Regurgitation and vomiting in children of the first year of life

Children under one year for any trouble in the upper sections of the gastrointestinal tract react with vomiting or regurgitation.Pediatricians call this phenomenon a regurgitation and vomiting syndrome( SSR).It occurs in more than 80% of toddlers of this age, due to the anatomical and physiological features of the digestive tube at the site of the esophagus into the stomach.
Table of contents: What is the difference between vomiting and regurgitation Causes of regurgitation and vomiting in children up to one year Functional causes of primary vomiting and regurgitation Organic causes of primary vomiting and regurgitation Causes of secondary vomiting and regurgitation in children up to the year Child with vomiting and regurgitation syndromeMethods for treating children with vomiting and regurgitationWhat is the difference between vomiting and regurgitation
Vomiting is a complex neural reflex act, during whichThere is an involuntary evacuation of the contents of the stomach through the esophagus, pharynx and mouth cavity outwards.During vomiting, the esophagus is shortened and widened, the bottom of the stomach relaxes, and the pylorus contracts.
At the same time, a gap is closed between the vocal chords, and the soft sky rises.And the muscles of the stomach, abdomen and diaphragm, abruptly and repeatedly contracting, empty the stomach.In "babies", especially those born before the term, due to the physiological immaturity of the body does not always happen that way.Therefore, there is a risk of vomiting in the respiratory tract and the onset of suffocation.
Not always, but often vomiting is preceded by nausea - an unpleasant sensation, accompanied by weakness, sweating, blanching, abundant salivation.But to inform adults about such discomfort can only a child who started talking, but not a newborn.
Regurgitation of is also a hit in the pharynx and oral cavity of the contents of the stomach, but only passive, occurring without the involvement of the abdominal muscles.
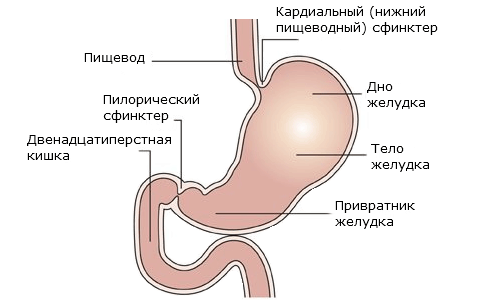
Anatomico-physiological features of esophageal transition in the stomach in children under one year:
- is a relatively short esophagus, the lower part of which is located on two vertebrae higher than in adults;
- underdevelopment of the feet of the diaphragm, which in the adult tightly wrapped the esophagus at the point of its passage into the stomach;
- horizontal position of the stomach and smoothed angle between the esophagus and the bottom of the stomach;
- weak development of the muscular layer of the walls of the esophagus and stomach, and as a result, the inferiority of the cardiac sphincter;
- underdevelopment of the mucosa of the esophagus, the fold of which in adults forms a kind of valve between the stomach and esophagus.In babies it is not formed;
- high sphincter tone in pyloric department;Ingestion of the innervation of the stomach and esophagus
- .
In a healthy adult, all the protective mechanisms that prevent the ingestion of gastric contents into the esophagus, work clearly and smoothly.In a child under the age of one year, these mechanisms are imperfect and inadequate.
Causes of regurgitation and vomiting in children up to the year
Vomiting and regurgitation can be of various origins.If they are associated with diseases or pathological conditions of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, then the is considered primary , and their causes are divided into functional and organic .If there is no connection with diseases of the digestive system - secondary .
Functional causes of primary vomiting and regurgitation
- Overfeed and disturbed feeding regimen. Here everything is extremely simple: with excess filling of the stomach with breast milk( a mixture), which often happens in disordered feeding, there is a disorder in the innervation of the organ.As a result, the contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus and pharynx.
- Aerophagia is the ingestion of air by a child during feeding and getting into the stomach with food.According to the laws of physics, air will inevitably come out - it is belching with air.But the air bubble often carries with it gastric contents, and the baby spits with milk( mixture).
- Cardiospasm is an increase in the motor activity of the lower third of the esophagus, with its upper parts functioning normally.Because of this imbalance, the cardial( lower) section of the esophagus does not relax after swallowing the food, which should normally not be.As a result, food can not enter the stomach, accumulates in the esophagus and immediately returns during feeding.There is a regurgitation or vomiting of undigested, just eaten food.Causes of cardiospasm: disorders from the autonomic and central nervous systems, disruption of the hypothalamic part of the brain.
- Gastroesophageal reflux( GER) is the flowing( stuffing) into the esophagus of the contents of the stomach caused by the immaturity and insolvency of the digestive system of the baby that has appeared.Reflux can be physiological and pathological.Physiological GER is observed in more than half of children under 3 months of age.It manifests infrequent belching( regurgitation) after feeding, which can be noted during sleep.Clinical symptomatology of the mucous membrane of the esophagus is absent, the general condition of the child is not changed, it normally adds weight.
With pathological GER, vomiting and regurgitation are almost always of a persistent nature.As a result, there are clinical signs of irritation of the esophagus mucosa with acidic contents of the stomach - reflux esophagitis develops( inflammation of the esophagus).The child's appetite worsens, he is capricious, does not sleep well.In severe cases, ulcers of the esophagus, persistent narrowing of its lumen, pathology of the respiratory system, developed as a result of ingress of respiratory tract gastric contents.
- Pylorospasm is a spasm( contraction) of the pylorus, that part of the stomach where he passes into the 12-colon.The reason for this phenomenon lies in the violation of the neuromuscular system.Since birth, a child with pylorospasm noted regurgitation, occasionally there is vomiting.Vomit( sometimes with bile) has an acidic smell, their volume does not exceed the amount of food eaten.The child eats well, but after a few months there are signs of hypotrophy, there may be constipation.Children with pylorospasm are often observed in a neurologist with a syndrome of increased nervous reflex excitability.
- Gastritis and duodenitis in infants occur with multiple, chaotic vomiting and regurgitation of coagulated milk, sometimes combined with diarrhea.Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum can be the result of a sudden transfer of the baby from breast milk to a milk mixture or a violation of the technology of preparing the mixture.Infectious gastritis develops when the baby swallows infected amniotic fluid, while feeding it with infected breast milk or a mixture contaminated with microbes.Drug-induced gastritis is a consequence of the prescription of medicines to the baby in tablets.
- The meteorism of ( accumulation of gases in the intestine) is accompanied by increased pressure in the abdominal cavity, which prevents the contents of the stomach from moving into the intestine.The stomach overflows, the cardiac sphincter relaxes, and the baby belches.With an even greater increase in gassing, regurgitation is replaced by vomiting.The causes of flatulence can become intestinal dysbiosis, improper feeding, constipation, lactase insufficiency.
- Perinatal encephalopathy( PEP), , namely, a syndrome of vegetative-visceral dysfunction, which sometimes begins to dominate in the clinic of PEP, when neurologic symptoms go to the background.It is in violation of the functions of internal organs.If we talk about the gastrointestinal tract, then the work of sphincters is upset, the motor skills of organs are disturbed, which in children up to a year is manifested by vomiting and regurgitation syndrome.
Organic causes of primary vomiting and regurgitation
This group includes congenital diseases, abnormalities and malformations of the gastrointestinal tract, such as:
- congenital stenosis( constriction) of the esophagus;
- atresia( infection or absence) of the esophagus, often associated with tracheo-esophageal fistula;
- achalasia and chalasia( insufficiency) of the cardiac esophagus, which are the consequence of an inborn defect or underdevelopment of the nerve nodes located in the walls of the lower part of the esophagus;
- hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm, at which part of the stomach leaves the abdominal cavity into the thoracic cavity and can return back.The reason is the underdevelopment of connective tissue elements, which strengthen the aperture of the diaphragm.

- short esophagus( brachioesophagus), when part of the stomach is located in the chest and never descends below the diaphragm;
- Pyloric stenosis - narrowing of the pyloric part of the stomach due to abnormal muscle hypertrophy;
- diaphragmatic hernia is characterized by the penetration of the stomach and intestinal loops into the chest cavity, not only through the esophagus, but also through other apertures of the diaphragm;
- stenosis and atresia of the duodenum;
- unfinished turn of the intestine, which causes the intestinal tube to overlap at the place where the 12-duodenum goes into the skinny;
- pancreas in the form of a ring, squeezing the descending section of the duodenum;
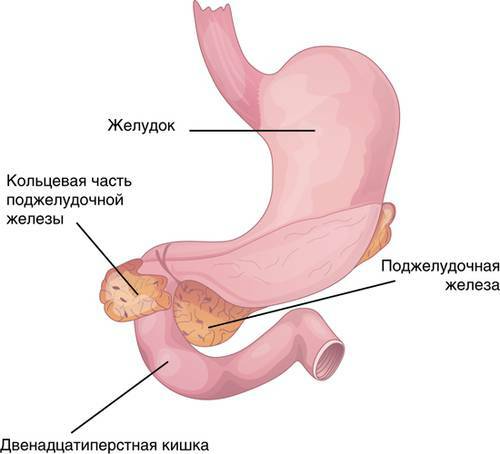
- Hirschsprung's disease( an anomaly of the development of the large intestine) and some others.
Symptoms of almost all these diseases appear in the first days or even hours after the birth of the child:
- the baby belches during feeding or immediately after eating;
- plentifully burps in a horizontal position, especially during sleep;
- vomiting during or immediately after feeding, a fountain or stream, freshly eaten food or curdled milk;
- vomit volume equal to or exceeds food intake,
- vomiting frequency increases, vomiting volume increases;
- an admixture of bile or blood in the vomit;
- the child chokes, swallows hard, wheezes or coughs while feeding;
- bad breath, bloating, propensity to constipation;
- the kid badly adds weight, seldom and poorly urinates.
Any of these symptoms should alert the parents and cause an immediate medical attention.
Causes of secondary vomiting and regurgitation in children up to the year
- Infectious diseases: intestinal infections, pneumonia and bronchitis, urinary tract infections, scarlet fever, neuroinfections( meningitis, encephalitis), otitis media, etc. In these cases, vomiting isOne of the symptoms of the disease.
- Pathology of the brain: perinatal encephalopathy, brain development abnormalities, volumetric process in the cranial cavity, etc. Such a vomiting is called cerebral( cerebral), it arises suddenly, has nothing to do with the feeding of the child.As a rule, such a child has neurological symptoms: tremor( trembling) of limbs, increased excitability, violation of muscle tone, nystagmus( involuntary movements of the eyeballs), etc.
- Diseases manifested by metabolic disorders: a saltative form of adrenogenital syndrome,Galactosemia, fructoemia, diabetes mellitus, cystic fibrosis, etc. If a child immediately after birth is noted persistent, with increasing frequency of vomiting, it is examined to exclude the pathology of metabolism.
Possible complications of the SSR:
- asphyxia( asphyxia) or aspiration pneumonia that develops due to ingestion of vomit;
- esophagitis arising from the effects of acidic stomach contents on the mucosa of the esophagus;
- dehydration( dehydration) and disturbances of acid-base balance due to loss of a large amount of salts and liquid by the body.
The causes of regurgitation in children are told by a pediatrician, Dr. Komarovsky:
Examination of a child with vomiting and regurgitation syndrome
- At the initial stage of diagnosis, the doctor finds out the following:
-
 burdened or not heredity of the baby for diseases of the digestive system, metabolic pathology, neurological diseases;
burdened or not heredity of the baby for diseases of the digestive system, metabolic pathology, neurological diseases; - when there is regurgitation and vomiting, how often they arise, whether or not related to the feeding of the child, what the nature and amount of vomit is;
- as a baby adds weight, is not there a tendency to constipation;
- is examined or not by the child specialists for perinatal pathology.
- A pediatrician examines a child: assesses physical and neuropsychological development, reveals neurological symptoms, if any.Examines the digestive organs, probing and examining the stomach.
- Based on the information received, the physician selects individual tactics for further diagnosis, depending on the nature of the proposed pathology.The examination implies consultations of specialists( pediatric neurologist, endocrinologist, surgeon, oculist, etc.), laboratory and instrumental studies.
From laboratory tests, the indications are clinical and biochemical blood tests, coagulogram, urine and feces( pH, carbohydrates).The biocenosis of the intestine is studied and the acid-base state of the organism is determined.
Instrumental examination( according to indications) is ultrasound of the abdominal cavity organs, pH-metry, fibro-esophagogastroduodenoscopy( FEGDS), roentgenography of the gastrointestinal tract, electroencephalography( EEG), echo-EG, neurosonography, computed tomography( CT), lumbar puncture.
Methods for treatment of children with vomiting and regurgitation syndrome
- Parents of the baby with SSR should carefully follow the recommendations on the regimen and feeding method given by the pediatrician:
-
 to increase the number of meals per day, while simultaneously reducing the amount of milkMixture);
to increase the number of meals per day, while simultaneously reducing the amount of milkMixture); - remove the night break in the food;
- to a child who is on artificial feeding, it is obligatory to give a special "anti-reflux" therapeutic mixture if she is appointed by a doctor;
- to feed the baby, keeping it in a semi-vertical position.After he has finished sucking, keep it upright until the air is out of the stomach;
- the head end of the baby's sleeping place is raised to 30-45 degrees.
- does not use a tight changing;
- of a nursing mother not to use products that cause flatulence and constipation;
- to fight constipation in the baby.
- Drug therapy of SSR, caused by the causes of a functional nature, is aimed at normalizing the operation of sphincters and muscles of the stomach and esophagus by prescribing special antireflux medications.In meteorism, enzymes, adsorbents, biopreparations are prescribed, spasmodics for spastic conditions.In the case of metabolic disorders, the doctor adjusts the baby's nutrition and adjusts the acid-base balance of the body.Physiotherapeutic procedures( ozocerite, UHF-inductothermy, etc.) accelerate the maturation of neuromuscular structures.
- Surgical treatment is indicated in cases where the cause of SSR is congenital malformation or an abnormality of the development of the gastrointestinal tract.These children are under the supervision of a child surgeon, who decides on the timing of the operation.
Zaluzhanskaya Elena Aleksandrovna, pediatrician