Vitamin E( tocopherol): what is needed and in what products is contained
 Vitamin E is a biologically active fat-soluble organic compound belonging to the group of unsaturated alcohols.
Vitamin E is a biologically active fat-soluble organic compound belonging to the group of unsaturated alcohols.
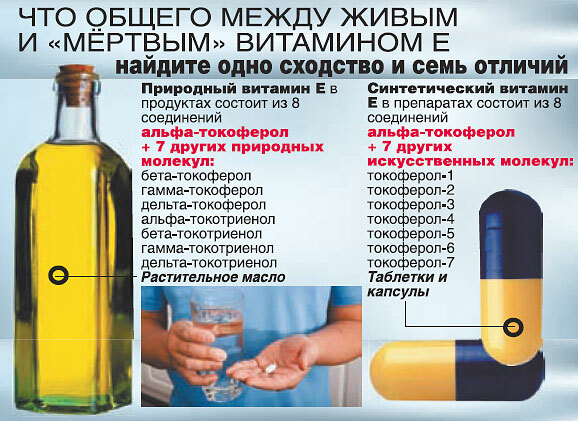
Note : Vitamin E of natural origin is called D-alpha-tocopherol, and its synthetic analogue is DL-alpha-tocopherol.
Table of contents: Functions of vitamin E in the human body Which foods contain vitamin E?Daily requirement E-hypovitaminosis Hypervitaminosis EFunctions of vitamin E in the human body
Tocopherol is present in large quantities in green plants and sprouted grain.The study showed that excluding it from the diet leads to serious violations of reproductive function.Experiments on laboratory animals have helped to reveal that E-hypovitaminosis negatively affects the reproductive organs of both male and female individuals.
Tocopherol plays an important role in the repair of damaged tissues.It significantly normalizes the coagulability of the blood, improves its circulation( especially - peripheral circulation) and lowers blood pressure.Vitamin E can prevent the development of fibrosis, cataracts, anemia and convulsive syndrome.
The compound is characterized by high antioxidant activity.It slows down the natural aging process and protects the body at the cellular level by inhibiting the oxidation of lipids.Due to tocopherol, other lipovitamins( in particular, vitamin A) are not destroyed by free oxygen radicals.
It was found that vitamin E interferes with the development of age-related skin pigmentation.It also helps to strengthen the skeletal muscles and the walls of small blood vessels.Tocopherol takes a direct part in the formation of intercellular substance, as well as connective tissue fibers( elastin and collagen).From this biologically active substance depends largely on the state of human immunity.

Important : at the end of the last century, it was found that a sufficient supply of tocopherol in the body( 2000 IU per day) somewhat slows development and facilitates the course of a serious ailment - Alzheimer's disease.
In the absence of vitamin E, normal placental development is impossible.Tocopherol affects the biosynthesis of gonadotropic hormones, protein compounds, as well as oxygen-carrying compounds of iron-heme.
The importance of this vitamin in the prevention of cancer.Daily dose of 400 IU tocopherol does not give nitrites, which are present in large amounts in sausages and smoked products, to be transformed into nitrosamines, which provoke the development of malignant tumors.Anticancer activity increases significantly if the body regularly receives sufficient amounts of ascorbic acid.
Finally, tocopherol prevents thrombogenesis;Vitamin therapy makes it possible to prevent the development of vascular thrombosis, as well as its consequences - myocardial infarction and ischemic strokes.
Note: unit of measure for vitamin E is an international unit.1 IU corresponds to 1 mg of α-tocopherol acetate.What products contain vitamin E?
. 
Products of animal origin:
- whole milk;
- eggs( yolk);Beef and pork liver
- ;
- lard;
- butter.
Vegetable food:
- oil( sunflower, olive, corn and flaxseed);
- leafy greens;
- broccoli cabbage;
- asparagus;
- cereals( in particular - oats and sprouted wheat);
- bran;
- beans( beans, peas, soybeans);
- chestnuts;
- turnips;
- rose hips( fruits);
- nuts( peanuts and almonds).
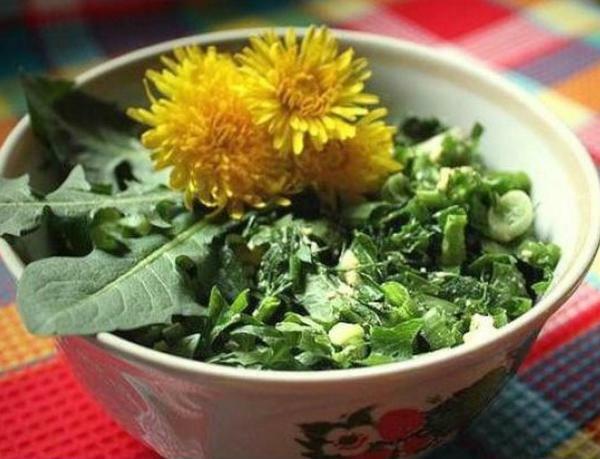 Note: contains a lot of tocopherol in the leaves of nettle, peppermint and raspberry, as well as flaxseed, alfalfa grass, celery tops and carrots.Vitamin salad to prevent hypovitaminosis can be prepared from dandelions.
Note: contains a lot of tocopherol in the leaves of nettle, peppermint and raspberry, as well as flaxseed, alfalfa grass, celery tops and carrots.Vitamin salad to prevent hypovitaminosis can be prepared from dandelions.
Products with vitamin E are recommended to consume together with vitamins A and C, which are in cream, egg yolk, sour-milk products, potatoes, cabbage and greens.To ensure optimal metabolism of tocopherol, adequate amounts of fat should be present in the food.
Daily need
 Adults need an average of 10 IU of tocopherol every day, and 8 IU for women.During pregnancy, future mothers need to consume less than 10 IU of vitamin E, and during lactation - 12 IU.
Adults need an average of 10 IU of tocopherol every day, and 8 IU for women.During pregnancy, future mothers need to consume less than 10 IU of vitamin E, and during lactation - 12 IU.
Important : it is possible to accurately calculate the individual need of an adult in vitamin E. It is 0.3 mg per 1 kg of body weight.
Breastfed from birth to six months of age requires 3 IU of vitamin E per day, babies from 6 months.Up to 1 year - 4 IU.Children from 1 to 3 years need 6 IU daily, and at the age of 4 to 10 years - 7 IU.
Note : The daily need for infants in tocopherol is completely covered by the amount of vitamin they receive with the mother's milk.
The need for a vitamin increases significantly when eating a large number of products containing polyunsaturated fatty acids.
E-hypovitaminosis
Tocopherol deficiency is often observed in people who live in regions with poor environmental conditions( especially in areas contaminated with radionuclides) and persons with occupational hazards in the form of exposure to toxic chemical compounds.
Important : pronounced hypovitaminosis in tocopherol is a phenomenon, fortunately, quite rare.It is noted with prematurity and in children it is manifested by hemolytic anemia and ataxia.
With the deficiency of tocopherol, the destruction of red blood cells( partial hemolysis) and a decrease in the activity of antioxidant enzymes are noted.In addition, the permeability of cell membranes increases and cytotoxins accumulate - products of lipid peroxidation.
Hypovitaminosis is manifested by a decrease in overall immunity( due to a decrease in the biosynthesis of immunoglobulins E, as well as T and B lymphocytes) and a violation of reproductive functions.With severe failure, such serious consequences as muscular dystrophy, softening of certain areas of the brain are possible.
Clinical manifestations of tocopherol deficiency:
- muscular dystrophy( predominantly diaphragmatic) with decay and necrosis of fibers;
- formation of calcifications in affected muscular tissues;
- fatty degeneration of the liver;
- necrosis of liver cells;
- drop in glycogen content;
- myocardial damage;
- shortens the life of red blood cells;
- infertility.
Indications for the beginning of course vitamin therapy:
-
 hypo- or avitaminosis;
hypo- or avitaminosis; - increased physical activity;
- dysmenorrhea;
- diagnosed threat of miscarriage;
- autonomic disorders in women during menopause;
- neurasthenia against a background of chronic mental and / or physical overstrain;
- male infertility( testicular dysfunction);
- primary muscular dystrophy;
- muscle pathology on the background of the suffered trauma;
- arthrosis of large joints;
- diseases of spine ligaments;
- skin diseases;
- period of recovery and recovery after a serious illness;
- epilepsy( to potentiate anticonvulsants);
- is elderly and senile( for general strengthening of the body).
Note : in pediatric practice, vitamin E preparations are widely used in the complex therapy of scleroderma and hypotrophy, as well as a number of other diseases.
Hypervitaminosis E
When the doses of tocopherol enter the body, 10-20 times higher than the requirements, the toxic effect does not develop.Excess vitamin E can be excreted with bile.
Sufficiently long reception of huge( up to 1 g per day) doses in a number of cases leads to hypertension and an increase in serum triglycerides.Possible development of dyspeptic disorders( nausea, diarrhea, excessive gassing in the intestine).
Important: large doses can reduce the need for insulin in patients with diabetes and normalize blood pressure in hypotensive patients.
Complications that develop against the background of E-hypervitaminosis are due to the suppression of free radical reactions in cells responsible for phagocytosis, as well as direct toxic effects on blood cells, epithelium of the intestine, kidneys and liver.In addition, large doses of tocopherol significantly reduce the activity of K-dependent carboxylase.

Additional intake of vitamin E in the form of pharmacological preparations is advisable to start with small doses, increasing them gradually.High dosages can cause the development of hypersensitivity reactions and trigger the appearance of such symptoms as pain in the stomach and intestinal disorders.
The following clinical manifestations may occur when toxoferol is intoxicated:
- septic process( in children);
- enlargement of the liver;
- increased serum bilirubin levels;
- signs of decreased kidney functional activity;
- ascites;
- hemorrhages in the ophthalmic retina.
Important : extreme caution in taking tocopherol should be observed with a high risk of thromboembolism, as well as against myocardial infarction and severe form of cardiosclerosis.
In which foods is vitamin E and why is it called the source of eternal youth?Answers to these questions you will learn by watching this video review:
Plisov Vladimir, phytotherapeutist, dentist