Hemotorax: signs, diagnosis, first aid and treatment
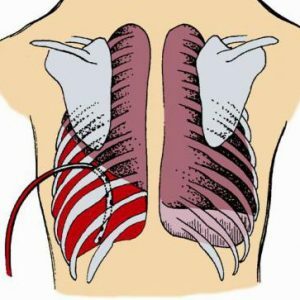 Hemotorax is a bleeding in the pleural cavity.Basically, hemothorax occurs due to damage to the organs and walls of the chest, and can occur with both open and closed injuries.
Hemotorax is a bleeding in the pleural cavity.Basically, hemothorax occurs due to damage to the organs and walls of the chest, and can occur with both open and closed injuries.
Causes and mechanisms of development of
Depending on the cause of hemothorax occurrence:
- traumatic - due to a chest injury;
- pathological - due to a pathological process that has developed in the wall or organs of the chest;
- iatrogenic - as a consequence of medical interventions;
- spontaneous - with it, blood flows into the pleural cavity spontaneously, the causes of this phenomenon are not established.
Iatrogenic hemothorax is actually a type of traumatic.Most often it occurs:
- after surgery - due to too extensive forced tissue trauma, or if the bleeding has not been stopped properly;
- during pleural puncture or thoracocentesis if they were performed with technical errors, or there were factors complicating the conduct;
- at the time of insertion of the catheter into the central venous vessel.
- curled - observed after surgical interventions, when the patient under the indications is coagulant therapy( it is aimed at increasing blood coagulation - in particular, to prevent bleeding). Because of the use of coagulants, blood discharges that have entered the pleural cavity are folded faster than with the usual hemothorax;
- pneumohemothorax - in the pleural cavity blood and air accumulate simultaneously.It is observed with traumatic rupture of the lung, melting of the focus of tuberculosis and injury of the thorax with a sharp massive object.
Upon the attachment of an infectious agent, forms of hemothorax are distinguished, such as:
- uninfected;
- is infected.It is often observed with a folded hemothorax, when there is a rapid "subsidence" of the infection on the intrapleural blood clot, and this, in turn, provokes the subsequent purulent process - pyotorax( pus in the pleural cavity) or empyema of the pleura( purulent diffuse lesions of the pleural sheets).
The list of the most common causes of hemothorax looks like this:
-
 chest injuries - most often gunshot, knife, compression( if the chest is crushed by a heavy massive object);
chest injuries - most often gunshot, knife, compression( if the chest is crushed by a heavy massive object); - rib fractures( as a result of an accident or too intensive pulmonary cardiac resuscitation);
- aortic aneurysm;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- malignant neoplasms of the thoracic wall or organs of the chest( lungs, pleura, or mediastinal organs), especially at the stage of decay;
- lung abscess;
- deterioration of blood coagulation properties( occurs with coagulopathy, hemorrhagic diathesis, and so on).
Immediate cause of hemothorax - violation of vessel wall integrity:
- of the chest;
- easy.
More rarely, a hemorrhage occurs due to a traumatism of the vessels of the mediastinal organs - the thymus gland( or the fatty tissue that replaces it), that part of the aorta that is located outside the hearth, trachea, esophagus, lymphatic ducts, blood vessels and nervous structures.They are partially covered by the lungs, which, under the influence of the traumatic factor, basically take a hit on themselves.
Hemotorax is more often unilateral. Bilateral lesion occurs due to a pronounced traumatic factor:
- at work( when falling from height);
- in case of accidents( in road accidents);
- during natural disasters( due to house collapses);
- during military operations;
- when practicing sports( especially by force methods).
Bilateral hemothorax in 90-95% of cases means pronounced. It is damaged by:
- intercostal arteries;
- aorta;
- hollow vein.
In these cases, the amount of blood flowing into the pleural cavity can reach two liters and more. First the blood fills the diaphragm pockets, but since the space of the pleural cavity is rather narrow, it fills up quickly, the blood begins to squeeze one or both of the lungs, because of what they can not normally straighten.
Symptoms of hemothorax
A small bleeding in the pleural cavity may not be clinically apparent . This happens:
- with unexpressed pathological conditions of the chest wall and chest cavity organs, when small vessels were damaged, and after some bleeding stopped spontaneously;
- because of more severe symptoms of the pathological process that led to the development of hemothorax and its signs drowns out signs of hemorrhage.
Expressed hemothorax manifests itself:
- with clinical symptoms on the part of the respiratory system;
- common signs from the whole body.
Signs on the part of the respiratory system:
-
 sensation of squeezing and heaviness in the chest.It can diminish if the patient lies on the affected side or tries to occupy a semi-sitting position, in which the bloody discharge drains into the lower parts of the pleural cavity, their pressure on the lung tissue wanes;
sensation of squeezing and heaviness in the chest.It can diminish if the patient lies on the affected side or tries to occupy a semi-sitting position, in which the bloody discharge drains into the lower parts of the pleural cavity, their pressure on the lung tissue wanes; - dyspnea( frequent shallow breathing);
- inability to breathe in full;
- feeling of lack of air( due to shutting off the blood-tight segments of the lung from the act of breathing);
- increased respiration( to compensate for the feeling of lack of air);
- cyanotic shade of skin and visible mucous membranes.It is more pronounced and appears much faster than with hydrothorax, which is analogous in volume to the fluids poured into the pleural cavity, since it will be caused not only by deterioration of ventilation of the squeezed lung, but also by bleeding;
- at a later stage due to infection - a rise in body temperature first to subfebrile digits( 37.0-37.3 degrees Celsius), then higher if the purulent process developed as a pyotorax or pleural empyema.
General signs of acute blood loss that occur with hemothorax:
- pallor and then cyanosis of the skin and visible mucous membranes( in the event that the lung is squeezed earlier than the effects of bleeding, pallor may not be observed, cyanosis is immediately fixed);
- increased perspiration, sweat to the touch cold;
- changes in hemodynamics( indicators characterizing the movement of blood through the vessels) - increased heart rate and pulse, hypotension.
Two-sided pneumothorax is regarded as an extremely unfavorable condition. Even if a small amount of blood was initially poured out into both the pleural cavity, the bleeding may recur and be more pronounced, causing both lungs to be poured out with blood, and this will lead to respiratory decompensation. With a massive bilateral hemothorax, a lethal outcome can occur within a few minutes of its onset .
Complications of hemorrhage in the pleural cavity
There are:
- early;
- later.
The early ones are:
- acute blood loss;
- compression( squeezing) of the lungs with blood, leading to acute respiratory failure ;
- Attachment of the infection and its "settling" on a blood clot, which becomes an excellent nutrient medium for microorganisms, resulting in purulent complications - pyotorax or empyema of the pleura.Infection of blood secretions with hemothorax is regarded as a very unfavorable factor.
The late complications are:
- the formation of adhesions in the pleural cavity, due to which the diaphragm movement may be impeded.In some cases, the formation of adhesions can lead to massive overgrowth of the lumen of the pleural cavity;
- respiratory failure, which most often occurs due to the adhesive process in the pleural cavity.
The degree of severity of complications depends on how pronounced bleeding was in the pleural cavity. With hemothorax, four levels of bleeding are distinguished:
-
 small - blood loss was up to half a liter, blood accumulated in the sinuses( pockets) of the pleural cavity;
small - blood loss was up to half a liter, blood accumulated in the sinuses( pockets) of the pleural cavity; - average - in the pleural cavity was poured up to a half liter of blood, its level is determined below the fourth rib;
- subtotal - blood loss reaches two liters, the blood level can reach the second rib;
- total - lost more than two liters of blood, it completely filled the pleural cavity and presses on the lungs from all sides.
Small, but continuing bleeding in many cases is more dangerous than more pronounced, but stopped. In this plan, two types of hemothorax are distinguished:
- with stable flow;
- with increasing current.
Diagnosis
In the diagnosis of hemothorax, they rely on symptoms - both manifestations from the respiratory organs and signs of bleeding.But as a small hemorrhage into the pleural cavity can not be clinically evident, additional diagnostics methods are used to refine the diagnosis:
- instrumental;
- laboratory.
In its turn instrumental methods are :
- non-invasive( without insertion into the pleural cavity);
- invasive( with the introduction).
The following non-invasive methods of instrumental examination of the patient are most informative for diagnosing hemothorax:
- fluoroscopy and chest imaging( in the first case they are examined on the screen of an X-ray machine, in the second - an X-ray photograph is taken);
- Ultrasonic scanning of the pleural cavity;
- tomography - computer and magnetic resonance imaging;
- bronchoscopy with biopsy( tissue extraction for their subsequent microscopic examination).
The most accessible method is fluoroscopy and chest imaging. With hemothorax on a screen or a picture, you can see a horizontal level of fluid in the pleural cavity( in a number of cases - an increasing amount of fluid in the continuing bleeding).Clinical symptoms of bleeding can help confirm that this fluid is blood.
Invasive methods include:
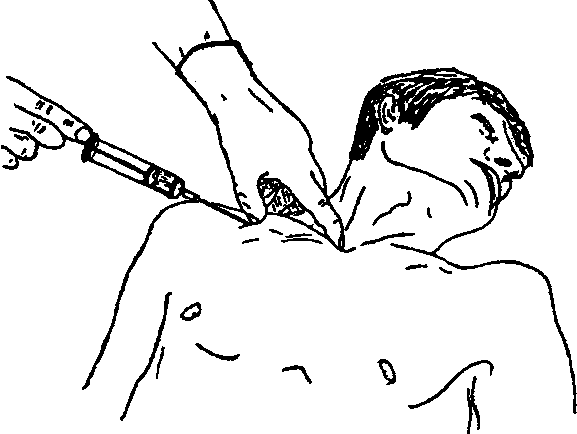
- pleural puncture - the chest wall and the inside of the pleural sheet pierce it with a needle attached to the syringe and make aspirations to make sure that there are bloody contents in the pleural cavity;
- thoracocentesis - the principle and tasks are the same as when performing a pleural puncture, but to pierce the chest wall use a thicker device than the needle - trocar, which is a tube with a sharp style inside.When piercing the thoracic wall with a trocar, an aperture with a larger diameter is obtained than with puncture with a conventional needle, through which it is already possible to insert drainage tubes into the pleural cavity;
- thoracoscopy - the introduction of a thoracoscope into the pleural cavity, through which it is possible to identify the source of bleeding;
- is less common - diagnostic thoracotomy, it is performed if it is impossible to establish the source of bleeding into the pleural cavity( for example, with expressed hemothorax) using other diagnostic methods.Often, diagnostic thoracotomy does not end with one examination-finding a source of bleeding, thoracic surgeons further perform surgery to stop bleeding.
In the diagnosis of hemothorax use of laboratory methods such as:
-
 general blood test - by its changes( in particular, the reduction of the number of erythrocytes and hemoglobin), one can judge the severity of blood loss;
general blood test - by its changes( in particular, the reduction of the number of erythrocytes and hemoglobin), one can judge the severity of blood loss; - test Petrova - with her help reveal a decrease in the transparency of blood flowing into the pleural cavity, which indicates the infection of blood contents;
- test of Rivilua-Gregoire - thanks to her determine the signs of blood coagulation from the pleural cavity, which will help to identify the coagulated hemothorax;
- Cytological examination of sputum under a microscope - it will help to identify a disease that could provoke blood discharge into the pleural cavity.
Emergency care and treatment of hemothorax
Therapeutic activities for hemothorax are divided into:
- first aid;
- treatment in a hospital.
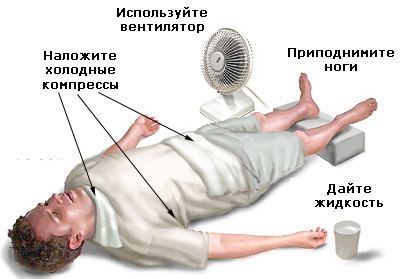
If you suspect a hemothorax as a first aid, the following actions should be taken:
- call an ambulance;
- to give the injured person a position with a raised head;
- put a cold object - ice, cold water in any container( if there is no suitable plastic bag at hand, it can be poured into a glass jar) to the injured part of the chest( for example, the place of injury or the place where the victim fell).
Treatment of a patient with hemothorax in a hospital is divided into:
- conservative;
- is invasive.
Invasive treatment methods, in turn, are divided into:
- puncture;
- operational.
Conservative therapy is directed at:
-
 stop bleeding( insert blood-thinning drugs);
stop bleeding( insert blood-thinning drugs); - resumption of circulating blood volume, which decreased as a result of bleeding into the pleural cavity( whole blood and its components - fresh-frozen plasma, erythrocyte mass, and saline and protein solutions are injected into the bloodstream);
- prevention of infection of blood flowing into the pleural cavity( using broad-spectrum antimicrobials and anti-inflammatory drugs);
- acceleration of blood resorption in the pleural cavity( injections of proteolytic enzymes - substances capable of destroying proteins, and also injecting them directly into the pleural cavity) are used for this.
With more severe bleeding( in particular, with symptoms of increasing respiratory failure), urgent evacuation of blood content from the pleural cavity is necessary. It is performed using:
- pleural puncture;
- thoracocentesis.
These manipulations are performed in the area of the sixth or seventh intercostal space along the back axillary line. A pleural puncture or thoracocentesis should be performed by the physician.The blood is sucked off with a syringe or medical suction, the pleural cavity is washed with antiseptics, then antimicrobials are injected into it, a sterile dressing is applied to the puncture site.
If the patient does not get better after pleural puncture or thoracocentesis, urgent thoracotomy is indicated. This operation happens:
- simple - between the ribs a cut is made, through which they penetrate the pleural cavity.It is performed in 7 or 8 intercostal spaces along the back axillary line;
- resection - perform a resection of the rib( its partial removal).The length of the resected fragment is about three centimeters.This kind of thoracotomy is used if the intercostal incision does not provide the necessary access to the pleural cavity.The patient should not worry about rib resection - when removing such a small fragment will not show any cosmetic defect, nor will the skeleton of the chest.
 With continuous bleeding, a wide thoracic opening of the can be performed to obtain a technical capability to stop bleeding( bandaging or plasty of damaged vessels).
With continuous bleeding, a wide thoracic opening of the can be performed to obtain a technical capability to stop bleeding( bandaging or plasty of damaged vessels).
After stopping bleeding, the pleural cavity is drained - one end of the drainage tube is introduced into it, the other is lowered into a container with a liquid.In this way, a so-called siphon system is created that allows blood to be released from the pleural cavity, but at the same time prevents back current into the pleural cavity.
Operative treatment must necessarily be accompanied by conservative treatment.
Prevention
The emergence of hemothorax is prevented, avoiding dangerous situations that can lead to chest trauma:
- domestic( fights, diving into shallow water, and also falling from height - especially such cases are increasing inTime of harvesting from fruit-berry trees);
- production( collapses in the mine);
- during large-scale natural disasters( earthquakes, tornadoes, tornadoes);
- during military operations.
If such trauma has occurred - urgent consultation of thoracic surgeons is necessary, which in a timely manner will establish the fact of bleeding into the pleural cavity and resort to actions preventing the accumulation of blood discharge in the pleural cavity.
Alertness with regard to hemothorax should also be shown with injuries of the abdominal cavity.
Also the prevention of hemothorax consists in the prevention of diseases that can cause it - first of all it is:
- aortic aneurysm;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- Malignant neoplasms of the chest - especially neglected, at the stage of decay.
In order not to cause iatrogenic hemothorax, chest manipulation( in particular, those that are blindly performed without visual control - these include pleural puncture and thoracocentesis), it is necessary to perform extremely carefully and monitor whether any trauma to the chest structures has occurredAccompanying her bleeding.The same goes for thoracic surgery.
For prevention of spontaneous hemothorax, it is necessary to react sensitively to any pathological changes on the part of the respiratory system and signs of internal bleeding. Quickly fixing it and taking hemostatic measures, you can prevent the accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity, which occurred with uncaused pleural bleeding.
Forecast
For intrapleural bleeding from the median , the prognosis can be complex and depends on:
- the severity of the chest lesions that caused hemothorax;
- speed and duration of blood loss;
- timeliness of diagnostic and treatment activities.
Forecast with bilateral hemothorax is always more difficult. Even if the bleeding is insignificant, it can become much more intense at any moment.Since both halves of the chest are affected, decompensation of breathing will occur.Also, the severity of the prognosis is aggravated by the coagulated form of hemothorax.The most pessimistic predictions - with a bilateral traumatic coagulated hemothorax with continued bleeding. It is more common than other varieties of hemothorax that results in:
- lethal;
- and if the patient survived - to protracted complications, which require more time and more resources for coping both from the patient's body and from the side of doctors.
The prognosis for life is favorable if the diagnosis and treatment of hemothorax have been carried out in the first hours since its inception. After the transferred hemothorax, the prognosis for health will be favorable in case of competent rehabilitation of the patient. To avoid late complications( the formation of adhesions in the pleural cavity worsening the breathing), patients should proceed as soon as possible:
- regular swimming lessons;
- walking;
- performance of special respiratory gymnastics.
After the transferred hemothorax, it should be adjusted to the fact that the recovery will be long - sometimes it takes at least a year to finally get rid of the effects of hemothorax.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical reviewer, surgeon, consulting physician