Aspergillosis: what it is, symptoms and treatment in humans
Content
- What is aspergillosis?
- Classification of aspergillosis
- How common is aspergillosis?
- What causes aspergillosis (causes)?
- Symptoms and complications of aspergillosis
- Complications
- How is aspergillosis diagnosed?
- How is aspergillosis treated?
- How to prevent aspergillosis (prevention and recommendations)?
- Forecast
What is aspergillosis?
Aspergillosis Is an infection or allergic reaction caused by various types of mold (a type of fungus). Mold often occurs outdoors on plants, soil, or rotting plant matter. Mold can also grow indoors on household dust, food such as ground spices and building materials. Aspergillus fumigatus Is the type of fungus that most commonly causes aspergillosis in some people when they inhale its spores.
Exposure to Aspergillus is unlikely to cause problems in most people with healthy immune systems. However, people with chronic lung problems or people with weak immune systems (immunosuppression) may be at greater risk of developing an infection. People with weakened immune systems include people who are undergoing chemotherapy or who have had organ transplants.
Classification of aspergillosis
There are several types of aspergillosis:
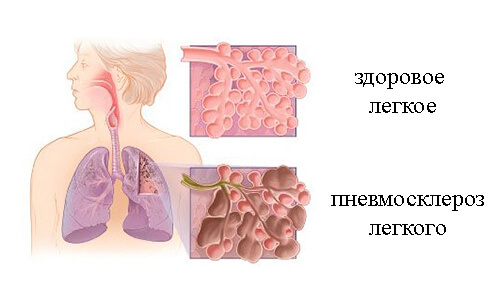
- Aspergillosis of the lungs most often develops in people with chronic pulmonary disease or damaged lungs. These people likely have problem areas in the lungs where the fungus can grow and multiply. The fungus can also rarely infect the sinuses and ear canals. Mold spores can colonize (grow) inside lung cavities that are caused by chronic diseases such as pulmonary tuberculosis, emphysema or progressive sarcoidosis of the lungs. Fungus fibers can form a clump when combined with white blood cells and blood clots. This lump or lump of fungus is called aspergilloma or mycetoma. In some cases, the fungus may be present in other organs of the body.
- Invasive aspergillosis, the most severe type, occurs when the infection spreads from the lungs into the bloodstream. Other organs, such as the kidneys, liver, skin, or brain, can become infected. This is a very serious condition that can be fatal if left untreated. People with very weakened immune systems are more prone to invasive aspergillosis. Other risk factors include low white blood cell count, long-term use corticosteroid drugs or hospitalization.
- Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is an allergic reaction that occurs in some people after being exposed to the Aspergillus fungus. The fungus causes inflammation in the lungs and airways. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis is more common in people with cystic fibrosis or asthmabecause they have more mucus in their airways. While it's unclear exactly why the allergic reaction occurs, mucus in their airways can provide a good environment for mold to grow. Unfortunately, an allergic reaction can cause symptoms similar to symptoms associated with asthma or cystic fibrosis, including wheezing, coughing, and labored breathing.
Read also:Pulmonary insufficiency
How common is aspergillosis?
It is estimated that up to 10% of people with cystic fibrosis or asthma experience an allergic reaction to Aspergillus. Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis is estimated to occur in about 2% of all asthmatics and in 2-15% of patients with cystic fibrosis.
What causes aspergillosis (causes)?

In most cases, aspergillosis is caused by a type of mold called Aspergillus fumigatus. Aspergillus mold can often be found on leaf litter, compost heaps and other decaying plant matter, stored grains, and even food and spices.
Mold spores can be carried indoors on shoes and clothing and can grow on carpets. Window unit air conditioners are susceptible to mold growth if the filters are not kept clean and water does not drain properly from the unit. Places where buildings have been torn down or renovated can be contaminated with mold spores.
Symptoms and complications of aspergillosis
Symptoms and signs can range from mild to severe, depending on the type of aspergillosis.
Pulmonary aspergillosis may not cause any symptoms, especially in the early stages. If the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
- cough, sometimes accompanied by mucus or blood;
- wheezing;
- fever;
- chest pain;
- labored breathing.
Symptoms of invasive aspergillosis may include:
- fever;
- chills;
- breathing problems such as shortness of breath;
- renal or liver failure;
- shock;
- bloody cough or massive bleeding from the lungs.
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis can cause:
- the cough is accompanied by mucus or blood;
- shortness of breath or worsening asthma;
- fever;
- increased secretion of mucus or phlegm;
- an inability to endure exercise or shortness of breath caused by exercise.
Many patients with asthma or cystic fibrosis already experience respiratory symptoms similar to those caused by allergic reaction, so allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis can be difficult to detect in these situations (ABLA). Sometimes, worsening symptoms such as cough and shortness of breath are the only sign that a person is experiencing an allergic reaction.
Read also:Cystic fibrosis disease: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
If the allergic reaction recurs over time and the lungs become inflamed repeatedly, damage to the lungs and central airways can occur. Recurrent allergic reactions can cause scarring of the lung tissue and enlargement of the central airways, a condition known as bronchiectasis.
Complications
Depending on the type aspergillosis disease can cause a number of serious complications.
- Bleeding. Invasive and pulmonary aspergillosis can cause severe bleeding in the lungs.
- Systemic infection The most serious complication of invasive aspergillosis is the spread of the infection to other parts of the body, especially the brain, heart, and kidneys. Invasive aspergillosis spreads quickly and can be fatal.
How is aspergillosis diagnosed?
Your doctor will likely ask you about your medical history, including the type and duration of symptoms, and whether you have a cough or fever. It can be difficult to diagnose the condition because the symptoms can mimic those of many other medical conditions.
Some of the diagnostic tests that may be required include:
- Skin and blood tests: These tests are useful for diagnosing ABPA, especially if the patient has asthma or cystic fibrosis. A doctor or technician injects a small amount of Aspergillus antigen under the skin, usually in the lower arm. A small red bump in or near the area will indicate that you have an allergic reaction. In addition, a sample of your blood can be analyzed to see if certain antibodies are present that indicate an allergic reaction.
- Visual examinations: a chest x-ray or computed tomography (CT) scan may be performed to examine the lungs.
- Sputum culture. The sputum sample can be stained and tested for the presence of Aspergillus.
- Biopsy: a small sample of tissue is removed from the lungs or sinuses to diagnose invasive aspergillosis.
How is aspergillosis treated?
Treatment options include oral corticosteroids, antifungal drugs, and surgery.
- Oral corticosteroid medications: for the treatment of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, solid or liquid oral preparations may be prescribed. These drugs reduce inflammation and prevent worsening of respiratory symptoms such as wheezing and coughing. Some of the most commonly used drugs are - prednisone, prednisone and methylprednisolone.
- Antifungal drugs. These medicines are commonly used to treat invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Voriconazole (synthetic antifungal drug of the triazole group) is currently the drug of the main of choice because it causes fewer side effects and appears to be more effective than others medicines. Amphotericin B or itraconazole are also effective in treating infection. Caspofungin sometimes used when the infection is resistant to other antifungal drugs. Antifungal drugs are sometimes used with oral corticosteroids to treat allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Antifungal medications can cause serious side effects such as kidney damage and liver.
- Surgical intervention: Surgery may be needed in cases where aspergillomas are present causing serious problems such as excessive bleeding. Antifungal drugs are usually not effective against aspergillomas, so surgery is recommended. Embolization can be the primary method of choice, blocking blood flow in an artery that supplies blood to the lung cavity, where the mushroom ball is located, it will help stop the bleeding, however, later the bleeding can repeat.
Read also:List of Inexpensive But Very Effective Cough Syrups
How to prevent aspergillosis (prevention and recommendations)?
Due to the prevalence of Aspergillus aerobic molds in the environment, it is very difficult to avoid exposure to them. It is best to avoid places with excessive dust or mold, such as construction sites or compost piles.
People with weakened immune systems or mold allergies should avoid jobs such as gardening or mowing lawns.
If there is a possibility of exposure to airborne dust or mold, consider wearing a face mask or N95 special mask. In some cases, with an increased risk factor, your doctor may recommend the use of an antifungal medication to prevent infection.
Forecast
With early detection and correct fast therapy. the forecast is positive.
However, unfortunately, if the disease remains unrecognized, untreated or insufficiently treated, the progression of the inflammatory response leads to a deterioration in lung function, bronchiectasis and, ultimately, to development fibrosis of the lung.