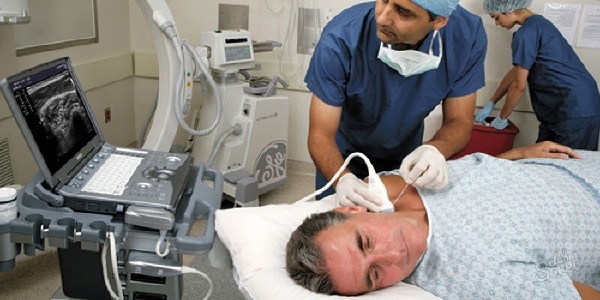
Hepatic tests: interpretation of the analysis, norms
Hepatic tests are laboratory tests of blood, the purpose of which is an objective assessment of the basic functions of the liver.Decoding of biochemical indicators allows to reveal the pathology of the organ and to track in the course of possible undesirable changes in the course of treatment with pharmacological preparations with a hepatotoxic effect.
Table of Contents: Basic Biochemical Indications Indications for Hepatic Sampling Rules for the Analysis of Hepatic Assays Decoding of the Analysis for Hepatic Samples in Adults Liver Holes in ChildrenBasic Biochemical Indices
Biochemical blood analysis allows the determination of the concentration of important compounds and the quantitative levelA number of enzymes in plasma.
To assess the functional activity of the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, the following indicators help:
- activity of the enzymes AST - aspartate aminotransferase, ALT - alanine aminotransferase, GGT - gamma glutamyltransferase and alkaline phosphatase;
- level of total protein and its fractions( in particular - albumin) in the blood serum;
- level of conjugated and non-conjugated bilirubin.
The degree of deviation from the normal values allows you to determine how bad the hepatic cells are, and what is the status of the synthetic and excretory function of the liver.
Note: in the human body, the liver plays the role of the main "biochemical laboratory", in which a huge number of reactions continuously flow.In the body, the biosynthesis of the components of the complement system and immunoglobulin, which are necessary for the control of infectious agents, occurs.It also synthesizes glycogen and undergoes biotransformation of bilirubin.In addition, the liver is responsible for detoxification, i.e. the cleavage of dangerous substances that enter the body with food, drinks and inhaled air.
 To evaluate by the analysis of blood how actively biochemical processes take place inside the liver cells is rather problematic, as the cell membranes separate the hepatocytes from the circulatory system.The appearance of liver enzymes in the blood indicates damage to the cell walls of hepatocytes.
To evaluate by the analysis of blood how actively biochemical processes take place inside the liver cells is rather problematic, as the cell membranes separate the hepatocytes from the circulatory system.The appearance of liver enzymes in the blood indicates damage to the cell walls of hepatocytes.
About pathology is often said not only increase, but also a drop in the content of certain organic substances in the serum.The decrease in the albumin fraction of the protein indicates a deficiency in the synthetic function of the organ.
Important: during the diagnosis of a number of pathologies, liver tests are performed in parallel with renal and rheumatological tests.
Indications for hepatic sampling
Hepatic tests are administered when the following clinical signs of liver pathology appear in patients:
- icterus of sclera and skin;
- Severity or pain in the hypochondrium right;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- nausea;
- rise in body temperature.
Hepatic tests are needed to assess the dynamics of liver disease and the hepatobiliary system - inflammation of the bile ducts, stagnation of bile, as well as viral and toxic hepatitis.
Important: liver tests help in the diagnosis of certain parasitic diseases.
These are important if the patient is taking medications that can damage hepatocytes - cells that form over 70% of the body tissue.Timely detection of deviations from the norm allows you to make the necessary adjustments to the treatment plan and prevent medical damage to the body.
Note: is one of the indications for carrying out liver tests is chronic alcoholism.Analyzes help diagnose such serious pathologies as cirrhosis and alcoholic hepatosis.
Rules for the analysis of liver tests
 The patient needs to come to the laboratory in the morning hours - from 7-00 to 11-00.Before taking blood for 10-12 hours is not recommended to eat.You can only drink water, but without sugar and still.Before the analysis you need to avoid physical exertion( including it is undesirable even to do morning exercises).On the eve it is forbidden to consume alcoholic beverages, as in this case the indicators will be highly distorted.In the morning, you must refrain from smoking.
The patient needs to come to the laboratory in the morning hours - from 7-00 to 11-00.Before taking blood for 10-12 hours is not recommended to eat.You can only drink water, but without sugar and still.Before the analysis you need to avoid physical exertion( including it is undesirable even to do morning exercises).On the eve it is forbidden to consume alcoholic beverages, as in this case the indicators will be highly distorted.In the morning, you must refrain from smoking.
Note: takes a small amount of blood for carrying out hepatic sampling from the vein in the area of the elbow fold.Tests are conducted using modern automated biochemical analyzers.
Factors influencing the results of hepatic samples:
- failure to comply with preparation rules;
- overweight( or obesity);
- reception of some pharmacological agents;
- excessive compression of the vein with a tourniquet;
- is a vegetarian diet;
- pregnancy;
- inactivity( insufficient physical activity).
To assess the functional activity of the liver, it is important to identify the presence / absence of stagnation of bile, the degree of cell damage and possible disruption of biosynthetic processes.
Any pathology of the liver causes a number of interrelated changes in quantitative indicators.With each disease, more or less, several parameters change at once.When evaluating liver samples, specialists are guided by the most significant deviations.
Diagnostic analysis for hepatic assays in adults
Indicators for the reference values of hepatic samples for basic parameters( for adults):
- AST( AsAT, aspartate aminotransferase) 0.1-0.45 mmol / h /L;
- ALT( alanine aminotransferase) 0.1-0.68 mmol / h / l;
- GGT( gamma-glutamyltransferase) - 0.6-3.96 mmol / h / l;
- alkaline phosphatase( alkaline phosphatase) - 1-3 mmol /( h / l);
- total bilirubin - 8.6-20.5 μmol / l;
- direct bilirubin - 2.57 μmol / l;
- indirect bilirubin - 8.6 μmol / l;
- total protein - 65-85 g / l;
- albumin fraction - 40-50 g / l;
- globulin fraction - 20-30 g / l;
- fibrinogen - 2-4 g / l.
Deviations from normal numbers allow us to talk about pathology and determine its nature.

A high level of AST and ALT indicates damage to liver cells against hepatitis virus or toxic origin, as well as autoimmune lesions or the use of hepatotoxic drugs.
Elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase and GGT in liver samples indicate bile congestion in the hepatobiliary system.It occurs when there is a violation of bile outflow due to overlapping of the ducts with helminths or concremental formations.
Decreased total protein indicates a violation of the synthetic function of the liver.
The shift in the ratio of protein fractions to the globulin side allows one to suspect the presence of an autoimmune pathology.
High unconjugated bilirubin combined with increased AST and ALT is a sign of liver cell damage.
High direct bilirubin is detected with cholestasis( simultaneously increases the activity of GGT and APF).
In addition to the standard set of hepatic samples, blood is often tested for total protein and separately for its albumin fraction.In addition, it may be necessary to determine the quantitative index of the enzyme HT( 5'-nucleotidase).Coagulogram helps to evaluate the synthetic function of the liver, since the vast majority of clotting factors are formed precisely in this organ.For the diagnosis of cirrhosis, it is very important to establish the level of alpha-1-antitrypsin.If there is a suspicion of hemochromatosis, an analysis is made for ferritin - its elevated level is an important diagnostic sign of the disease.

Accurately establish the nature and severity of pathological changes allow additional methods of instrumental and hardware diagnostics, in particular - duodenal sounding and ultrasound scanning of the liver.
Hepatic tests in children
Normal values of liver samples in children differ significantly from the reference values in adult patients.
Blood sampling in newborns is carried out from the heel, and in older patients - from the ulnar vein.
Important: is recommended not to eat for 8 hours before the test, but this recommendation is not acceptable for babies.
In order for a doctor to be able to properly interpret the results of hepatic tests, he should be informed when and what the child was eating.If the baby is on breastfeeding, it is specified if the mother does not take any medications.
Normal values vary depending on the child's age, growth activity and hormone levels.
Indicators may be affected by some congenital anomalies, which gradually become smoother with age or disappear altogether.
One of the main markers of cholestasis( bile stasis) in adults is a high level of alkaline phosphatase, but in children the activity of this enzyme rises, for example, during the period of growth, i.e., is not a sign of pathology of the hepatobiliary system.
Analysis of ALT in children
Normal indices of ALT in children in units per liter:
- newborns of the first 5 days of life - up to 49;
- babies of the first six months of life - 56;
- 6 months-1 year - 54;
- 1-3 years - 33;
- 3-6 years - 29;
- 12 years - 39.
The level of ALT in children rises in the following pathologies:
- hepatitis( viral, chronic active and chronic persistent);
- toxic damage to hepatocytes;
- infectious mononucleosis;
- cirrhosis;
- leukemia;
- non-Hodgkin's lymphoma;
- Reye syndrome;
- primary hepatoma or metastasis in the liver;
- obstruction of the bile duct;
- liver hypoxia against decompensated heart disease;
- metabolic disorders;
- celiac disease;
- dermatomyositis;
- progressive muscular dystrophy.
Analysis of the analysis of AST in children
Normal indices of AST in children in units per liter:
- newborns( the first 6 weeks of life) - 22-70;
- infants up to 12 months of age.- 15-60;
- children and teenagers under 15 years - 6-40.
Reasons for increasing the activity of AST in children:
- liver disease;
- heart disease;
- pathology of skeletal musculature;
- poisoning;
- cytomegalovirus infection;
- infectious mononucleosis;
- blood pathology;
- acute inflammation of the pancreas;
- hypothyroidism;
- Kidney infarction.
Decoding of GGT analysis in children
Reference values (normative values) of GGT when decoding liver samples in a child:
- newborns up to 6 weeks-20-200;
- children of the first year of life - 6-60;
- from 1 year to 15 years - 6-23.
Reasons for increasing the indicator:
- disease of the hepatobiliary system;
- malignant tumors of the pancreas;
- heart defects;
- cardiac insufficiency, accompanied by congestion;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hyperthyroidism.
Important: for hypothyroidism( hypothyroidism of the thyroid gland), the level of GGT is reduced.
Analysis of the analysis of alkaline phosphatase in children
Reference values of alkaline phosphatase( SHF) in liver samples in children and adolescents:
- newborns - 70-370;
- children of the first year of life - 80-470;
- 1-15 years old - 65-360;
- 10-15 years - 80-440.
Reasons for increasing the indexes of AS:
- diseases of the liver and hepatobiliary system;
- pathology of the bone system;
- kidney disease;
- pathology of the digestive system;
- leukemia;
- hyperparathyroidism;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- Cystic fibrosis.
The level of this enzyme decreases with hypoparathyroidism, lack of growth hormone in the pubertal period and genetically determined phosphatase deficiency.
The norm of total bilirubin in the liver samples of newborns is 17-68 μmol / l, and in children from 1 to 14 years - 3.4-20.7 μmol / l.
The reason for the increase in figures are:
- blood transfusion;
- hemolytic jaundice;
- heart defects;
- hepatitis;
- cystic fibrosis;
- violation of bile outflow.
Note: In evaluating liver function tests in children, a number of factors need to be addressed.Deviations from the values given here are by no means to be regarded as the presence of pathology in the child.Decoding of the results must be done only by a specialist!
Plisov Vladimir, medical consultant