Non-diabetes mellitus: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
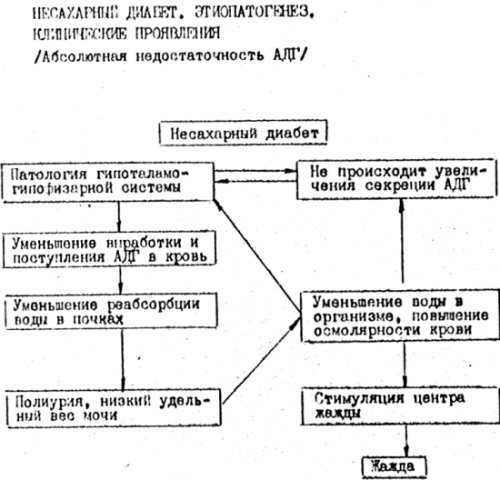
Non-diabetes is a disease caused either by a decrease in the production of vasopressin( antidiuretic hormone) or a decrease in receptor sensitivity to the perception of this hormone.The disease is most often found among people aged twenty-thirty, but it is often recorded in childhood.Non-diabetes mellitus is a rare pathology, but there is a tendency to increase the incidence, mainly due to the central form of the disease.
Table of contents:Causes of diabetes insipidus
Vasopressin is synthesized in the hypothalamus, then enters the pituitary gland.Already directly from the pituitary gland the hormone enters the blood.The main function of vasopressin is the regulation of the water balance.
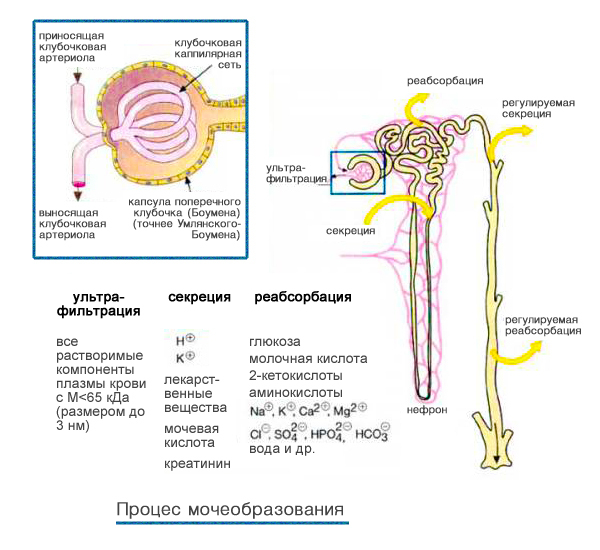
In the renal tubules reabsorption is performed - the reverse absorption of essential microelements and water into the blood.When the level of vasopressin decreases, the reabsorption of water decreases.Thus, water is not absorbed back, but is excreted in the urine in large quantities.So, with diabetes insipidus, the volume of daily diuresis can reach twenty liters!
There are several types of diabetes insipidus:
- Central - is due to a violation of the synthesis of vasopressin hypothalamus or a violation of its secretion by the pituitary gland.
- Nephrogenic - is due to resistance to vasopressin receptors in the kidneys.
- Primary polydipsia - occurs with pathological thirst( dipsogen polydipsia) or obsessive desire to drink( psychogenic polydipsia).In these cases, excessive water consumption compensates for vasopressin production.
- Gestagenic - is associated with excessive activity of a specific enzyme produced by the placenta - arginine aminopeptidase, which breaks down vasopressin.
- Functional - it is observed in children under one year of age due to age imperfection of the concentration function of the kidneys.Excessive activity of the enzyme phosphodiesterase type 5 leads to a deterioration in the receptivity of vasopressin renal receptors.
- Iatrogenic - caused by the intake of diuretics.
Non-diabetes mellitus can be congenital or acquired.The congenital type of diabetes insipidus is associated with genetic disorders.And acquired can arise under the influence of many factors.
Causes leading to the development of central diabetes insipidus:
- Brain trauma;
- Operations performed on the brain;
- Tumors and metastases of the brain;
- Hypoxic, ischemic brain damage;
- Vascular pathology - malformation of blood vessels, aneurysm;
- Granuloma of the brain;
- Infectious diseases.The causes leading to the development of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus:
- Metabolic disorders - hypercalcemia, hypokalemia;
- Chronic renal failure in the polyuric stage;
- Admission of nephrotoxic drugs;
- Polycystic kidney disease;
- Amyloidosis of the kidney;
- Pyelonephritis;
- Syndrome of Sjogren.
Symptoms of diabetes insipidus
The earliest sign of the disease is polyuria - an increase in diuresis.On average, patients have an increase in diuresis to five to six liters of urine per day.Desires for urination occur even at night.With the restriction of water intake, the patient's condition worsens: there is a headache, increased heart rate, lower blood pressure, fever, vomiting, psychomotor agitation.
Against the background of excessive loss of fluid there is a compensatory polydipsia - thirst.And it is characteristic that you can quench your thirst only with the help of cool water.In addition, dry skin and mucous membranes are observed, as well as a decrease in saliva and sweating.
In infants, the clinical symptomatology differs from that in adults.This is due to the fact that if there is thirst, the child can not report it, which means that the lost liquid does not resume fully. In children, the following symptoms are observed:
-
 Weight loss;
Weight loss; - Development delay;
- Pale skin;
- Lack of appetite;
- Absence of tears and sweat;
- Vomiting;
- Increased body temperature.
Note: in young children on the background of dehydration rapidly develop hypernatremia and hyperosmolarity of the blood, accompanied by the appearance of seizures and the development of coma.
Diagnosis of diabetes insipidus
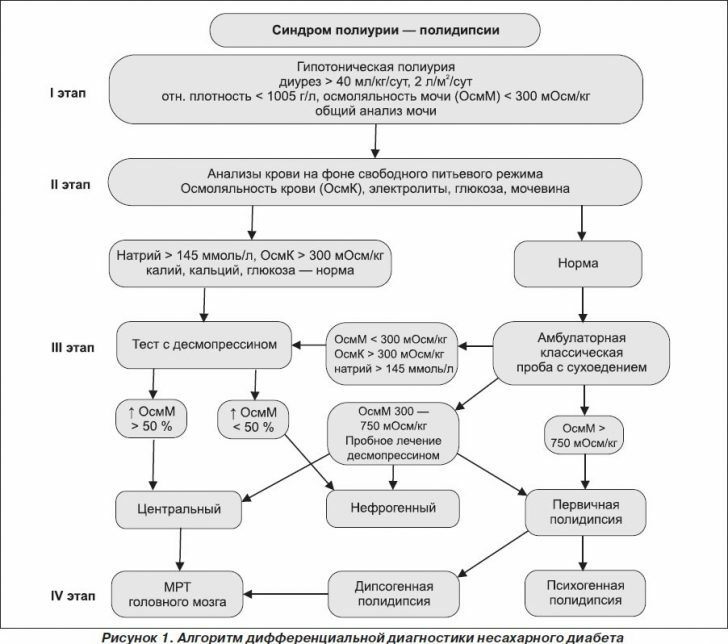
For the identification of diabetes insipidus, the following research package is performed:
- General urinalysis - low relative density is determined( 1,000-1,005);
- Clinical blood test - high hematocrit, increased erythrocyte;
- Blood test for sugar-glucose within normal limits;
- Biochemical blood test - increasing sodium;
- Urinalysis by Zemnitsky - abundant urine separation, low relative density( 1,000-1,005);
- Sample with dryness;
- Sample with desmopressin;
- MRI of the brain;
- Kidney ultrasound.
ASD5ASAS
The patient is weighed in the morning on an empty stomach, the blood pressure and pulse are measured.In the blood determine the level of sodium, as well as osmolarity.And in the urine, the osmolarity and density are measured.Then the patient completely stops taking fluids for 6-14 hours, and food for eight.Every 1 to 2 hours the patient is weighed and repeated all studies.
The study is discontinued in the following situations:
- If more than three to five percent of body weight is lost;
- With severe general feeling;
- Intolerable thirst;
- Increased sodium and osmolarity of blood above the norm;
- Increased osmolarity of urine over 300 mOsm / l.
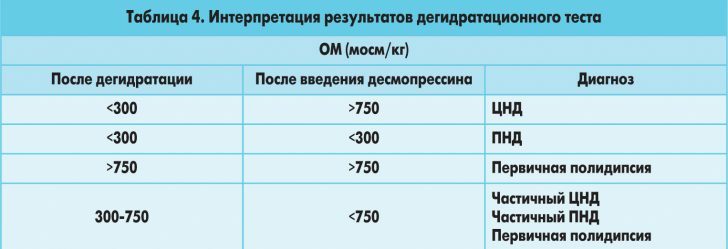
In favor of the central genesis of diabetes insipidus is an increase in osmolarity and sodium blood, as well as weight loss by three to five percent.

And in the nephrogenic genesis of diabetes insipidus there is a decrease in the volume of diuresis, no change in body weight, sodium in the blood is within normal limits.
Assay with desmopressin
A test with desmopressin is performed to determine the cause of diabetes insipidus.For this, a person takes 0.1 mg of desmopressin.After two, and then four hours, urine is taken to determine its volume and osmolarity.
If the osmolality level has increased by more than 50%, then the patient has a central diabetes insipidus.If the osmolarity of urine increases by less than 50%, then the patient has a nephrogenic form of the disease.
Treatment of diabetes insipidus
Patients with diabetes insipidus should not be restricted to fluid intake.The exception is only those patients who have violations of the center of thirst.In this case, a fixed fluid intake is indicated.
The main drug used in the treatment of diabetes insipidus is the analogue of vasopressin - desmopressin, available in the form of tablets, as well as nasal drops.The goal of the therapy is to select the minimum effective dose of the drug to eliminate thirst and polyuria.
Note: Food intake reduces the absorption of the drug and its effectiveness.Therefore, tablet desmopressin should be taken forty minutes before meals or two hours later.
In patients with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, patients are prescribed a diet low in sodium( salt), as well as thiazide diuretics( hydrochlorothiazide, cyclomethiazide).As a supplement to the treatment can also be used drugs from the NSAID group( indomethacin, ibuprofen).
Grigorova Valeria, medical reviewer