanocobalamin( vitamin B12) into the body;
| suprarenal jaundice | hepatocellular jaundice | mechanical jaundice | |
| Total bilirubin | Norm / Increased | Increased | Increased |
| unconjugated bilirubin | IncreasedNormal / Normal Increased | ||
| conjugated bilirubin Normal | Increased Increased | ||
| Urobiliogen | Increased | Norm / Increased | Decreased / Negative |
| urine color | orange-yellow | weakly colored | Dark( foaming, color of beer) |
| color chair | Dark | Bleached Bleached | |
| Alkaline phosphatase | Norma | Increased | Increased |
| ALT and AST | Norma | Increased | Norma |
detailed classification of jaundice is shown in the video review:
Features increase of bilirubin in infants
 In children, jaundice appears more often.This is due to the fact that the baby has a large number of red blood cells.After delivery, hemolysis goes much faster than before delivery.Neutralizing function of the liver is still imperfect.The child is determined by a high bilirubin with external manifestations of skin coloring in icteric color.
In children, jaundice appears more often.This is due to the fact that the baby has a large number of red blood cells.After delivery, hemolysis goes much faster than before delivery.Neutralizing function of the liver is still imperfect.The child is determined by a high bilirubin with external manifestations of skin coloring in icteric color.
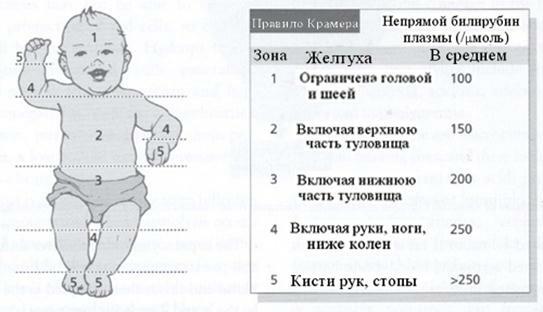
Children have some peculiarities of bilirubin exchange.The appearance of conjunctive jaundice, caused by the inferior binding of the free fraction of bilirubin, leads to its accumulation in the blood.This condition occurs in 80% of newborns and is called physiological jaundice. It appears after 3 days of birth and lasts about 2 weeks.Yellowness gradually spreads on the face, trunk, arms, legs, mucous membranes of the mouth, nasopharynx and conjunctiva of the eyes.
The level of bilirubin becomes maximum at the end of the first week and reaches a value of 140 μmol / l to 240 μmol / l.Jaundice often occurs in children born with prematurity.The duration of it in this case can be prolonged to 4-5 weeks.
If a glucuronyltransferase enzyme deficiency is present at birth, a rare disease called , congenital non-hemolytic hyperbilirubinemia with nuclear jaundice develops in children.The figures of bilirubin in the blood can reach 200-800 μmol / l.The norm of bilirubin in a newborn is 51-60 μmol / l.
In some cases, the genetic association of glucuronyltransferase insufficiency is traced.The capture of liver cells by free bilirubin is violated.Indirect bilirubin is kept at the level of 80-140 μmol / l.
older children bilirubin values are increased in patients receiving antibiotics, hormonal drugs, sulfa drugs, non-specific infections that cause acute respiratory infections and other diseases.
What to do to reduce bilirubin
In any case, if you have signs of icteric staining of the skin and sclera, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Important: should not self-medicate and use drugs and traditional medicine to determine the cause of jaundice and increased bilirubin, especially in young children.
In case of detection of infectious hepatitis, toxic liver damage will require hospitalization and treatment with the introduction of detoxification solutions.
The patient needs to create a sufficient drinking regime, apply diet food, and limit physical exertion.
Stepanenko Vladimir, Surgeon