Clinic and treatment of hypoglycemic coma in children

The manifestation of hypoglycemic coma in children is a pathological condition, manifested due to a certain sequence of reactions of the nervous system, associated with a sharp drop in the level of glycemia or in other words the level of carbohydrates in the blood plasma. The development of coma occurs very quickly, sometimes almost suddenly. There are cases when a loss of consciousness occurred within a few minutes.
Hypoglycemic coma - the last stage of hypoglycemia, develops as a result of low glucose levels in the blood plasma and a drop in the utilization of glucose by the brain. The clinic and treatment of hypoglycemic coma is quite problematic.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia that precede the coma stage are very diverse and are caused by two mechanisms:
- Reactions associated with the excitation of the adrenolin-sympathetic system - vasospasm, azycardia, vegetative disturbances, sensation of tension, perspiration, fear, anxiety, pilomotor reaction.
- Reducing the level of glucose in the brain - neurological manifestations, behavioral disorders, convulsions, loss of consciousness, coma.
Causes of hypoglycemic coma development
The main reason for the development of hypoglycemic coma in patients with diabetes mellitus is the inconsistency of the dose of insulin administered or the use of drugs on the basis of sulfonylurea, also a considerable influence is provided by food with a high content of carbohydrates.
Typically, hypoglycemia occurs in patients with a particularly severe form of insulin dependence, in which it is almost impossible to establish the cause of an increase in insulin sensitivity. In other situations, provocative moments are increased physical activity, prolonged breaks between meals, as well as diarrhea, vomiting and other pathological conditions. Conjugated with diabetes mellitus, dysfunction of the intestine, liver, development of kidney failure can also lead to hypoglycemia. Most often hypoglycemic coma develops in cases of excessive insulin administration, which often occurs in the following situations:
- differences in the types of syringes, or incorrectly typed insulin rate;
- error when injecting the drug is not under the skin, but intramuscularly, which greatly enhances and accelerates the action of the hormone;
- increased physical activity in the absence of carbohydrate inflow. This chain can be represented as follows: insulin injection & gt;Did not eat & gt;No additional carbohydrates & gt;Ski trip, football, swimming pool & gt;Hypoglycaemia & gt;coma.
- physical effect on the injection site of insulin;
- release of the active hormone in large amounts upon rupture of the antibody-insulin complex;
- alcohol intake;
- presence of fatty liver;
- chronic renal failure;
- insulin shocks and suicidal behavior;
Drugs based on sulfonamide are rarely the cause of hypoglycemic reactions. As a rule, the reaction can occur only in elderly people with diabetes and kidney disease or on the background of cardiovascular insufficiency. The use of sulfonamides in combination with other drugs can cause a coma, so when taking these substances should be on the alert.
The process of treating hypoglycemia
There are several degrees of severity of hypoglycemia:
- 1st degree( mild) - is diagnosed and treated independently by taking sugar;
- 2nd degree( medium severity) - the patient can not independently eliminate hypoglycemia, he needs help from outside. Treatment with sweet drinks or sugar remains relevant.
- 3rd degree( severe) - the patient is unconscious or half-conscious, intravenous treatment is required.
In cases of the first and second degree, the clinic and the treatment of hypoglycemic coma in children are performed on an outpatient basis. First of all, it is desirable to measure glycemia in order to be convinced of the presence of hypoglycemia. In cases where hypoglycemia occurs before eating, you must first take easily digestible carbohydrates, and then the main food. With mild hypoglycemia, you need to take 15-20 grams of high-speed carbohydrates( candy, sugar, sweet fruit or drinks).At medium gravity, take a tighter portion of carbohydrates, but add to it two small pieces of bread. After a lapse of twenty minutes, it is necessary to measure the level of glycemia, if it is low, then another piece of bread should be added.
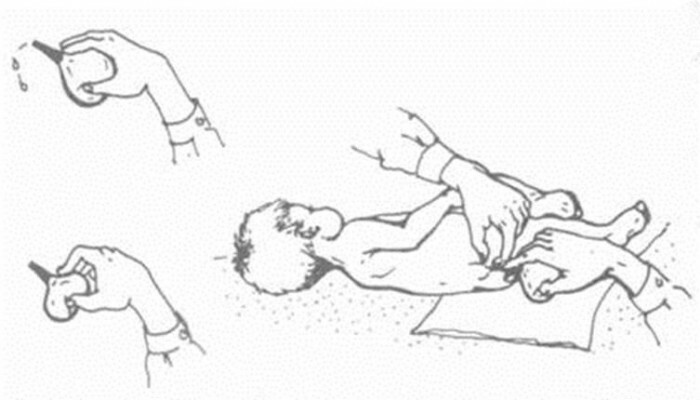
For severe hypoglycemia, before hospitalization for children under 5 years of age, a glucagon injection of 0.5 mg should be given. The injection is done subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Children over 5 years of age need 1.0 mg. Every 20-30 minutes, you should check your blood sugar.
Further treatment of hypoglycemic coma in children is carried out permanently, in intensive care units or resuscitation, by intravenous administration of slightly concentrated solutions of glucose.
The greatest danger of hypoglycemia is that their development and frequent repetition harms the nervous system and, in particular, the brain. Therefore, against the background of this disease, physical, mental and sexual development is delayed, intellect is significantly reduced.
The most difficult to navigate and make the right decision when a child has not previously had diabetes. Moreover, at home there may not be only glucagon and glucose in ampoules, but also a device for measuring blood sugar level. Therefore, in such situations, the child must be immediately delivered to the nearest medical facility, where he will be examined and provided with the necessary assistance.
Prevention of nocturnal hypoglycemia
To prevent nighttime hypoglycemia, several rules should be observed:
- Before going to bed, the blood glucose level should not be less than 7.5 mmol / l;
- Before going to bed you should eat slowly digestible carbohydrates, the food should be protein and contain a minimum of fat.