What to do if urine is delayed by a man?
Urine retention in men is a pathological condition in which it becomes impossible to urinate in the presence of urine in the bladder, while maintaining an intense urge to urinate( exceptions - spine trauma, neurological pathology).
Contents
- 1 Classification of
- 1 Causes of urinary retention
- 2.1 Obstructive obstructions due to mechanical obstructions
- 2.2 Outflow obstruction due to nervous disorders
- 3 Urinary retention symptoms
- 3.1 Acute urinary retention
- 3.2 Chronic urinary retention
- 4 Diagnosis and treatment
- 4.1 First aid at home
- 4.2 Acute form
- 4.3 Chronic form
- 5 Complications
- 6 Prevention
- 1 Causes of urinary retention
Classification
ozhny following embodiments ischuria( urinary retention).
- Acute ishuria. It develops rapidly, within a few hours. A man feels pain in the lower abdomen, a sharp urge to urinate, but urinate does not work.
- Chronic ishuria - urination is possible and seems to be carried out, but some urine remains in the bladder, which should not be the case with a normal act. With this form, there is no acute urge to urinate.
- Separately, we can distinguish paradoxical ishuriyu - with a full bladder appears incontinence. This is due to the overstretch of the valves in the urethra.
Causes of urinary retention
Difficulties of outflow due to mechanical obstructions of
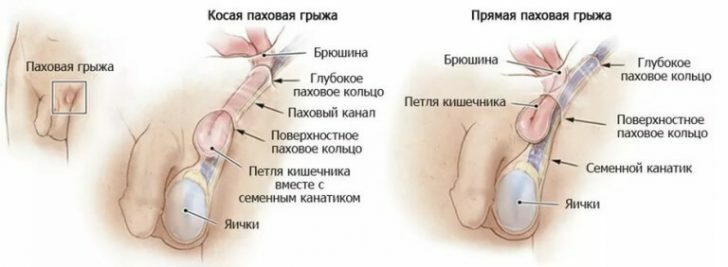
- tumors of the prostate, both benign and malignant;
- trauma to the urethra;
- stricture( constriction) of the urethra;
- stones in the bladder or urethra;
- urethral tumor;
- tumors of the rectum, compressing the urethra;
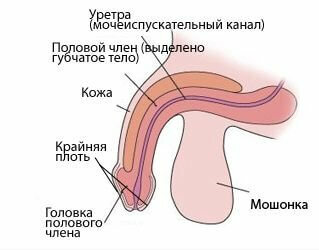
- phimosis is a narrowness of the prepuce, which does not allow to open the head completely;
- congenital malformations of the urethra( valve or hypertrophy of the seminal tubercle);
- infections of the genitourinary system, causing sharp edema and narrowing of the urethra.
Outflow obstruction due to nerve regulatory disorders
Neurological diseases that cause inhibition or lack of impulse to the bladder:
- neoplasms of the spinal cord or brain;
- spinal cord injury due to trauma;
- demyelinating diseases( destructive shells of nerve cells).
The transient inhibition of the nervous system and, as a consequence, the retention of urine can cause:
- stress, fright, any strong emotion;
- alcohol intoxication;
- surgery on the abdominal or pelvic organs;
- prolonged immobility( bedridden patients).
Symptoms of urine retention
First of all, one must be able to distinguish between urinary retention and anuria, a pathology in which urine is absent in the bladder, and therefore there is no possibility of urinating.
Acute urinary retention
The patient feels severe discomfort, pain that comes from the place of obstruction( obstruction) of the urethra. There is an irresistible desire to urinate a little, but it does not work. The abdomen becomes strained in the lower parts, it is painful when touched.
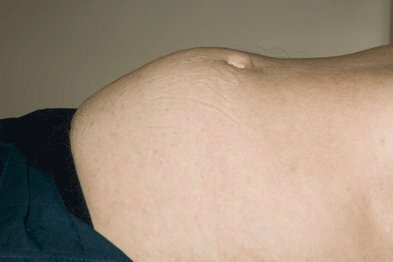
Possible manifestation of acute urinary retention.
Chronic urinary retention
As described above, there is no pain or urge to urinate. But there are some uncomfortable sensations that are of a permanent, debilitating nature. The act of urination itself is difficult, the man at the same time strongly strains the abdominal press. And sometimes you have to press on the lower abdomen in order to urinate. All these actions do not facilitate the process, the urine stream goes under a small head and is often interrupted. After there is no feeling of emptying the bladder, which causes new attempts to urinate.
Diagnosis and treatment
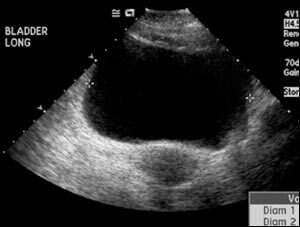
For accurate diagnosis use ultrasound of the bladder.
In the detection of characteristic symptoms, additional studies are used:
- ultrasound of the bladder and prostate;
- X-ray with contrast agent;
- cystoscopy of the bladder.
In addition, a man must pass the general tests of blood and urine.
Men, whose age is more than 40 years, must examine the condition of the prostate gland, including an analysis of PSA( a tumor marker that allows to detect adenoma at early stages).
First aid at home

As a first aid for urinary retention, take no-shpu.
In case of acute urinary retention, an ambulance should be urgently called. In her expectation, you can try to improve the outflow yourself."Home remedies" are usually aimed at relaxing the smooth muscles of the urinary tract, which can, at least in part, restore the outflow of urine.
- take no-shpu, best in the form of rectal suppository( or put candles with papaverine);
- warm( not hot!) Shower, directed to the bottom of the stomach;
- is sometimes helped by a cleansing enema.
Treatment of acute and chronic urinary retention will be different.
Acute form of
In acute form, the most commonly used catheterization of the bladder: a urethra is inserted a flexible catheter through which stagnant urine leaves. In some cases, the placement of the catheter is not possible, then a special system for drainage is established, the tube in which is noticeably thinner. After the outflow of urine is restored, the illness that caused its delay is treated.
Chronic form
If the ishuria has taken a chronic course, then first you need to eliminate the cause, which violates the outflow of urine. If this is caused by mechanical causes, then it can be corrected by surgery or using an endoscope, which can reveal the cause of the outflow disturbance. Most often, the outflow of urine is caused by prostate adenoma. Her treatment can be both surgical and medicamentous. The tactics of treatment will be chosen by the doctor.
Complications of
One of the complications of chronic urinary retention is cystitis.
Acute urinary retention can cause overgrowth and rupture of the bladder. Perhaps the development of acute renal failure due to the fact that the kidneys "nowhere" to filter urine.
In chronic delay, complications are more likely to occur due to the multiplication of pathogenic flora in the "stagnant" urine:
- cystitis;
- pyelonephritis.
Prevention
All activities aimed at delaying urine can be described as taking care of one's own health:
- timely diagnosis and treatment of infections;
- refusal from excessive drinking;
- annual visit to a urologist after reaching 40 years;
- regular blood donation for PSA;
- if on the background of taking medication there are changes in urination - immediately inform the appointing specialist;
- avoiding urethral injuries.
Recommended for viewing: