Revmoproby( markers of autoimmune diseases)
A laboratory study of venous blood that allows to identify rheumatoid pathological processes and other systemic diseases, in medicine it is customary to call rheumatproges, or markers of autoimmune diseases.
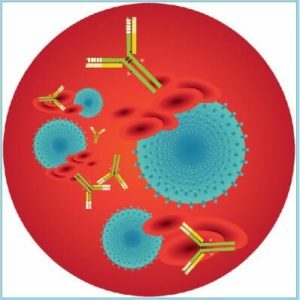
Autoimmune( systemic) diseases include pathologies in which the body's immunity "attacks" its own tissues.The immune system produces specific protein molecules( antibodies), which normally should attack viruses and bacteria, but as a result of failure, they have a harmful effect on the body's own cells.It is noteworthy that the more healthy cells are affected, the immune system produces more antibodies and their attack becomes more aggressive.In simple terms, a person with an autoimmune disease falls into a vicious circle, so this type of pathology most often occurs in a chronic form.
During rheumatology, physicians can determine the level of total protein, circulating immune complexes, rheumatoid factor, albumin, uric acid, C-reactive protein and antistreptolysin O.
Table of contents: How to prepare for the study Who shows the blood test for rheumatic tests GeneralProtein: Norms and Explanation Albumin: Norms and Explanation Rheumatoid Factor Antistreptolysin O: Norms and Explanation C-reactive protein: norms and transcription Circulating immune complexes Uric acidHow to g

In order to obtain the most reliable results, the doctor must inform the patient about three important points before giving blood to the markers of autoimmune diseases:
- Blood for such a study needs to be given on an empty stomach - for 8-12 hours it is impossibleNothing to eat.
- In the morning before the test, you can not smoke, drink tea( even unsweetened), juice or coffee.
- 24 hours before the test, you need to reduce physical activity, exclude from the diet fatty foods and alcoholic beverages.
If these rules of preparation for rheumatic tests are not met, the surrender of blood will be meaningless - the reliability of the results will be a big question.
To whom the blood test for rheumatological tests
is shown Doctors do not assign a laboratory blood test to markers of autoimmune diseases for each patient. But the type of assays considered is shown with:
- rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis;
- systemic lupus erythematosus and autoimmune glomerulonephritis;
- Multiple Sclerosis and Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus;
- autoimmune reactive arthritis and autoimmune thyroiditis;
- polymyositis and autoimmune prostatitis;
- Sjogren's syndrome and scleroderma.
A doctor can prescribe a blood test for rheumatic tests not only with the already diagnosed above pathologies, but also at the stage of suspicion of their development in a particular patient.The purpose of the study of blood on the markers of autoimmune diseases is early diagnosis of autoimmune pathologies, assessment of the severity of the patient's condition, and if a diagnosis is already available, then an evaluation of the effectiveness of the treatment.

Total protein: norms and transcript
This term means the sum of all proteins that circulate in the blood.These proteins perform a huge number of functions: they provide normal immune responses, transport various substances to tissues and organs, ensure normal blood clotting, and others.
The following indicators are the norm of the amount of total protein in the blood test for rheumatological tests:
- children under 12 months of age - 46-73 g / l;
- children aged 12 months to 4 years - 61-75 g / l;
- children aged 8 to 15 years - 58-76 g / l;
- adults aged 16 to 60 years - 65-85 g / l;
- adults over 60 years of age - 63-83 g / l.
The following factors can increase the results of blood tests for rheumatic tests( specifically the total protein values):
- administration of diuretics;
- administration of drugs of the hormonal group - for example, hormonal contraceptives, prednisolone or estrogens;
- peritonitis, extensive burns, vomiting and diarrhea, increased sweating - these pathological conditions are accompanied by loss of fluid, which provokes the results of rheumatic tests with an increased amount of total protein;
- reception of asparaginase, ibuprofen, chlorpropamide, phenytoin, allopurinol, isoniazid and dextran.
The result for a common protein can be reduced, which usually provokes fasting, drinking too much water per day( over 2, 5 liters), heavy physical work and low-protein diets.
If the results indicate too much total protein, then this may be the following reasons:
-
 Acute inflammatory processes.In the first hours of the disease, when the pathological process is in the acute phase, the body comes into conflict with viruses and pathogens, which is manifested by an increase in the level of acute phase proteins.SARS, influenza, pneumonia and sore throat just can give the considered variant of indications.
Acute inflammatory processes.In the first hours of the disease, when the pathological process is in the acute phase, the body comes into conflict with viruses and pathogens, which is manifested by an increase in the level of acute phase proteins.SARS, influenza, pneumonia and sore throat just can give the considered variant of indications. - Chronic pathologies.If the body has a pathological process in a chronic form, then there is increased production of immunoglobulins, which are designed to fight the pathogens of the disease.Bronchitis, tonsillitis, cholecystitis and hepatitis, which occur in a chronic form, can also appear in rheumoprobes with an elevated level of total protein.
- Systemic diseases.Naturally, such pathologies will necessarily increase the overall protein, because the immune system simply in incredible amounts produces modified antibodies.Such systemic diseases include scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism and rheumatoid arthritis.
Causes that cause a decrease in the level of total protein in blood tests for markers of autoimmune diseases:
-
 Poor protein absorption.Such a disorder can develop as a result of the progression of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, pancreatitis, malignant tumors of the stomach and intestines, enterocolitis or stenosis of the pylorus.The lack of protein can also be a consequence of dietary nutrition, built on the principle of eating a low protein.
Poor protein absorption.Such a disorder can develop as a result of the progression of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, pancreatitis, malignant tumors of the stomach and intestines, enterocolitis or stenosis of the pylorus.The lack of protein can also be a consequence of dietary nutrition, built on the principle of eating a low protein. - Liver pathology.In cirrhosis, liver cancer, amyloidosis or fatty lesions of the body, liver cells are damaged, which leads to the impossibility of synthesizing plasma proteins in normal volumes.
- Radiation sickness.
- Swelling of extensive character.With this pathology, proteins from the blood together with the liquid come out into the intercellular space.Such edema can develop against a background of congestive heart failure and / or nephrotic syndrome.
- Catabolism.This term refers to the increased resolution of the protein, which is associated with increased / accelerated metabolism.Such a pathology is found in the case of the Itenko-Cushing disease( hypersecretion of steroid hormones) and thyrotoxicosis.
- Loss of blood plasma.This occurs with extensive wet eczema and / or extensive burns.
In addition, a reduced content of total protein in the blood can be observed against a background of long-term current diseases, when the immune system is already depleted and unable to produce antibodies.This can happen, for example, with chronic intoxication.
Albumin: norms and transcript
This protein, which is synthesized in the liver, accounts for 55% of all protein fractions in the serum.Albumin transports bilirubin, calcium and potassium ions, hormones, and also maintains blood plasma pressure.
The norm of albumin in the analysis of blood on the markers of autoimmune diseases will be the following:
- children under the age of 14 years - 38-54 g / l;
- adults aged 14-60 g / l;
- adults aged more than 60 years - 34-48 g / l.
Vitamin A( retinol), oral contraceptives, diuretics, estrogens, steroid hormones, as well as dehydration, can increase albumin levels.Smoking can be reduced, pregnancy and lactation period, low-protein diet.But these reasons are exclusively physiological in nature.
Decreased albumin levels in blood tests for rheumatological tests may indicate:
- Systemic disease progression - systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatism.
- Plasma loss in case of burn disease, peritonitis, trauma, cavity swelling, as well as against operative interventions on the diaphragm, thorax or clavicles.
- Renal or cardiac edema.
- Diabetic nephropathy, renal necrosis or ischemia of these paired organs.
- Diabetes mellitus, viral hepatitis A, B and C, liver cirrhosis, benign and / or malignant liver tumors.
- Heart failure.
- Pancreatitis, cholecystitis or chronic constipation.
- Purulent processes, acute infectious pathologies.
- Lymphoma, metastasis of cancer in the bone and myeloma.
Rheumatoid factor
This is an autoantibody, which is produced in the synovial membrane of the joints, so they are most often present in blood tests for rheumatic tests in the development of rheumatic processes. Normally, the rheumatoid factor index will be as follows:
- children under 12 years of age - no higher than 12, 5 IU / mL;
- adults - not higher than 14 IU / ml.
Note: in general, normal, rheumatoid factor should not be detected in the blood, but the above values are normal.
If you do not take into account the pathological processes in the body, then increase the result can age changes( concerns people over 50 years old) or too high levels of fats in the serum, which happens when you consume a large amount of fatty foods.A decrease in the result can be such physiological factors as chileosis( excess fat in the blood) and the drug methyldop.
The pathological causes of a high level of rheumatoid factor include:
- Sjogren's syndrome;
- Vessel damage;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- systemic scleroderma;
- infectious diseases( influenza, measles, rubella, tuberculosis, endocardin of bacteriological etiology and syphilis);
- malignant neoplasms;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- polymyositis.
Antistreptolysin O: Norms and Explanation
Under this concept, antibodies fall into the toxins of beta-hemolytic streptococcus.As a rule, these antibodies can appear in the body after a disease caused by streptococcus - tonsillitis, erysipelas, scarlet fever.It is very important to accurately and accurately determine the signs of streptococcal infection, as it is the cause of the development of rheumatism.
The highest antistreptolysin D value is determined for rheumatism, and for rheumatoid arthritis it is much lower - it helps to differentiate the two diseases, as the symptoms are usually identical.Increase the result can physical exercise, eating immediately before giving blood for analysis, the existing pathology of the kidney and liver, the current inflammation of purulent nature, high cholesterol, lower rates - taking antibiotics and / or corticosteroids.
If an increase in anti-streptolysin O is detected in the absence of the above-mentioned physiological reasons, the following pathologies will be considered:
- systemic diseases - glomerulonephritis, rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis;
- infectious diseases provoked by streptococcus - osteomyelitis, tonsillitis, pyoderma, tonsillitis in chronic form and scarlet fever.
Note: for infectious diseases, an increase in the level of antistreptolysin O will be temporary, so doctors can refer the patient to re-delivery of tests for rheumo-tests in one to two weeks.
C-reactive protein: norms and transcript
It is a protein of the blood plasma, its level can increase with inflammatory processes in the body, and this will indicate the inflammatory pathology in both acute and chronic( with exacerbation).Most often, an increase in the level of C-reactive protein indicates bone and / or joint diseases.
The decay time of C-reactive proteins is only 6 hours, so this indicator is excellent demonstrates the effectiveness of the treatment.If the re-examination of the marker is not found in the blood, then we can talk about the process of recovery.
Circulating immune complexes
These complexes consist of antibodies and enzymes, which are produced by the body's immune system.In the case of an increase in the level of complexes, the constituents accumulate in the tissues of the body and, in the first place, renal glomeruli suffer.In norm in both adults and children, the circulating immune complexes should have a value of 30-90 U / ml.
The reasons for this increase are
- autoimmune diseases - vasculitis, scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis and cryoglobulinemia;
- kidney disease - glomerulonephritis and lupus nephritis;
- increased permeability of blood vessels;Benign / malignant tumors;
- ;
- infectious processes;
- allergic reactions.
If the indicator of circulating immune complexes is reduced, this has no diagnostic significance.
Uric acid
This is a product of purine exchange, an increase in the level of which indicates the presence of serious diseases. The following indicators are the norms for the content of uric acid in the blood:
- children under 1 month of age - 80-311 μm / ml;
- children aged 2-12 months - 90-372 μm / ml;
- children aged 12 months - 14 years - 120-362 μm / ml;
- adult men - 200-480 μm / ml;
- adult women - 140-380 μm / ml.The high level of uric acid indicates the presence of the following pathologies:
- renal failure, pyelonephritis, amyloidosis;
;
- malignant tumors;
- depletion, cachexia;
- gout;
- hydronephrosis;
- occlusion of ducts with stones.
But a significant reduction in the level of uric acid will indicate the development of AIDS, xantynuria of hereditary nature, diabetes, hepatitis or cirrhosis.
It is worthwhile to know that no doctor will make a final diagnosis exclusively on blood tests for rheumatological tests - the results are considered only taking into account the general state of health, the available symptoms and other studies.Often, healthy people can have the results of rheumatic tests that do not fit the norms, and patients, on the contrary, can demonstrate literally perfect health.
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical reviewer, therapeutist of the highest qualification category